Abstract
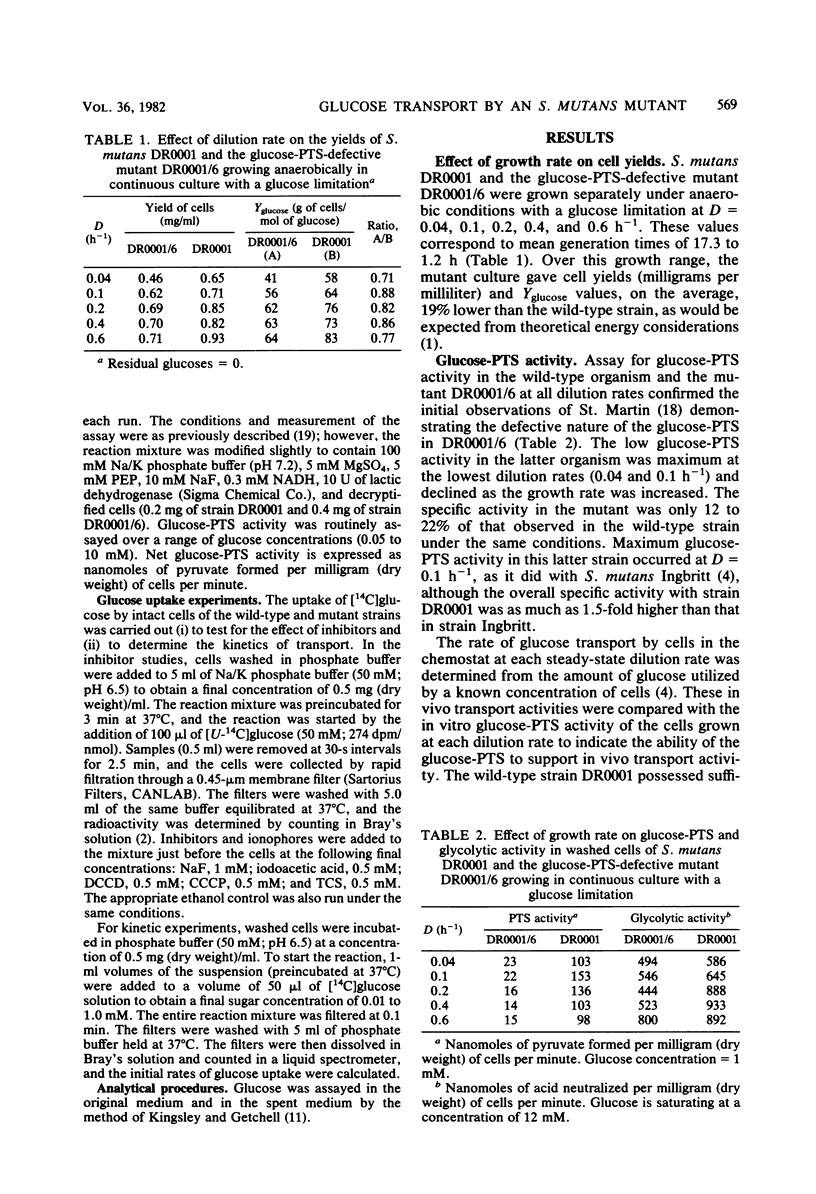
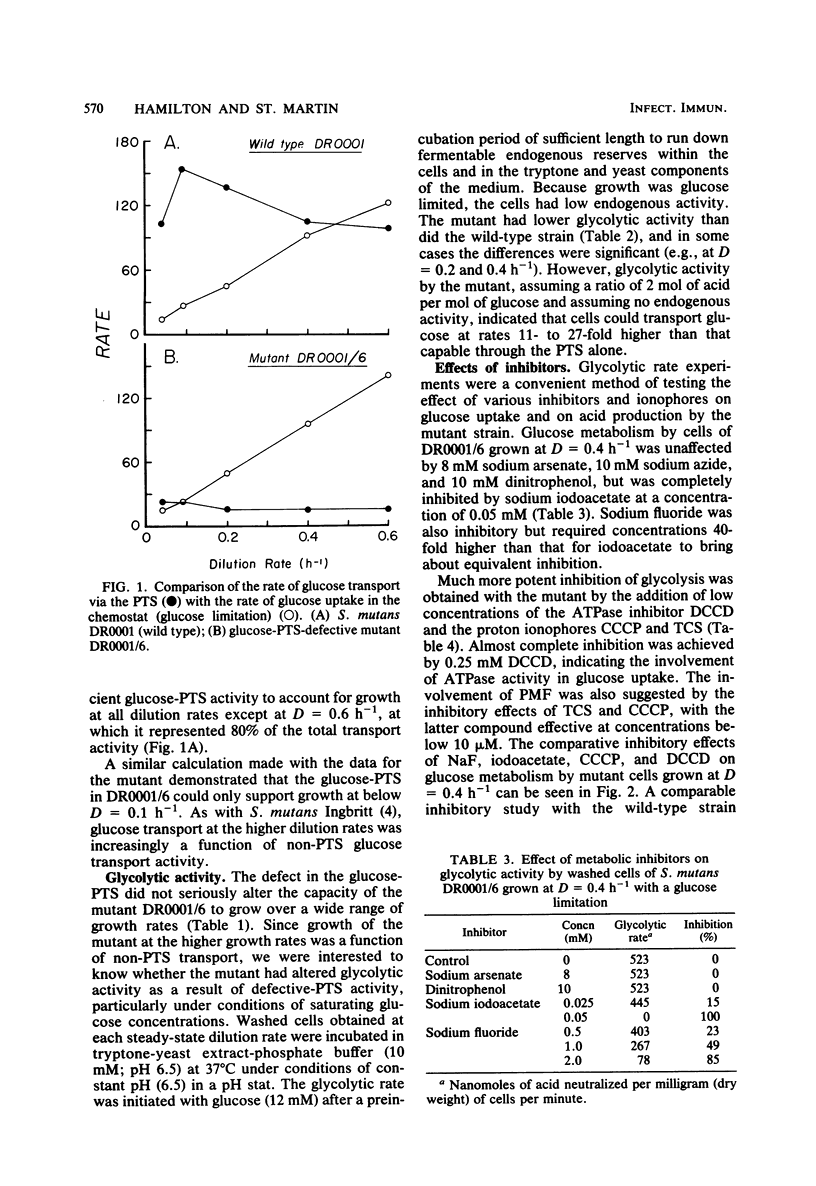
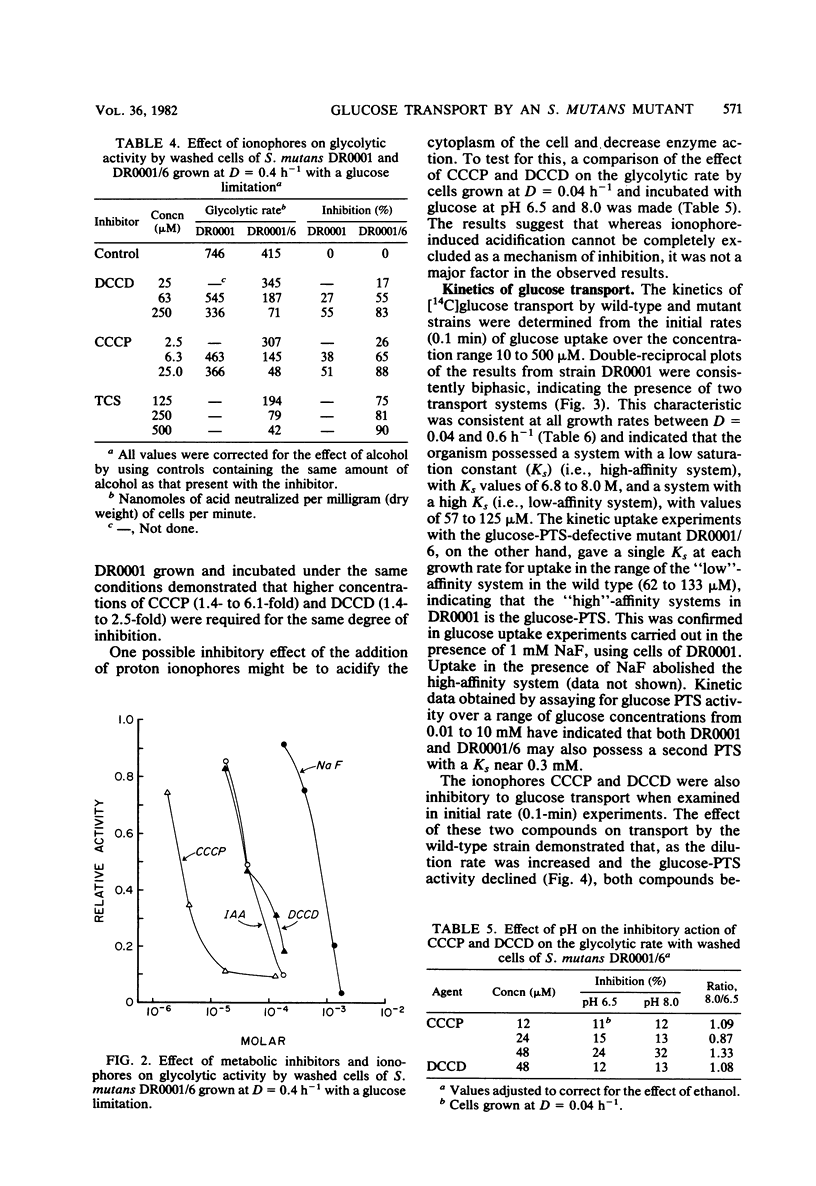
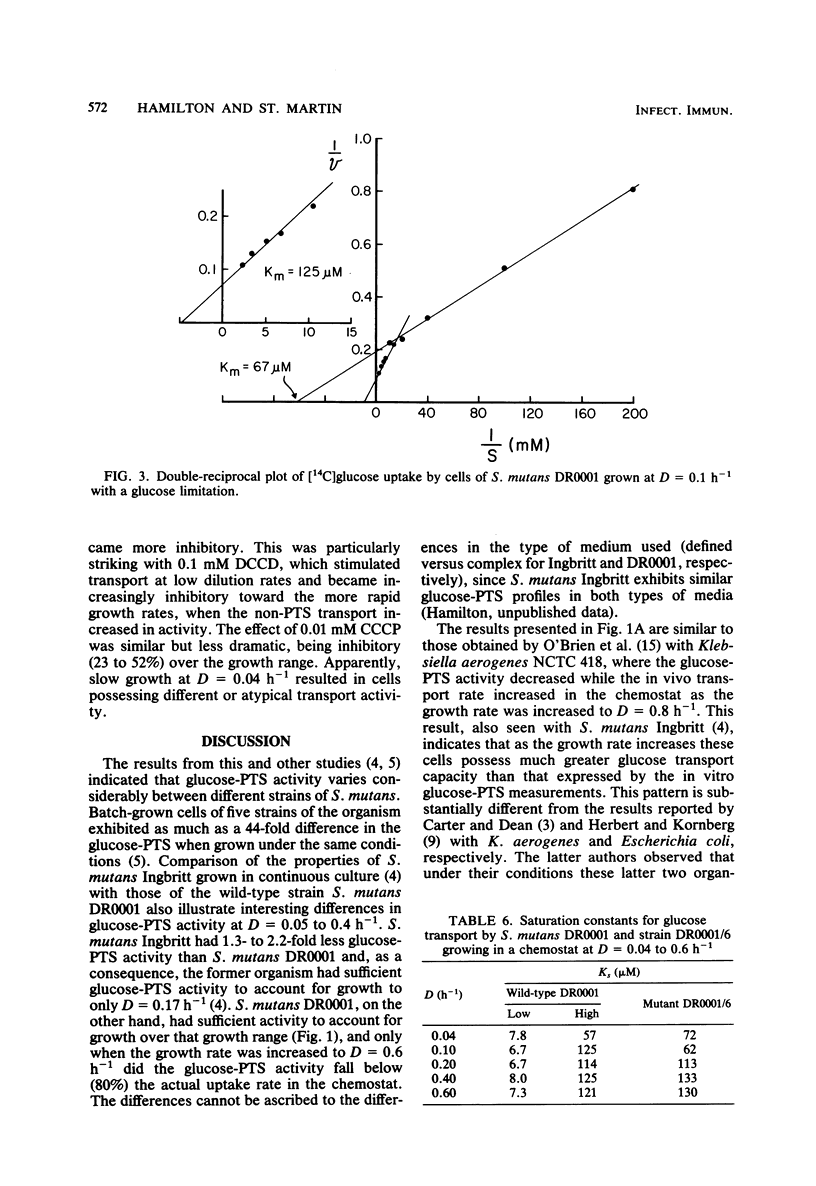
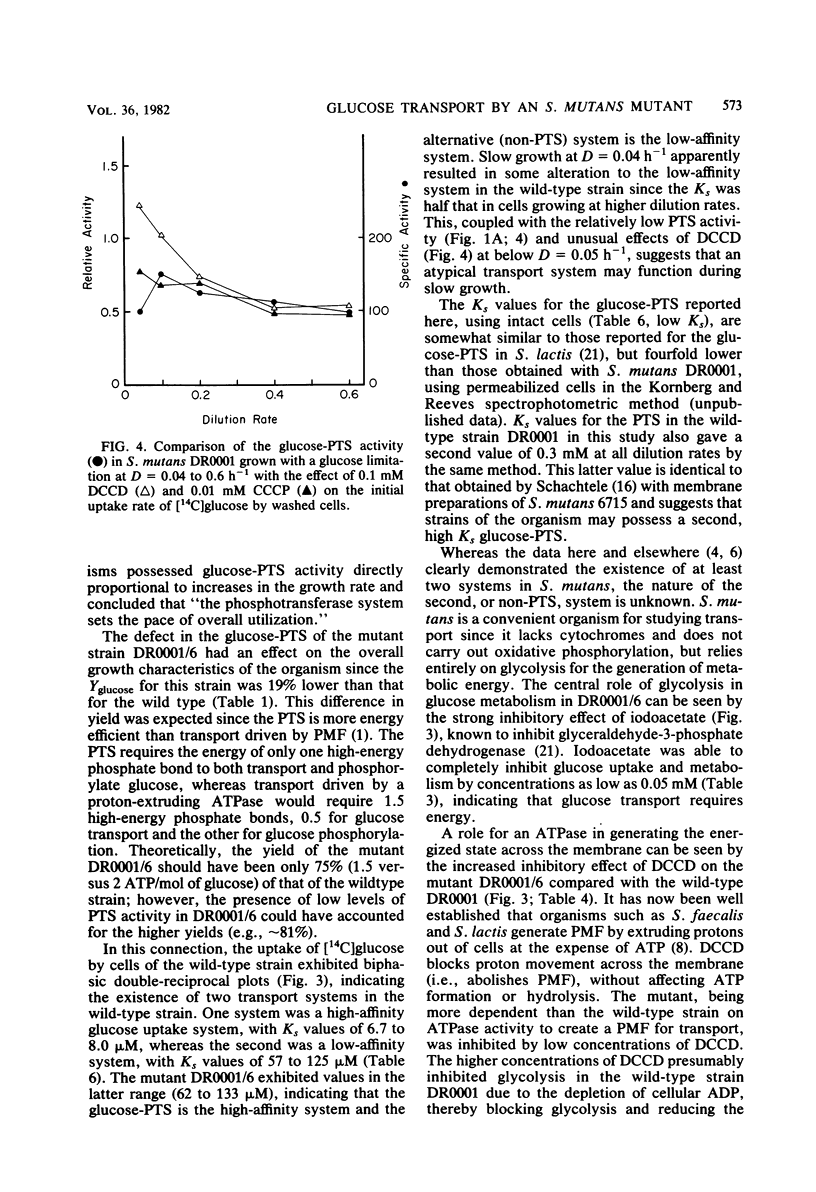
Streptococcus mutans DR0001 and a glucose-phosphotransferase (PTS)-defective mutant, DR0001/6, were grown anaerobically in a chemostat with a glucose limitation at dilution rates (D) of 0.04 to 0.6 h−1 (mean generation time, 17 to 1.2 h). The mutant possessed only 15% of glucose-PTS activity of the wild type and gave cell yields (19%) less than those of the wild type. Glucose-PTS activity in strains DR0001 was maximum at D = 0.1 h−1 and was adequate to account for transport in the chemostat at all dilution rates except D = 0.6 h−1, at which it was 80% of the actual glucose uptake activity. The mutant DR0001/6, on the other hand, possessed only sufficient glucose-PTS activity to sustain growth at below D = 0.1 h−1, indicating the presence of an alternate transport activity. This was confirmed in glycolytic rate experiments with washed cells, which demonstrated that the mutant showed rates 11- to 27-fold higher than that accountable via glucose-PTS activity alone. The wild-type organism contained both a high (Ks, 6.7 to 8.0 μM)- and a low (Ks, 57 to 125 μM)-affinity transport system, whereas the glucose-PTS-defective mutant contained only the low-affinity system (Ks, 62 to 133 μM). The glucose-PTS was shown to be the high-affinity system. Glucose uptake by the mutant was unaffected by 8 mM sodium arsenate, 10 mM azide, and 10 mM dinitrophenol but was completely inhibited by 0.05 mM sodium iodoacetate. Glycolysis in the organism was almost completely inhibited by 0.25 mM N′,N′ -dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD), indicating the involvement of an ATPase in glucose uptake. The ionophores carbonylcyanide-m-chlorophenylhydrazone and tetrachlorosali-cylanilide were inhibitory at concentrations of 10 μM, suggesting that a proton gradient was important in the transport process. Higher levels of DCCD and the ionophores were required to inhibit the wild-type organism to the same degree. A mechanism is proposed for the alternative transport system whereby proton motive force is created by the extrusion of protons by the DCCD-sensitive ATPase and glucose is transported down a proton gradient in a symport with protons.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews K. J., Lin E. C. Selective advantages of various bacterial carbohydrate transport mechanisms. Fed Proc. 1976 Aug;35(10):2185–2189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter I. S., Dean A. C. Hexokinase and glucose-phosphoenolpyruvate phosphotransferase synthesis in Klebsiella aerogenes strains growing in continuous culture. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 15;166(3):643–646. doi: 10.1042/bj1660643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C., Phipps P. J., Hamilton I. R. Effect of growth rate and glucose concentration on the activity of the phosphoenolpyruvate phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt grown in continuous culture. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):224–231. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.224-231.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton I. R. Effects of fluoride on enzymatic regulation of bacterial carbohydrate metabolism. Caries Res. 1977;11 (Suppl 1):262–291. doi: 10.1159/000260304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton I. R., Ellwood D. C. Effects of fluoride on carbohydrate metabolism by washed cells of Streptococcus mutans grown at various pH values in a chemostat. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):434–442. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.434-442.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton I. R., Lebtag H. Lactose metabolism by Streptococcus mutans: evidence for induction of the tagatose 6-phosphate pathway. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1102–1104. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1102-1104.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert D., Kornberg H. L. Glucose transport as rate-limiting step in the growth of Escherichia coli on glucose. Biochem J. 1976 May 15;156(2):477–480. doi: 10.1042/bj1560477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert D., Phipps P. J., Tempest D. W. The chemostat: design and instrumentation. Lab Pract. 1965 Oct;14(10):1150–1161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINGSLEY G. R., GETCHELL G. Direct ultramicro glucose oxidase method for determination of glucose in biologic fluids. Clin Chem. 1960 Oct;6:466–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNDIG W., GHOSH S., ROSEMAN S. PHOSPHATE BOUND TO HISTIDINE IN A PROTEIN AS AN INTERMEDIATE IN A NOVEL PHOSPHO-TRANSFERASE SYSTEM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1067–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg H. L., Reeves R. E. Inducible phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent hexose phosphotransferase activities in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1339–1344. doi: 10.1042/bj1281339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. W., Neijssel O. M., Tempest D. W. Glucose phosphoenolpyruvate phosphotransferase activity and glucose uptake rate of Klebsiella aerogenes growing in chemostat culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Feb;116(2):305–314. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F. Glucose transport in Streptococcus mutans: preparation of cytoplasmic membranes and characteristics of phosphotransferase activity. J Dent Res. 1975 Mar-Apr;54(2):330–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., Mayo J. A. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent glucose transport in oral streptococci. J Dent Res. 1973 Nov-Dec;52(6):1209–1215. doi: 10.1177/00220345730520060801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Martin E. J., Wittenberger C. L. Characterization of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):865–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.865-868.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Martin E. J., Wittenberger C. L. Regulation and function of ammonia-assimilating enzymes in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):220–224. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.220-224.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. Galactose transport systems in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):683–691. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.683-691.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. Lactose metabolism in Streptococcus lactis: phosphorylation of galactose and glucose moieties in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):774–785. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.774-785.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



