Abstract
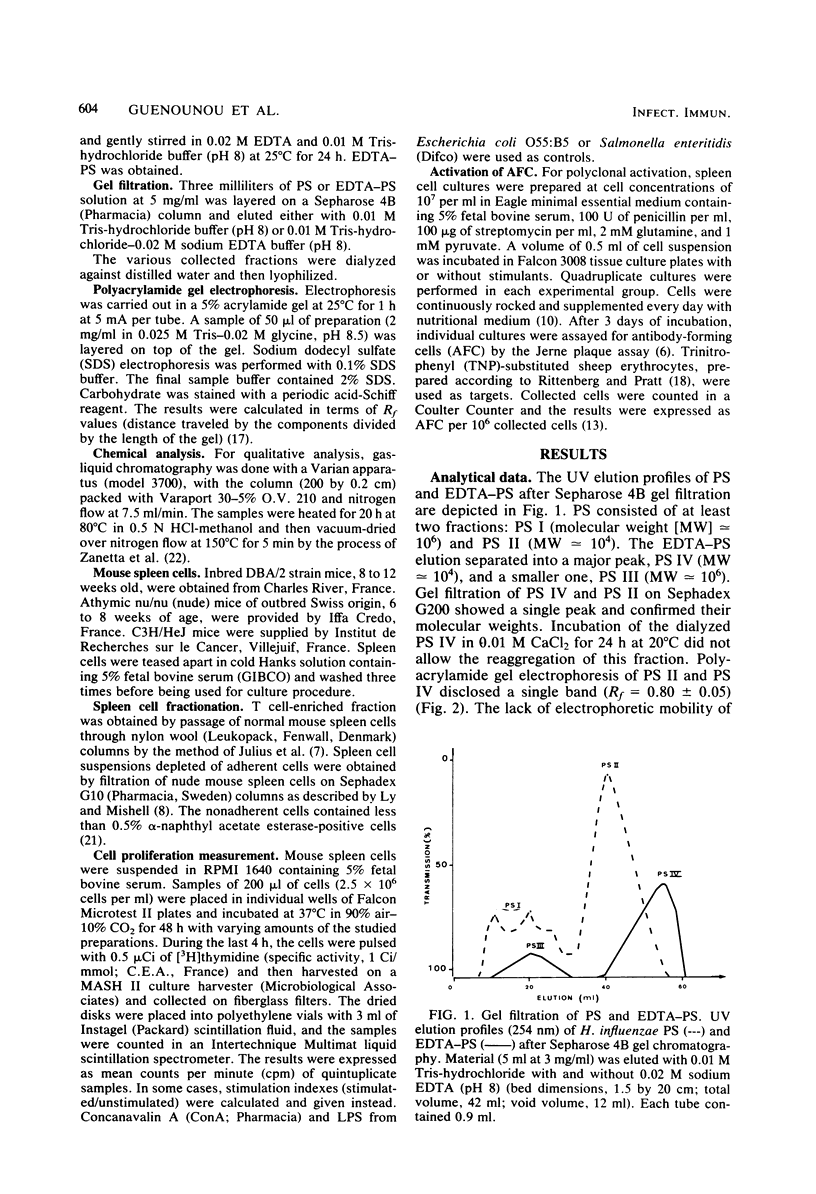
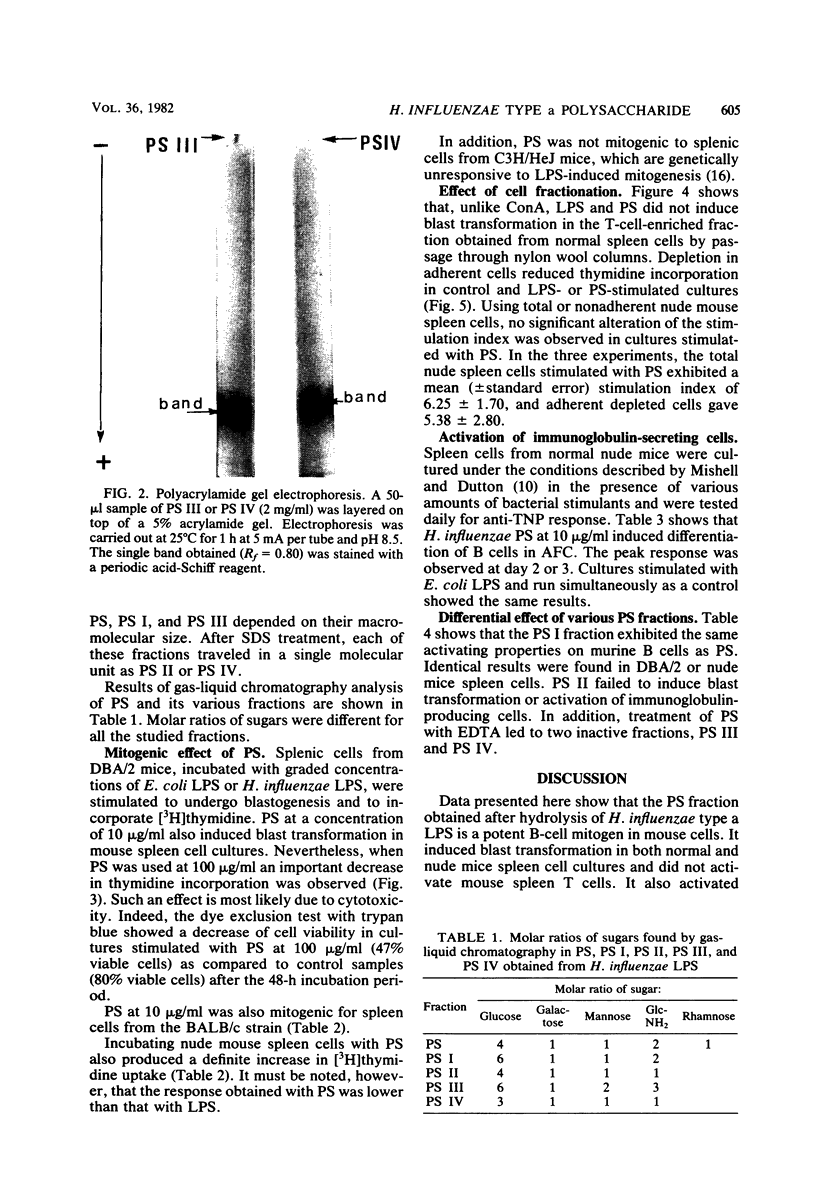
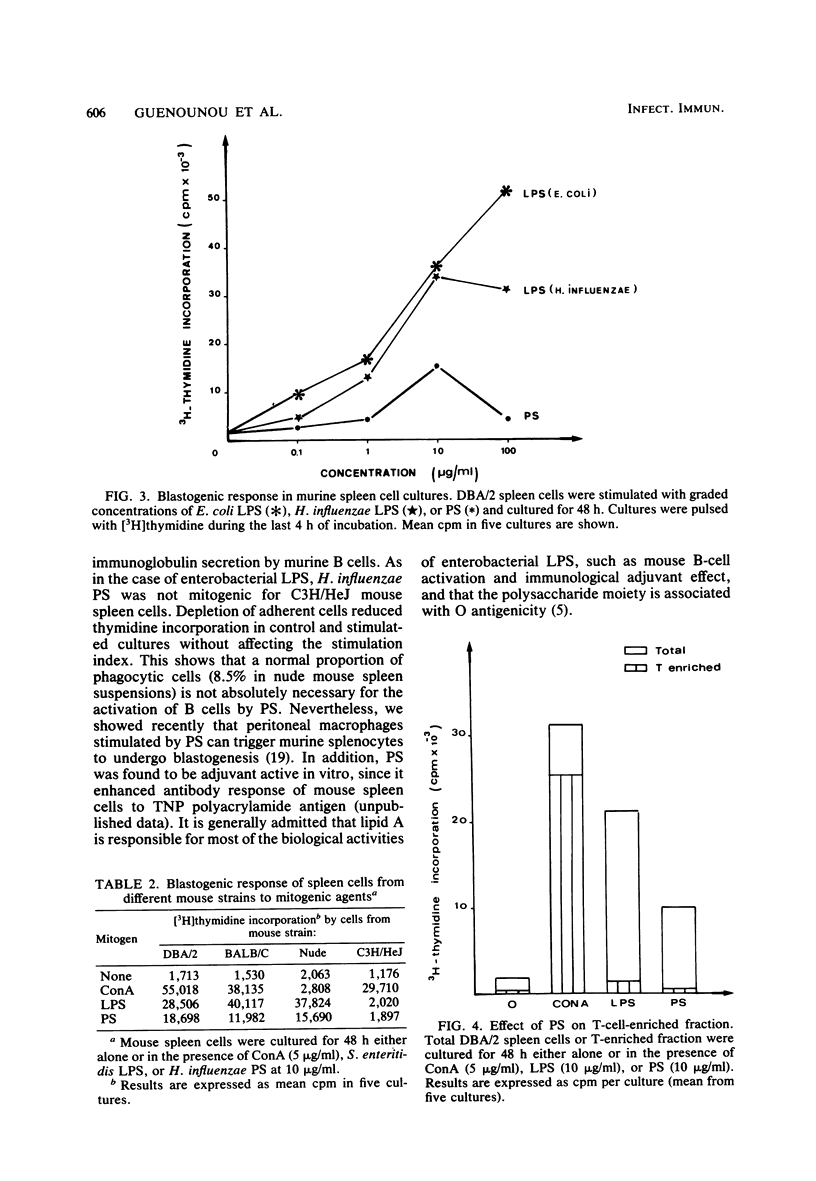
Mild hydrolysis of Haemophilus influenzae type a lipopolysaccharide by ion exchangers in the presence of chloroform, to remove the lipid moiety, yielded a nontoxic and immunogenic polysaccharide fraction. This polysaccharide selectively triggered murine B lymphocytes in vitro: (i) it induced enhancement of thymidine incorporation and stimulated antibody secretion in cultures of normal and nude mouse spleen cells; (ii) it did not stimulate splenic T lymphocytes; (iii) the activation of B lymphocytes was not absolutely dependent on the presence of macrophages. Sepharose 4B gel filtration showed that this polysaccharide consisted at least of two fractions: PS I (molecular weight [MW] 10(6)) and PS II (MW 10(4)). Only PS I was found to act as a polyclonal B cell activator. EDTA treatment dissociated the polysaccharide into PS III (MW 10(6)) and PS IV (MW 10(4)), which was not reassembled after the addition of 0.02 M CaCl2. Both fractions PS III and PS IV were unable to stimulate B lymphocytes. The immunological active fraction of H. influenzae polysaccharide is PS I. This fraction consists of a high-molecular-weight group (10(6)) and an association of 10(4)-MW aggregated units.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DePamphilis M. L. Dissociation and reassembly of Escherichia coli outer membrane and of lipopolysaccharide, and their reassembly onto flagellar basal bodies. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1184–1199. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1184-1199.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny F. W. Effect of a toxin produced by Haemophilus influenzae on ciliated respiratory epithelium. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):93–100. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S., Specter S., Nowotny A., Friedman H. Immunocycte stimulation in vitro by nontoxic bacterial lipopolysaccharide derivatives. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):855–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K., Nordin A. A. Plaque Formation in Agar by Single Antibody-Producing Cells. Science. 1963 Apr 26;140(3565):405–405. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3565.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ly I. A., Mishell R. I. Separation of mouse spleen cells by passage through columns of sephadex G-10. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Hargie M. P., Schenck J. R., Finley R. A., Sievert H. W., Rietschel E. T., Rosenstreich D. L. Biologic properties of nontoxic derivatives of a lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli K235. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):674–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raichvarg D., Brossard C., Agneray J. Chemical composition and biological activities of a phenol-water extract from Haemophilus influenzae type a. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):415–421. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.415-421.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raichvarg D., Brossard C., Agneray J. Preparation of a nontoxic and immunogenic polysaccharide fraction from a Haemophilus influenzae phenol-water extract. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):171–174. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.171-174.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raichvarg D., Guenounou M., Brossard C., Agneray J., Alouf J. E. Comparative study of biological activities and mitogenic effect of extracts from Haemophilus influenzae type a. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1980;168(3):201–210. doi: 10.1007/BF02122854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raichvarg D., Guenounou M., Brossard C., Agneray J. Characteristics of a lipid preparation (lipid A) from Haemophilus influenzae type a lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):49–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.49-53.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg M. B., Pratt K. L. Antitrinitrophenyl (TNP) plaque assay. Primary response of Balb/c mice to soluble and particulate immunogen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):575–581. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. W., Gilleland H. E., Jr, Eagon R. G. Characterization of a protein-lipopolysaccharide complex released from cell walls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jul;15(7):743–748. doi: 10.1139/m69-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore B. J., Chiller J. M., Weigle W. O. Immunologic properties of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). IV. Cellular basis of the unresponsiveness of C3H/HeJ mouse spleen cells to LPS-induced mitogenesis. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):274–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetta J. P., Breckenridge W. C., Vincendon G. Analysis of monosaccharides by gas-liquid chromatography of the O-methyl glycosides as trifluoroacetate derivatives. Application to glycoproteins and glycolipids. J Chromatogr. 1972 Jul 5;69(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)92897-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Zwan J. C., Orie N. G., de Vries K. Biphasic reaction after inhalation of Haemophilus influenzae in patients with chronic nonspecific lung disease. Clin Allergy. 1975 Jun;5(2):225–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1975.tb01856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]