Abstract
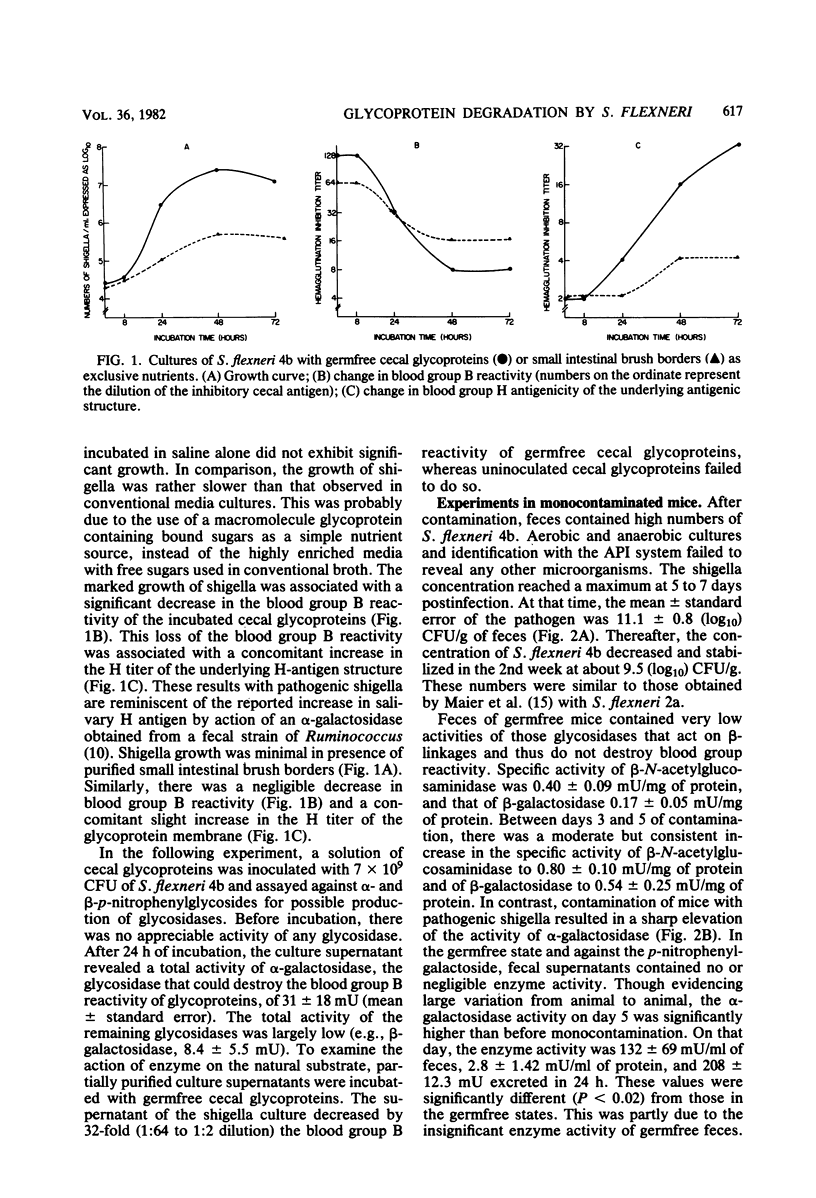
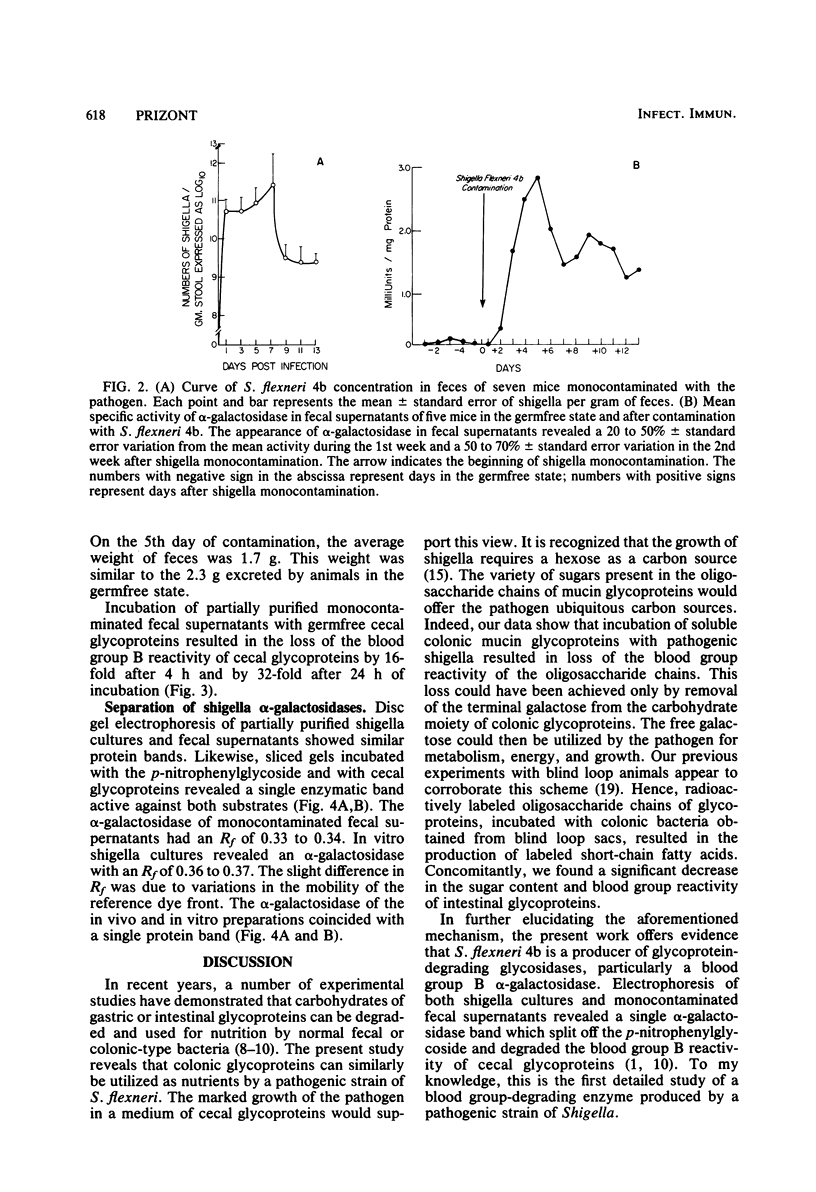
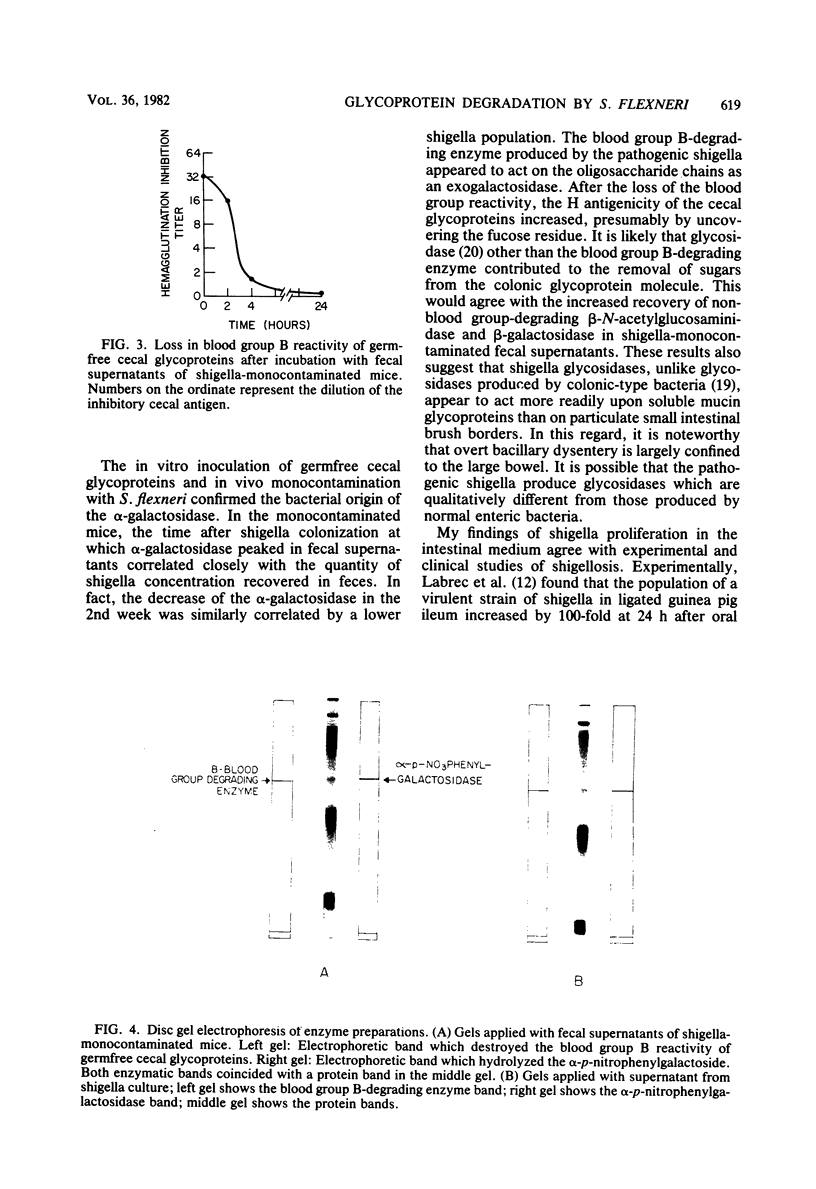
Intestinal mucin glycoproteins were examined for their ability to sustain growth of pathogenic shigella. Inoculation of germfree cecal mucin glycoproteins with Shigella flexneri 4b resulted at 48 h in a 940-fold increase in the enteropathogen concentration. Investigation in vitro of enzymatic degradation by the pathogen led to the identification of a blood group B-degrading glycosidase produced by the bacteria. In in vivo experiments, fecal supernatants of mice monocontaminated with S. flexneri 4b contained an alpha-galactosidase active against the p-nitrophenyl-glycoside. This fecal alpha-galactosidase peaked 5 days after shigella contamination, showing 2.8 +/- 1.4 mU of enzyme activity per mg of protein. Contaminated fecal supernatants similarly destroyed the blood group B reactivity of cecal mucin glycoproteins. These data suggested that S. flexneri 4b could proliferate within ileocolonic environment by enzymatically degrading mucin glycoprotein sugars.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahl O. P., Agrawal K. M. Glycosidases of Phaseolus vulgaris. I. Isolation and characterization of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):98–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., LABREC E. H., SCHNEIDER H. PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY IN LABORATORY ANIMALS. Fed Proc. 1965 Jan-Feb;24:29–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G., Sabesin S. M., Isselbacher K. J. Rat intestinal microvillus membranes. Purification and biochemical characterization. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):381–390. doi: 10.1042/bj1060381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoskins L. C. Bacterial degradation of gastrointestinal mucins. II. Bacterial origin of fecal ABH(O) blood group antigen-destroying enzymes. Gastroenterology. 1968 Feb;54(2):218–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoskins L. C., Boulding E. T. Degradation of blood group antigens in human colon ecosystems. I. In vitro production of ABH blood group-degrading enzymes by enteric bacteria. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):63–73. doi: 10.1172/JCI108270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoskins L. C. Ecological studies of intestinal bacteria. Relation between the specificity of fecal ABO blood group antigen-degrading enzymes from enteric bacteria and the ABO blood group of the human host. J Clin Invest. 1969 Apr;48(4):664–673. doi: 10.1172/JCI106024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T. Ecological control of the bacterial diarrheas: a scientific strategy. Am J Clin Nutr. 1978 Dec;31(12):2208–2218. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/31.12.2208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Takeuchi A., Gangarosa E. J., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P. Pathogenesis of Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga) dysentery. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):261–270. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier B. R., Onderdonk A. B., Baskett R. C., Hentges D. J. Shigella, indigenous flora interactions in mice. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1433–1440. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old D. C. Inhibition of the interaction between fimbrial haemagglutinins and erythrocytes by D-mannose and other carbohydrates. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):149–157. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prizont R. Glycoprotein degradation in the blind loop syndrome: identification of glycosidases in jejunal contents. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):336–344. doi: 10.1172/JCI110040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prizont R., Konigsberg N. Identification of bacterial glycosidases in rat cecal contents. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Sep;26(9):773–777. doi: 10.1007/BF01309607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prizont R., Reed W. P. Possible role of colonic content in the mucosal association of pathogenic shigella. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1197–1199. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1197-1199.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Formal S. B., Sprinz H. Exerimental acute colitis in the Rhesus monkey following peroral infection with Shigella flexneri. An electron microscope study. Am J Pathol. 1968 Mar;52(3):503–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]