Abstract
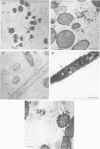
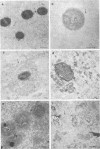
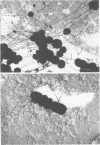
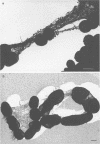
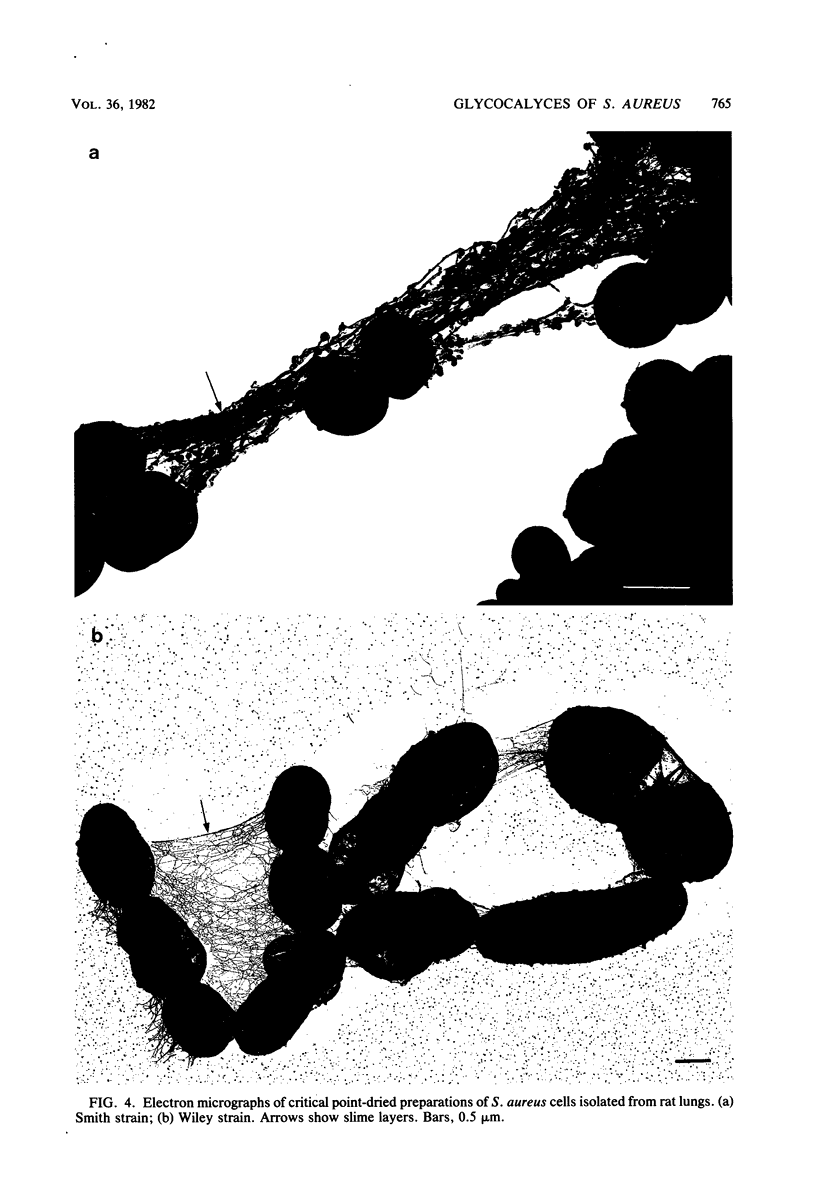
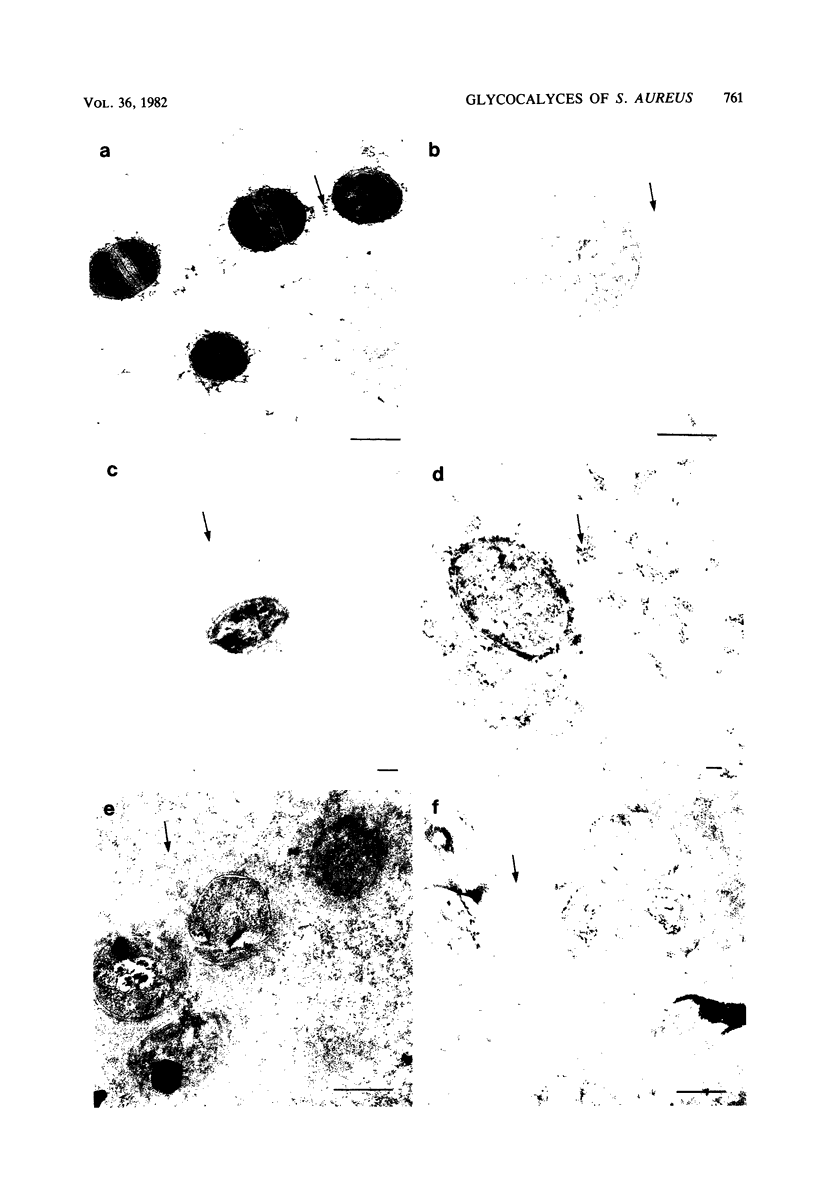
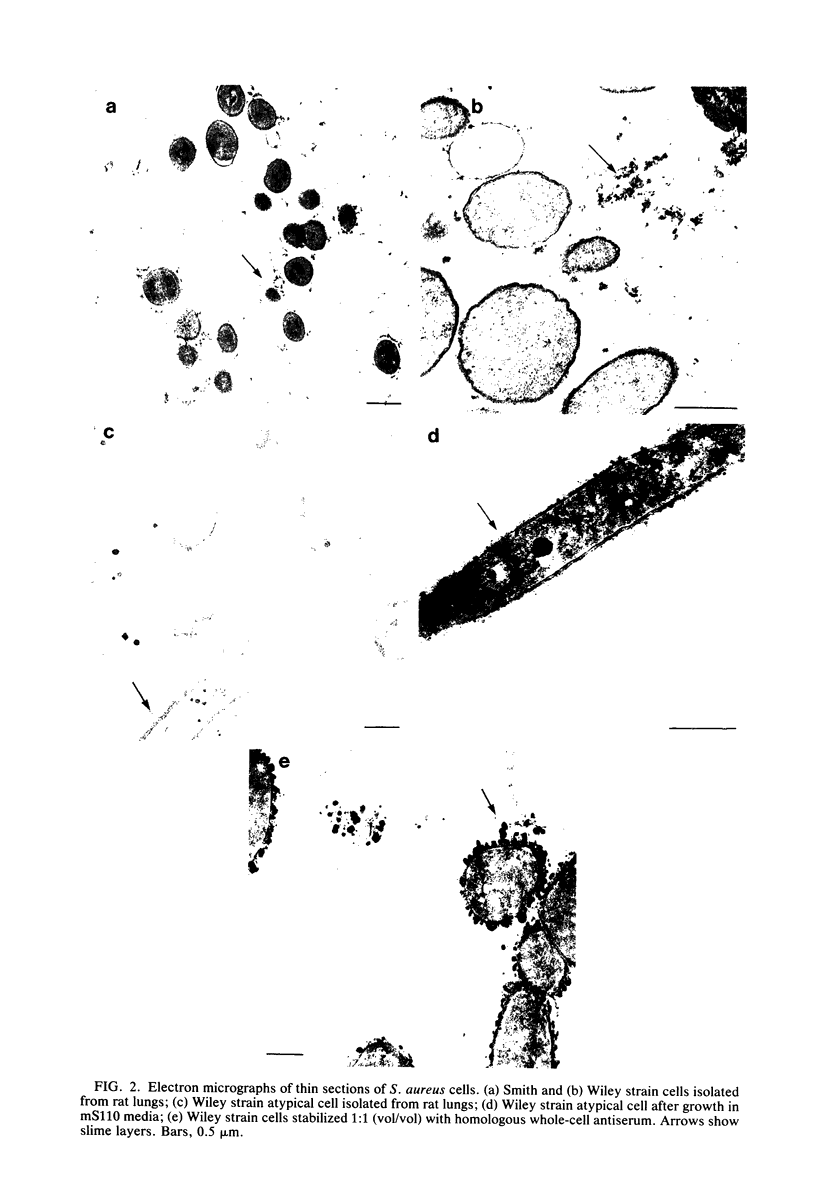
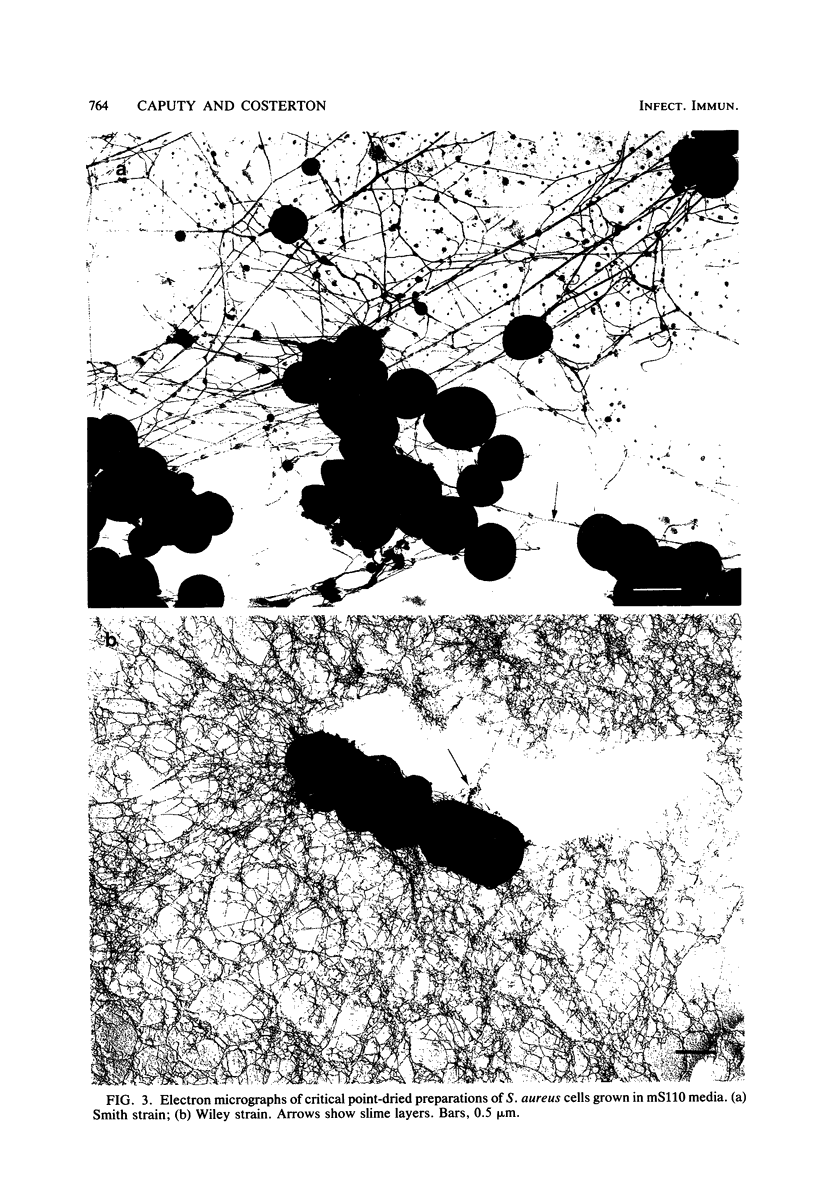
The glycocalyces of gram-positive bacteria have only been studied to a limited extent, with most studies being directed at the elucidation of capsules. With modern methods of electron microscopy, it has been shown that an extensive, diffuse polyanionic matrix surrounds Staphylococcus aureus cells of the Smith and Wiley strains, both in vivo and in modified staphylococcus 110 media. This slime layer was extracapsular in the case of the Smith strain, yet appeared to be the only layer peripheral to the teichoic acid in the Wiley strain. It is proposed that these glycocalyces serve a protective function and that their production is induced not only by excess nutrients in the growth medium but also by metabolic stress.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer M. E., Thurow H. Polysaccharide capsule of Escherichia coli: microscope study of its size, structure, and sites of synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):911–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.911-936.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cagle G. D. Fine structure and distribution of extracellular polymer surrounding selected aerobic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Mar;21(3):395–408. doi: 10.1139/m75-055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash H. A., Woods D. E., McCullough B., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. A rat model of chronic respiratory infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Mar;119(3):453–459. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.3.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. The formation of microcolonies by rumen bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Sep;26(9):1104–1113. doi: 10.1139/m80-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Geesey G. G., Cheng K. J. How bacteria stick. Sci Am. 1978 Jan;238(1):86–95. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0178-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The role of bacterial surface structures in pathogenesis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1981;8(4):303–338. doi: 10.3109/10408418109085082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN R. A., SULKIN S. E. Characteristics of coagulase positive and coagulase negative staphylococci in serum-soft agar. J Bacteriol. 1958 Mar;75(3):339–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.3.339-344.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb S. F., Pakman L. M. Effect of high oxygen tensions on the growth of selected, aerobic, gram-negative, athogenic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1003–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1003-1010.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst A., Hughes A., Pontefract R. Mechanism of the temperature protective effect of salts on Staphylococcus aureus. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Apr;26(4):511–517. doi: 10.1139/m80-086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khouw B. T., McCurdy H. D. Tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes and morphogenesis in Blastocladiella emersonii. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):197–205. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.197-205.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J., Chan R., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Production of mucoid microcolonies by Pseudomonas aeruginosa within infected lungs in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):546–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.546-556.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUDD S., DECOURCY S. J., Jr INTERACTION OF VISCID MATERIAL OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS WITH SPECIFIC IMMUNE SERUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:874–879. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.874-879.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. B., Brown K. N., Lam J., Costerton J. W. Morphological stabilization of capsules of group B streptococci, types Ia, Ib, II, and III, with specific antibody. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):609–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.609-617.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Lam J., Costerton J. W. Bacterial adhesion to uroepithelial cells: a morphologic study. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):239–246. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melly M. A., Duke L. J., Liau D. F., Hash J. H. Biological properties of the encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):389–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.389-397.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtomo T., Yoshida K. Encapsulation by transformation of strains of Staphylococcus aureus determined by the serum-soft agar technique. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1978 Dec;242(4):436–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Kim Y., Wilkinson B. J., Schmeling D., Michael A. F., Quie P. G. Dichotomy between opsonization and serum complement activation by encapsulated staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):770–775. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.770-775.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Influence of encapsulation on staphylococcal opsonization and phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):943–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.943-949.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom J. P., Larson C., Gorman J. M., Tulve S. Heterogeneity of antibody response to Salmonella lipopolysaccharide measured by passive hemagglutination and hemolysis in mice. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):909–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.909-915.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley B. B., Maverakis N. H. Capsule production and virulence among strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):221–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Holmes K. M. Staphylococcus aureus cell surface: capsule as a barrier to bacteriophage adsorption. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):549–552. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.549-552.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Peterson P. K. Factors affecting complement activation by Staphylococcus aureus cell walls, their components, and mutants altered in teichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):216–224. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.216-224.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G., Michael A. F. Activation of complement by cell surface components of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):388–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.388-392.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Cryptic peptidoglycan and the antiphagocytic effect of the Staphylococcus aureus capsule: model for the antiphagocytic effect of bacterial cell surface polymers. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):502–508. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.502-508.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Sisson S. P., Kim Y., Peterson P. K. Localization of the third component of complement on the cell wall of encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M: implications for the mechanism of resistance to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1159–1163. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1159-1163.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte W. Kapselbildung bei Staphylococcus aureus als Ursache für die Nicht-Typisierbarkeit durch Phagen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975 Dec;233(4):447–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K. Demonstration of Serologically Different Capsular Types Among Strains of Staphylococcus aureus by the Serum-Soft Agar Technique. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):535–539. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.535-539.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Ohtomo T., Minegishi Y. Mechanism of compact-colony formation by strains of Staphylococcus aureus in serum soft agar. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jan;98(1):67–75. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-1-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Takahashi M., Ohtomo T., Minegishi Y., Ichiman Y., Haga K., Kono E., San Clemente C. L. Application of fluorescent antibody for detecting capsular substances in Staphylococcus aureus. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;46(1):147–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb02592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]