Abstract
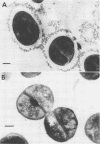
Various bile acids were added to cultures of encapsulated strains of Staphylococcus aureus growing in serum-soft agar medium of brain heart infusion broth. We examined effects of these compounds on cellular characteristics such as growth type, cell volume index, clumping factor reaction, slime yield, taurine content, and L-(--)-cysteic acid decarboxylase activity. Upon addition to the medium of either taurochenodeoxycholic acid, taurocholic acid (25 to 50 microgram/ml), or cholic acid (10 to 25 microgram/ml), the colonial morphology of taurine-positive cells (strain S-7) was altered from the diffuse to the compact type in serum-soft agar. Also, the titer of the clumping factor reaction increased, while the cell volume index and slime yield were markedly decreased. Tauro-bile acids, including taurocholic acid, taurochenodeoxycholic acid, taurodehydrocholic acid, and taurodeoxycholic acid (50 microgram/ml) inhibited the synthesis of taurine and resulted in decreased L-(--)-cysteic acid decarboxylase activity. Among all of the derivatives cholic acid itself was found to inhibit slime production and L-(--)-cysteic acid decarboxylase activity to the greatest extent. Glyco-bile acid derivatives and taurolicholic acid (50 to 100 microgram/ml) had no effect on L-(--)-cysteic acid decarboxylase activity. Compounds such as glycodeoxycholic acid (50 to 100 microgram/ml) had no effect upon any of the cellular characteristics tested. No effect was observed upon addition of any of these compounds to cultures of the taurine-negative strain (T-26-B). We did find a correlation between the inhibition of taurine biosynthesis and decreased slime production. Electron micrographs indicated that this encapsulated strain was converted to an unencapsulated state in the presence of bile acids.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALAMI S. Y., KELLY F. C. Demonstration of staphylococcal clumping factor and free coagulase in soft agar media. J Bacteriol. 1959 Oct;78:539–544. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.4.539-544.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aries V., Hill M. J. Degradation of steroids by intestinal bacteria. I. Deconjugation of bile salts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 5;202(3):526–534. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschko H. l(-)-Cysteic acid decarboxylase. Biochem J. 1942 Sep;36(7-9):571–574. doi: 10.1042/bj0360571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE E. S. The action of fibrinogen on certain pathogenic cocci. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Oct;13(2):383–393. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-2-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekstedt R. D., Bernhard J. M. Preparation and characterization of a slime layer material produced by Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jan;142(1):86–91. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-36964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN R. A., SULKIN S. E. Characteristics of coagulase positive and coagulase negative staphylococci in serum-soft agar. J Bacteriol. 1958 Mar;75(3):339–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.3.339-344.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLY A. P., WEED L. L. TAURINE AS A CONSTITUENT OF A BACTERIAL CELL WALL. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2519–2523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. A., Rabkin A. E., Karakawa W. W. Demonstration of the capsular antigens of bovine group B streptococci by the serum-soft agar method. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jul;2(1):35–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.1.35-41.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau D. F., Hash J. H. Structural analysis of the surface polysaccharide of Staphylococcus aureus M. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):194–200. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.194-200.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau D. F., Melly M. A., Hash J. H. Surface polysaccharide from Staphylococcus aureus M that contains taurine, D-aminogalacturonic acid, and D-fucosamine. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):913–922. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.913-922.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE M. L., ALIRE M. L. An agar medium indicating acid production. J Bacteriol. 1958 Sep;76(3):270–271. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.3.270-271.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN A., GRUBB R. Hydrolysis of conjugated bile acids by Clostridia and enterococci; bile acids and steroids 25. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1955;36(6):537–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1955.tb04651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtomo T., Usui Y., Yoshida K., Kawamura S., Suyama Y., San Clemente C. L. Biochemical and immunological properties of cell surface teichoic preparations from encapsulated strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Mar;163(3):425–431. doi: 10.3181/00379727-163-40791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtomo T., Yoshida K., Clemente C. L. Relationship of capsular type to biochemical and immunological properties of teichoic acid preparations from unencapsulated strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1976 Nov;14(5):1113–1118. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.5.1113-1118.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtomo T., Yoshida K. Encapsulation by transformation of strains of Staphylococcus aureus determined by the serum-soft agar technique. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1978 Dec;242(4):436–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtomo T., Yoshida K., Iizuka H., San Clemente C. L. Relative stability of biological properties in encapsulated strains of Staphylococcus aureus after freezing and freeze-drying. Cryobiology. 1978 Aug;15(4):461–468. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(78)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENTZ E. I., DAVENPORT C. H., GLOVER W., SMITH D. D. A test for the determination of taurine in urine. J Biol Chem. 1957 Sep;228(1):433–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirie N. W. The formation of sulphate from cysteine and methionine by tissues in vitro. Biochem J. 1934;28(1):305–312. doi: 10.1042/bj0280305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. Binding of human serum high density lipoprotein apoprotein with aqueous dispersions of phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):711–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley B. B. Capsule size, coagulase production, and egg virulence among certain strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jun;14(6):685–689. doi: 10.1139/m68-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K. Demonstration of Serologically Different Capsular Types Among Strains of Staphylococcus aureus by the Serum-Soft Agar Technique. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):535–539. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.535-539.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Nakamura A., Otomo T., Iwami S. Detection of capsular antigen production in unencapsulated strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1974 Apr;9(4):620–623. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.4.620-623.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Ohtomo T., Minegishi Y. Mechanism of compact-colony formation by strains of Staphylococcus aureus in serum soft agar. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jan;98(1):67–75. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-1-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Ohtomo T., Usui Y. Interaction of an alkali stable polysaccharide from cell surface of Staphylococci with human fibrinogen. Experientia. 1978 Jul 15;34(7):885–886. doi: 10.1007/BF01939683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Takahashi M., Takeuchi Y. Pseudocompact-type growth and conversion of growth types of strains of Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):162–166. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.162-166.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Takeuchi Y. Comparison of Compact and Diffuse Variants of Strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):523–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.523-527.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]