Abstract
Aim:
The purpose of this study was to evaluate and compare the post operative healing, using primary versus second closure techniques after impacted mandibular third molar removal.
Materials and Methods:
The study consisted of twelve patients, Seven males and five females under 30 years of age were divided into two groups as Group A and Group B in the randomized fashion. In the Group A, closure was done by primary intention and in the Group B, by secondary closure. A comparison between both groups was done with a follow-up period of 6 h to 6 days with regards to postoperative pain and swelling.
Results:
The statistical analysis (analysis of variance for repeated measures, P < 0.05) showed that pain was greater in Group A, although it decreased over time similarly in the two groups. Pain and swelling was less severe with secondary healing than with primary healing.
Conclusion:
The outcome of this study suggested that secondary closure technique is better than primary closure technique for removal of impacted mandibular third molar with regards to postoperative pain and swelling.
Keywords: Impaction, postoperative pain and swelling, third molar surgery
INTRODUCTION
Surgical removal of impacted mandibular third molar contributes a major chunk of an Oral Surgeon's work load. In spite of the various precautions taken, the postoperative period following surgical removal of third molar is frequently associated with pain, swelling and temporary restriction of mouth opening along with decreased masticatory capability. One of the factors most closely linked to the intensity of postoperative pain and swelling is the type of healing of the surgical wound.[1]
There is a certain amount of controversy regarding the type of healing based on whether it is of the primary or secondary type. Conflicting opinions have been expressed in the literature concerning these two types of healing. Some authors are in favor of closed healing, whereas other authors report that primary healing frequently causes greater pain and swelling than secondary healing.[2] Other authors are of the opinion that postoperative progress does not differ in the two types of healing.[3]
This comparative study compares primary and secondary healing after surgical removal of impacted third molars, evaluating the incidence of postoperative complications, and monitoring the extent of swelling and the severity of pain.
Also, this study compares the primary and secondary healing following surgical removal of impacted mandibular third molars by monitoring the extent of postoperative swelling and severity of pain.
Following criteria will be evaluated after post-surgical period:
Pain (based on VAS) and
Swelling (based on VAS)
In this prospective study, patients with partially erupted mesio-angular mandibular third molars were included for homogeneity. Patients were randomly divided into two groups.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twelve patients (7 males, 5 females, age range 20-30 years) were included in the series. Panoramic radiographs were taken to assess third molar eruption and angulation versus the adjacent second molar.
Swelling and pain were evaluated with the visual analogic scale (VAS), which is an efficacious tool to evaluate clinical parameters that influence subjective experience. The readings are taken at 6th hour postoperatively and each subsequent day for a period of 6 days.[4]
Inclusion criteria
Mesioangularly impacted, Class I, II and III, position A, B and C mandibular third molars (Winter's classification):
Group A or B requiring ostectomy and odontotomy
No history of systemic disease with good general health
No evidence of acute inflammation orally
No contraindication to use routine medications like anesthetic agents or antibiotics/analgesics.
All patients enrolled in the study gave their informed consent to the procedure.
In all the patients, routine blood and urine examination was carried out. Patient was asked to rinse the mouth thoroughly with 0.2% chlorhexidine and normal saline, in equal proportions. Extra oral skin preparation was done with 5% betadine and the patient was draped with sterile drapes. All the procedures were carried out under local anesthesia, 2% lignocaine with adrenaline 1:200000.
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
Incision
A standard third molar incision (Ward's incision: vertical cut starting from gingiva just below the distobuccal cusp of 2nd molar to mesiobuccal cusp of the same teeth. Joined by gingival sulcular incision then it is extended posterior laterally parallel to external oblique ridge 1 to 1.5 cm and then finishing the incision just mucosal) was given with Bard Parker handle No. 3 with No. 15 blade for all the impacted teeth [Figure 1]
Figure 1.

Standard Ward's incision
Preparation of wound for closure
After tooth was elevated from its socket, the wound was gently irrigated with sterile saline solution. Residual tooth sac from distal surface of mucosa, granulation tissue and small-detached fragments of bone and bone dust were removed from socket and from beneath the soft tissue flap. Sharp irregular edges and inter-radicular bone were trimmed. Cross-cut vulcanite bur was used for final smoothening of the socket margins. Bleeding was controlled by pressure packs and the wound was again irrigated with 0.2% chlorhexidine and saline, in equal proportions.
Closure of surgical wound
(Group ‘A’ Primary closure)
Excess tissue was trimmed from the flap margins with scissors before suturing. Primary closure was accomplished using interrupted sutures 3-0 silk. The ends of the sutures after knotting were cut so that approximately 3-5 mm of length remained [Figure 2].
Figure 2.
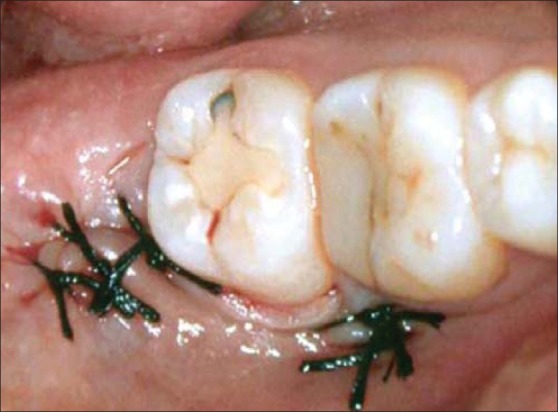
Group A, Primary closure: Flap design and clinical image
(Group ‘B’ Secondary closure)
In secondary closure technique, all surgical procedure will be same as in the primary closure technique, but in the time of closure a wedge of mucosa, width 5–6 mm was next removed from the second molar and the flap was repositioned and sutured with 3-0 silk sutures [Figure 3].
Figure 3.

Group B, secondry closure: flap design and clinical image
Patients were prescribed analgesics and antibiotics for five days. The patients were asked to avoid smoking, exertion and limit activity for at least remainder of the day. They were also given a daily pain and swelling record to be completed during the subsequent 7 days. Sutures were removed on the seventh postoperative day.
EVALUATION CRITERIA
Patients entered the degree of pain and swelling on the record, day by day, making reference to predefined values (VAS: Visual Analogic Scale). The pain scale was 5 cm long, subdivided into five equal parts, one end corresponding to no pain, the other to extremely severe pain.
Patients were asked to measure VAS scale readings postoperatively at 6th h, 1st day, 2nd day, 3rd day, 4th day, 5th day and 6th day after surgery.
The patients were examined at 7 and 30 days post-surgery. Any other complications were recorded.
STATISTICAL METHODS
The statistical analysis was done using SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) Version 15.0 Statistical Analysis Software. The values were represented in number (%) and mean ± SD. Wilcoxon Signed Rank test is used to compare between two groups.
RESULTS
The present study was conducted in the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Kothiwal Dental College and Research Centre, Moradabad (U.P.), with an objective to compare primary and secondary closure technique after removal of bilaterally impacted mandibular third molars. The postoperative pain and swelling was assessed by VAS. The study was conducted on 12 patients, 5 (41.7%) subjects in the age group 20–25 years and 7 (58.3%) subjects in the age group 26–30 years. The mean age of the subjects was 26.17 ± 3.35 years.
Out of 12 patients enrolled for the study, 7 (51.3%) were males and 5 (41.7%) were females. The male to female ratio of the study subjects was 1.4 : 1.
Postoperative assessment of patients in terms of pain at 6-h time interval shows the mean pain score of primary group as 1.67 ± 1.44, while that of secondary group as 1.00 ± 0.43; although the mean score of primary group was higher as compared to that of secondary group, yet the difference between the two groups was not significant statistically (P = 0.131). [Table 1]. As for swelling, the mean score in primary group was 1.00 ± 0.00, while in secondary group was 0.75 ± 0.62 [Table 2]. On comparing the data statistically the difference was found to be not significant.
Table 1.
Pain: Statistical analysis of data
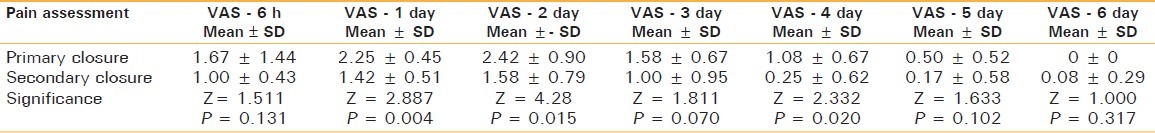
Table 2.
Swelling: Statistical analysis of data

Postoperative assessment of patients in terms of pain at day 1 was 2.25 ± 0.45 and 1.42 ± 0.51, respectively, in the primary and secondary groups [Table 1], while the mean swelling score was 2.58 ± 0.79 in primary group and 1.50 ± 0.52 in secondary group [Table 2]. Mean score of pain as well as swelling was found to be significantly higher in primary group as compared to secondary group (P = 0.004 and 0.006).
At day 2, the mean pain score was found to be 2.42 ± 0.90 in the primary group and 1.58 ± 0.79 in the secondary group [Table 1], while the swelling was found to be 2.67 ± 0.89 and 1.58 ± 0.67 in the primary and secondary groups, respectively [Table 2] The difference between the two groups was found to be statistically significant both for pain (p = 0.015) as well as for swelling (P = 0.006).
The mean pain score was found to be 1.58 ± 0.67 in the primary group and 1.00 ± 0.95 in the secondary group [Table 1], while the mean swelling score was found to be 2.08 ± 0.79 in the primary group and 1.08 ± 1.08 in the secondary group on third postoperative day Table 2. Statistically significant difference between two groups was seen for swelling (P = 0.018) but not for pain (P = 0.070).
The mean pain score was found to be 1.08 ± 0.67 in the primary group and 0.25 ± 0.62 in the secondary group [Table 1], while the mean swelling score was found to be 1.08 ± 0.67 in the primary group and 0.33 ± 0.65 in the secondary group on the fourth day [Table 2]. On comparing the data statistically, a significant difference between two groups was seen for both pain (P = 0.020) as well as swelling (P = 0.021) [Tables 1 and 2]. The mean pain score was found to be 0.50 ± 0.52 in the primary group and 0.17 ± 0.58 in the secondary group [Table 1], while the mean swelling score were also found to be same in two groups on the fifth day [Table 2]. However, no statistically significant difference between two groups could be seen (P = 0.102). The mean pain score was found to be 0 in the primary group and 0.08 ± 0.29 in the secondary group [Table 1], while the mean swelling score was found to be 0.25 ± 0.45 in the primary group and 0.08 ± 0.29 in the secondary group on the 6th day [Table 2]. On comparing the data statistically no significant difference between two groups was seen for both pain as well as swelling (P = 0.317).
DISCUSSION
Removal of impacted third molar constitutes a large number of various oral and maxillofacial procedures performed by surgeons. It is a procedure that demands technical skill, sound judgment, sound knowledge of anatomy and surgical principles, rationale of antibiotic therapy, good anesthesia, proper medication, nutritional balance and total patient care.[5]
Many a times removal of impacted third molar is followed by some unwanted postoperative complications like pain, swelling, paresthesia, postoperative infections, dry socket etc.[4] Many workers believe that postoperative complications occur due to either surgeon's negligence during removal (overstretching of tissues, mishandling of surgical instruments or by iatrogenic injury) or by patient not following postoperative instructions properly.[6]
The extent of swelling and the severity of pain are the chief indicators of patient comfort during the post-operative period after third molar removal. Swelling and pain were evaluated with the VAS scale,[7] which is considered to be an efficacious tool to evaluate clinical parameters that influence the subjective experience of an individual, such as pain.[8]
The results obtained in the present study determined secondary healing to be more comfortable for the patient with regard to these two parameters. These results are in agreement with many of those reported in the literature. The comparison of the two techniques within each individual patient showed that complete closure resulted in more pain and swelling postoperatively in a significant number of patients, but that the use of a dressing delayed satisfactory healing in a few patients.
Rakprasitkul and Pairuchvej[9] compared insertion of a small surgical tube drain with primary wound closure (drain group) to a simple primary wound closure (no drain group) after removal of impacted third molars. Surgery was performed on 23 patients in a randomized cross-over fashion. They concluded that the postoperative problems, in general, were less in the small surgical drain group as compared to the no drain group.
Pasqualini et al[10] did a study on 200 patients (122 women, 78 men; age range 19–27 years) with totally or partially bone-impacted mandibular third molar, Class C with mesial inclination included in the series. The conclusion of this study indicated that secondary closure of the socket causes less inconvenience to the patient as it appears to minimize post-extraction swelling and pain.

In 1995, Ayad[11] did a study on surgical removal of mandibular wisdom teeth with and without rubber drainage. This investigation compared the two types of wound closure, primary closure technique with and without Penrose drains (Naturallatex) after removal of mandibular third molar. The evaluation of findings shows that secondary closure technique was far better than primary closer and patients were more comfortable with secondary closer.
Saglam[12] compare the effects of placement of a surgical tube drain before primary closure with the effects of primary closure alone after removal of fully impacted mandibular third molars. They observed the facial swelling experienced by the drain group was significantly less than that experienced by the no drain group. The degree of trismus was greater in the no drain group than in the drain group, but the difference was not statistically significant. They concluded that use of a surgical drain, especially after removal of impacted third molars, will reduce postoperative facial swelling.
CONCLUSION
The outcome of this study suggested that secondary closure technique is better than primary closure technique for removal of impacted mandibular third molar with regards to postoperative pain and swelling.
Since the sample size in the study was very small, a larger sample size should be taken to validate the finding of this study.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared
REFERENCES
- 1.Archer WH. Impacted Teeth: Oral and Maxillofacial surgery. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 1975. pp. 275–390. [Google Scholar]
- 2.van Gool AV, Ten Bosch JJ, Boering G. A photographic method of assessing swelling following third molar removal. Int J Oral Surg. 1975;4:121–9. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9785(75)80004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.de Brabander EC, Cattaneo G. The effect of surgical drain together with a secondary closure technique on postoperative trismus, swelling and pain after mandibular third molar surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1988;17:119–21. doi: 10.1016/s0901-5027(88)80164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Holland CS, Hindle MO. The influence of closure or dressing of third molar sockets on post-operative swelling and pain. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1984;22:65–71. doi: 10.1016/0266-4356(84)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Killei KE, Kay LW. The impacted wisdom tooth. Philadelphia: Livingstone; 1975. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Garcia Garcia A, Gude Sampedro F, Gandara Rey J, Gallas Torreira M. Trismus ana pain after removal of impacted lower third molars. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997;55:1223–6. doi: 10.1016/s0278-2391(97)90172-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Berge TI. Visual analogue scale assessment of postoperative swelling. A study of clinical inflammatory variables subsequent to third-molar surgery. Acta Odontol Scand. 1988;46:233–40. doi: 10.3109/00016358809004772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Howe GL. The Management of impacted third molars: Minor oral surgery. London: Wright; 1988. pp. 109–43. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rakparasitkul S, Pairuchvej V. Mandibular third molar surgery with primary closure and tube drain. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997;26:187–90. doi: 10.1016/s0901-5027(97)80817-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pasqualini D, Cocero N, Castella A, Mela L, Bracco P. Primary and secondary closure of the surgical wound after removal of impacted mandibular third molars: A comparative study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;34:52–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2004.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ayad W, Jöhren P, Dieckmann J. Results of a comparative prospective randomized study of surgical removal of mandibular wisdom teeth with and without rubber drainage. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;8:6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ordulu M, Aktas I, Yalcin S. Comparative study of the effect of tube drainage versus methylprednisolone after third molar surgery. 2006;101:96–100. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


