Abstract
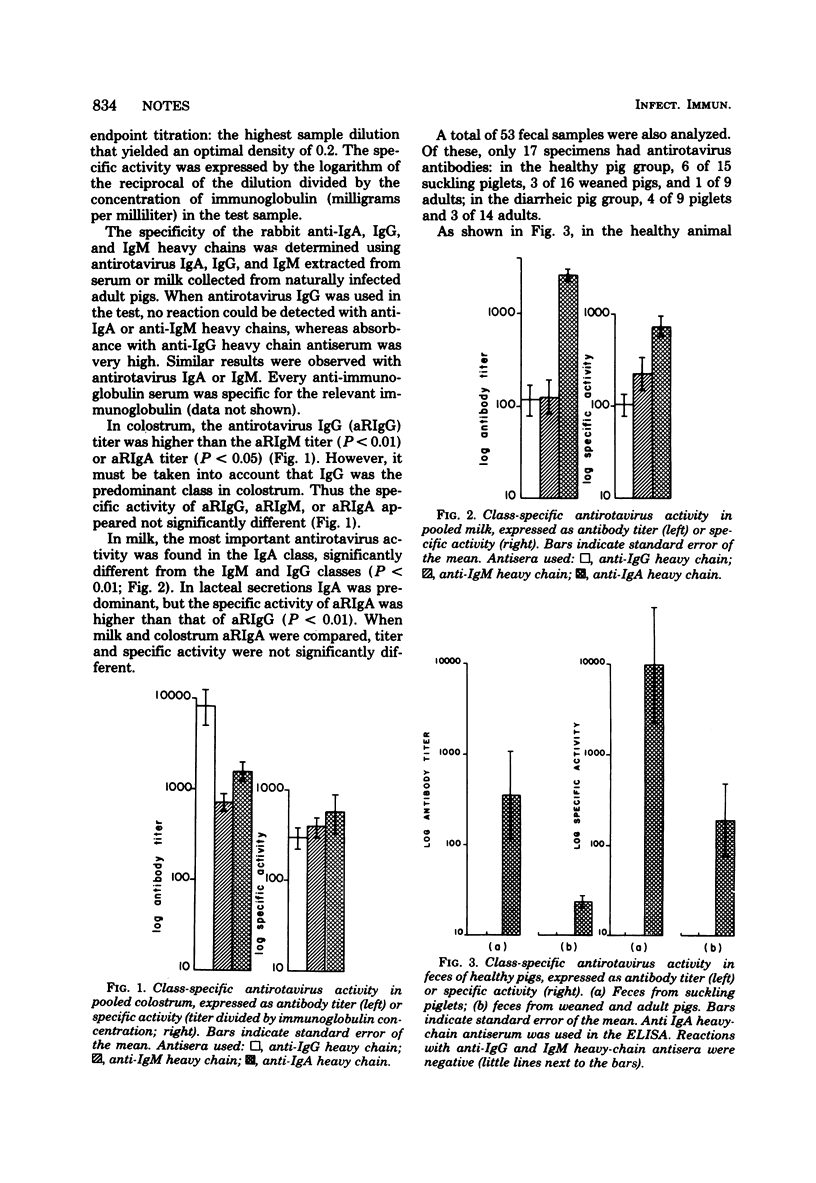
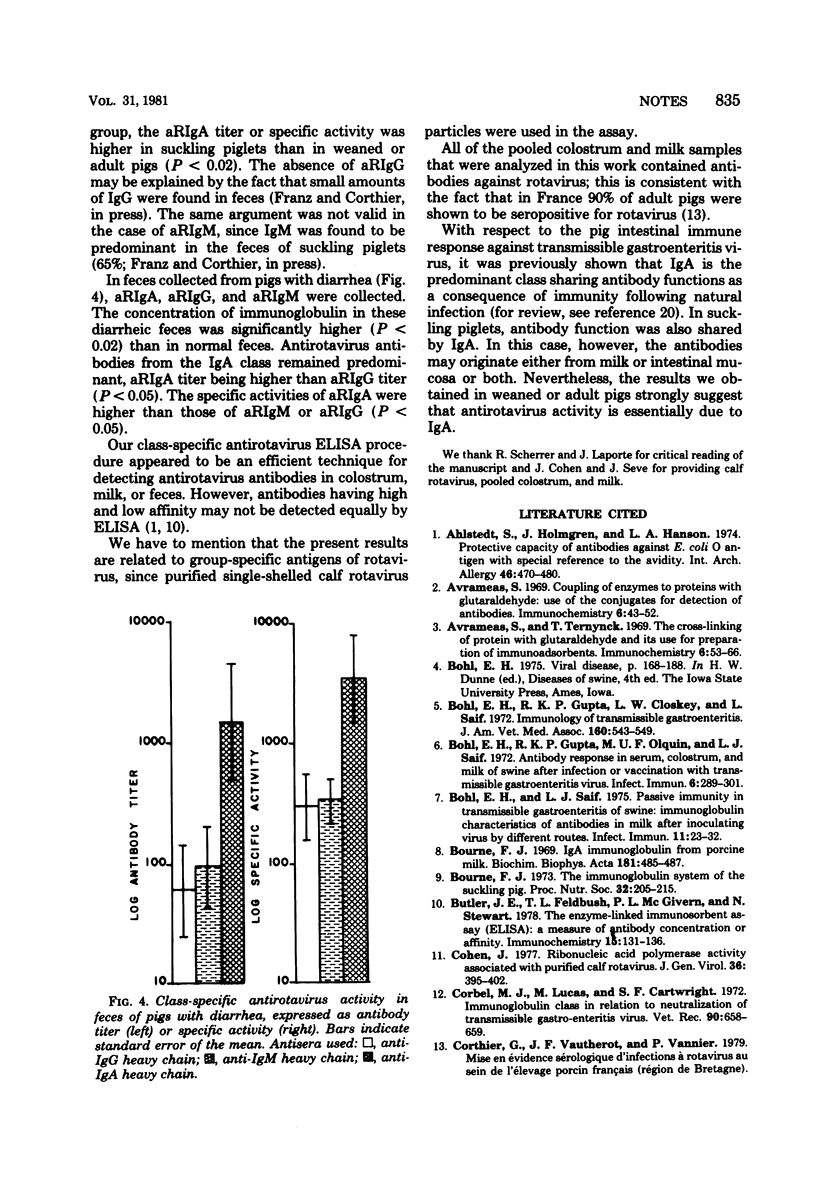
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was developed to allow direct detection of class-specific antirotavirus antibodies. In colostrum and in milk, antirotavirus antibodies were found in the three immunoglobulin classes. Antirotavirus immunoglobulins G and M were predominant in colostrum, whereas antirotavirus immunoglobulin A was predominant in milk and feces.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlstedt S., Holmgren J., Hanson L. A. Protective capacity of antibodies against E. coli O antigen with special reference to the avidity. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1974;46(3):470–480. doi: 10.1159/000231150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S. Coupling of enzymes to proteins with glutaraldehyde. Use of the conjugates for the detection of antigens and antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Gupta R. K., McCloskey L. W., Saif L. Immunology of transmissible gastroenteritis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Feb 15;160(4):543–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Gupta R. K., Olquin M. V., Saif L. J. Antibody responses in serum, colostrum, and milk of swine after infection or vaccination with transmissible gastroenteritis virus. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):289–301. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.289-301.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J. Passive immunity in transmissible gastroenteritis of swine: immunoglobulin characteristics of antibodies in milk after inoculating virus by different routes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):23–32. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.23-32.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne F. J. IgA immunoglobin from porcine milk. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 1;181(2):485–487. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne F. J. The immunoglobulin system of the suckling pig. Proc Nutr Soc. 1973 Dec;32(3):205–215. doi: 10.1079/pns19730041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. E., Feldbush T. L., McGivern P. L., Stewart N. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): a measure of antibody concentration or affinity. Immunochemistry. 1978 Feb;15(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. Ribonucleic acid polymerase activity associated with purified calf rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Sep;36(3):395–402. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel M. J., Lucas M., Cartwright S. F. Immunoglobulin class in relation to neutralisation of transmissible gastro-enteritis virus. Vet Rec. 1972 Jun 3;90(23):658–659. doi: 10.1136/vr.90.23.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis J., Bourne F. J. Immunoglobulin quantitation in sow serum, colostrum and milk and the serum of young pigs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 27;236(1):319–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittmar D., Cleary T. J., Castro A. Immunoglobulin G- and M-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of dengue antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):498–502. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.498-502.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for cholera serology. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):759–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.759-763.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin A antibodies to Shigella flexneri antigens. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):441–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.441-448.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Coulepis A. G., Stratton A. M., Kaldor J., Gust I. D. Solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of hepatitis A-specific immunoglobulin M. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):459–465. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.459-465.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristic M., Abou-Youssef M. H. Comments on the immunology of transmissible gastroenteritis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Feb 15;160(4):549–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprino P. J., Morilla A., Ristic M. Intestinal immune response of feeder pigs to infection with transmissible gastroenteritis virus. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Feb;37(2):171–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. S., Kemeny L. J., Woods R. D., Jensen M. T. Efficacy of isolated colostral IgA, IgG, and IgM(A) to protect neonatal pigs against the coronavirus of transmissible gastroenteritis. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Sep;38(9):1285–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Kim H. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Immunological response to infection with human reovirus-like agent: measurement of anti-human reovirus-like agent immunoglobulin G and M levels by the method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):540–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.540-546.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


