Abstract
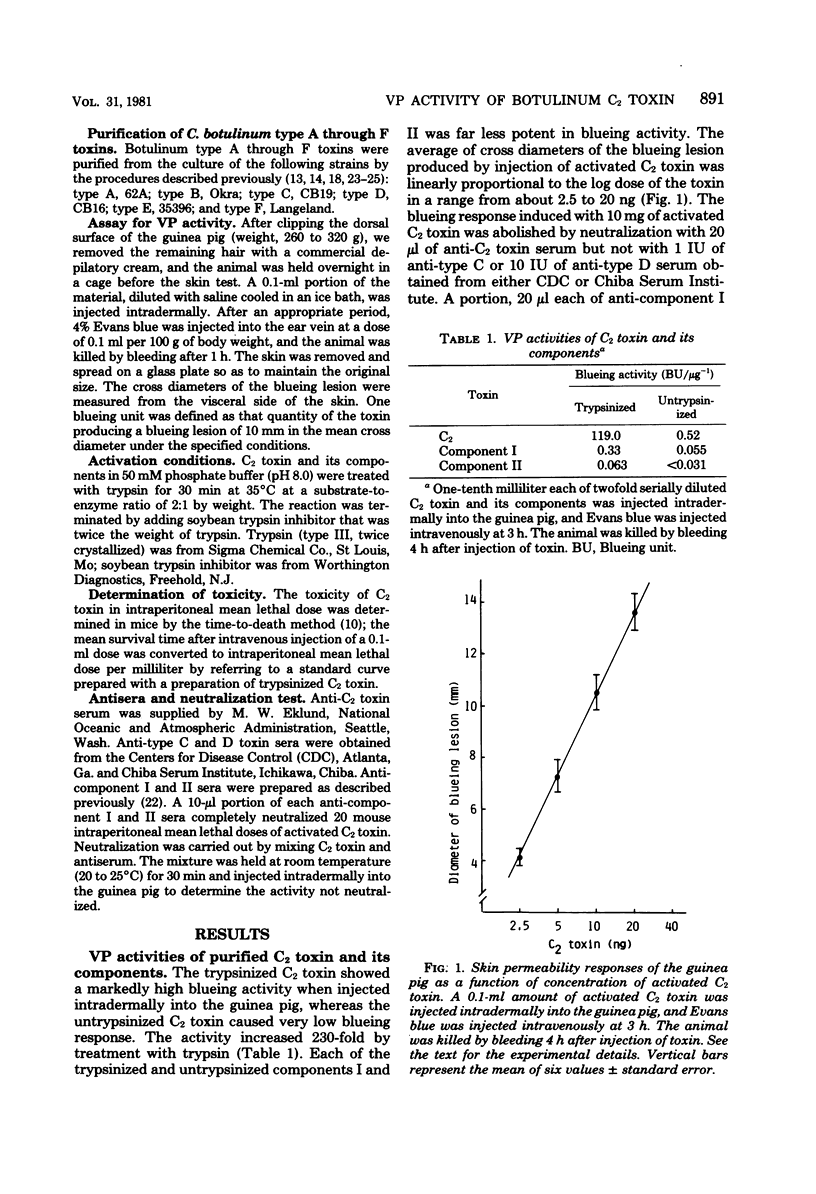
Botulinum C2 toxin has vascular permeability as well as lethal activities. Both activities are elicited by cooperation of two dissimilar protein components, designated components I and II, which individually have very low activities. The vascular permeability activity of C2 toxin, demonstrated as blueing response after intravenous injection of Evans blue, was markedly enhanced by treatment with trypsin and was abolished by neutralization with either anti-component I or II serum. Inflammatory reactions, such as edema, congestion, and hemorrhage, were found at the site of intradermal injection of trypsinized C2 toxin. No vascular permeability activity was demonstrated by the intradermal injection of the toxin of Clostridium botulinum types A through F. These results indicate that C2 toxin has a novel biological activity, which is not possessed by the neurotoxin elaborated by C. botulinum types A through F. This suggests that C2 toxin causes lethality in a different way from that of botulinum neurotoxin, which is known to inhibit the presynaptic release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beers W. H., Reich E. Isolation and characterization of Clostridium botulinum type B toxin. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4473–4479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta B. R., Boroff D. A. Separation of toxin and hemagglutinin from crystalline toxin of Clostridium botulinum type A by anion exchange chromatography and determination of their dimensions by gel filtration. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):1065–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund M. W., Poysky F. T. Activation of a toxic component of Clostridium botulinum types C and D by trypsin. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jul;24(1):108–113. doi: 10.1128/am.24.1.108-113.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund M. W., Poysky F. T., Reed S. M. Bacteriophage and the toxigenicity of Clostridium botulinum type D. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 5;235(53):16–17. doi: 10.1038/newbio235016a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund M. W., Poysky F. T., Reed S. M., Smith C. A. Bacteriophage and the toxigenicity of Clostridium botulinum type C. Science. 1971 Apr 30;172(3982):480–482. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3982.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Iida H. Conversion of toxigenicity in Clostridium botulinum type C. Jpn J Microbiol. 1970 Jan;14(1):87–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1970.tb00495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Iida H. Phage-conversion of toxigenicity in Clostridium botulinum types C and D. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1971 Feb;24(1):53–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki M., Ohishi I., Sakaguchi G. Evidence that botulinum C2 toxin has two dissimilar components. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):390–394. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.390-394.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen B. C., Knoetze P. C. Tryptic activation of Clostridium botulinum type C beta toxin. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1971 Dec;38(4):237–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen B. C. The toxic antigenic factors produced by Clostridium botulinum types C and D. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1971 Jun;38(2):93–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura M., Sakaguchi S., Sakaguchi G. Purification and some properties of Clostridium botulinum type-E toxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 21;168(2):207–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozaki S., Sakaguchi G. Antigenicites of fragments of Clostridium botulinum type B derivative toxin. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):932–936. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.932-936.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozaki S., Sakaguchi S., Sakaguchi G. Purification and some properties of progenitor toxins of Clostridium botulinum type B. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):750–756. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.750-756.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S., Iwasaki M., Sakaguchi G. Clostridium botulinum type D toxin: purification, molecular structure, and some immunological properties. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):395–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.395-401.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Serikawa T., Yamakawa K., Nishida S., Kozaki S., Sakaguchi G. Sporulation and C2 toxin production by Clostridium botulinum type C strains producing no C1 toxin. Microbiol Immunol. 1978;22(10):591–596. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1978.tb00409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A. [Production of the trypsin-activable toxin by Clostridium botulinum type C and D strains (author's transl)]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1977 Nov;32(6):805–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohishi I., Iwasaki M., Sakaguchi G. Purification and characterization of two components of botulinum C2 toxin. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):668–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.668-673.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohishi I., Sakaguchi G. Oral toxicities of Clostridium botulinum type C and D toxins of different molecular sizes. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):303–309. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.303-309.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi I., Sakaguchi G. Purification of Clostridium botuliunum type F progenitor toxin. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):923–928. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.923-928.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugii S., Sakaguchi G. Molecular construction of Clostridium botulinum type A toxins. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1262–1270. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1262-1270.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Das Gupta R., Yang K. H. Disulfide-toxicity relationship of botulinal toxin types A, E, and F. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jul;143(3):589–591. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syuto B., Kubo S. Isolation and molecular size of Clostridium botulinum type C toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):400–405. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.400-405.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syuto B., Kubo S. Structure and toxicity of Clostridium botulinum type C toxin. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1979 Apr;32(2):132–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



