Abstract
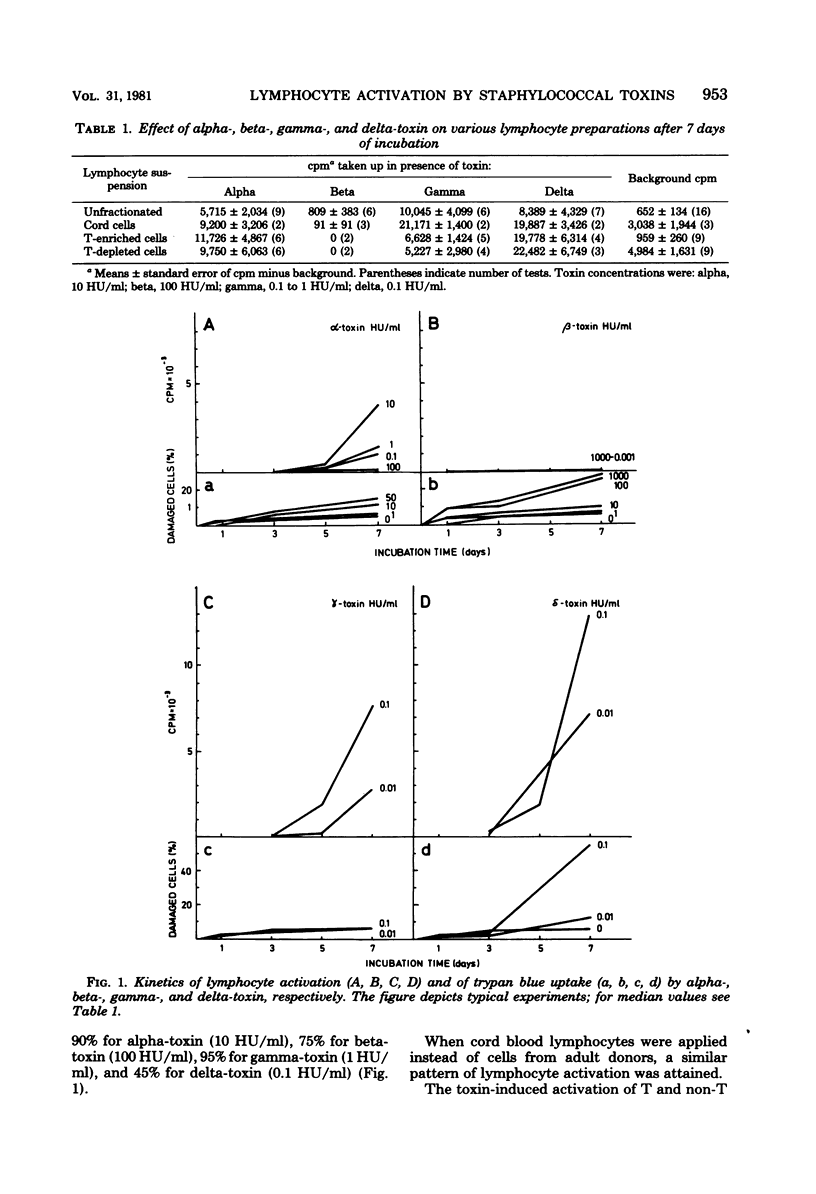
Purified staphylococcal alpha-, gamma-, and delta-toxin were shown to cause activation of lymphoid cells from adult human donors and of cord cells in vitro as measured by [14C]thymidine incorporation after 7 days of incubation. T cell-enriched and T cell-depleted lymphocyte suspensions were activated in a similar fashion. Beta-toxin, on the other hand, exerted no valid stimulation of the various lymphocyte preparations. The lymphocyte-activating properties of alpha- and gamma-toxin were shown to be independent of their hemolytic capacity. The results probably reflect unspecific mitogen effects, but a component of specific reactivity cannot be excluded. We suggest that the unspecific triggering of lymphocytes in vitro is caused by surface-active properties of the toxins.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S., Grushoff P. Lytic effects of staphylococcal alpha-toxin and delta-hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):487–491. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.487-491.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colacicco G., Basu M. K., Buckelew A. R., Jr, Bernheimer A. W. Surface properties of membrane systems. Transport of staphylococcal delta-toxin from aqueous to membrane phase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 1;465(2):378–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerski P., Jeljaszewicz J., Szmigielski S., Zak C. Blastoid transformation of rabbit lymphocytes by staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin and leukocidin. Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1968;90(4):328–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R., Dziarski A. Mitogenic activity of staphylococcal peptidoglycan. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):706–710. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.706-710.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Glynn A. A. Effect of cyclophosphamide on delayed hypersensitivity to Staphylococcus aureus in mice. Immunology. 1977 Nov;33(5):767–776. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Glynn A. A. The cellular control of delayed hypersensitivity to Staphylococcus aureus in mice. Immunology. 1979 Sep;38(1):103–108. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L., Lack C. H. The action of staphylococcal delta-lysin on lysosomes and lymphocytes. Life Sci. 1969 Jul 15;8(14):677–681. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Svedjelund A., Wigzell H. Lymphocyte stimulation by protein A of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Mar;6(3):207–213. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Cuppari G., Taranta A. Isolation by electrofocusing of two lymphocyte mitogens produced by Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):723–727. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.723-727.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Adler W. H., Smith R. T. The mitogenic effects of endotoxin and staphylococcal enterotoxin B on mouse spleen cells and human peripheral lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1453–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrini B., Bergqvist G., Palmblad J., Wasserman J., Arneborn P., Jarstrand C., Carlström A. Immunologic investigation in children with recurrent pneumonia. Scand J Infect Dis. 1977;9(3):197–203. doi: 10.3109/inf.1977.9.issue-3.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrini B., Wasserman J., Biberfeld G., Baral E., Blomgren H. The effect of in vitro irradiation on PHA-mediated cytotoxicity and lymphocytes with receptors for the Fc part of Ig. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1979 Nov;2(4):333–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Schoettle D. J., Watson D. W. Nonspecific T-lymphocyte mitogenesis by pyrogenic exotoxins from group A streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):1075–1077. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.1075-1077.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmigielski S., Blankenship M., Robinson J. P., Harshman S. Injury of myelin sheaths in isolated rabbit vagus nerves by alpha-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Toxicon. 1979;17(4):363–371. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(79)90264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmigielski S., Janiak M., Möllby R., Wadström T., Jeljaszewicz J. Metabolism of rabbit kidney cells incubated in vitro with phospholipase C from Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium perfringens. Toxicon. 1978;16(6):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(78)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Classification of microbial, plant and animal cytolysins based on their membrane-damaging effects of human fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):156–169. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R., Wadström T. Effects of staphylococcal alpha-, beta-, delta-, and gamma-hemolysins on human diploid fibroblasts and HeLa cells: evaluation of a new quantitative as say for measuring cell damage. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):938–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.938-946.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


