Abstract
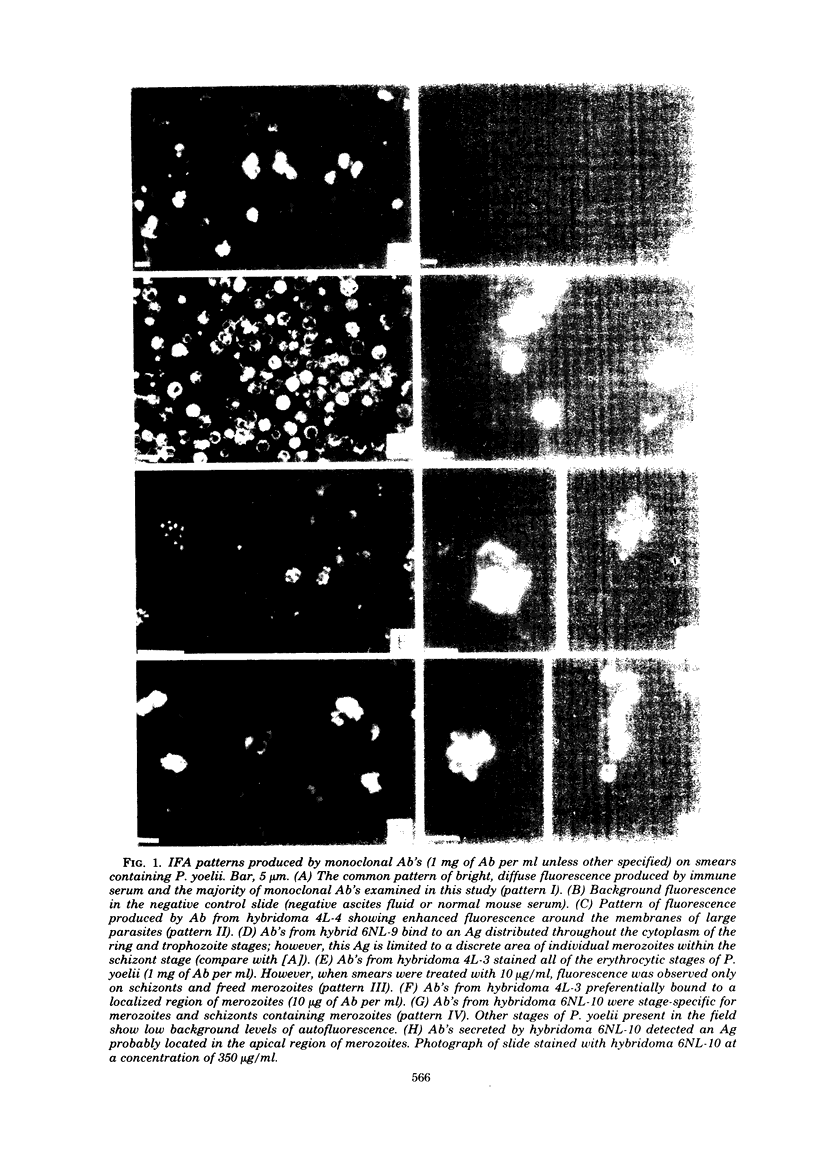
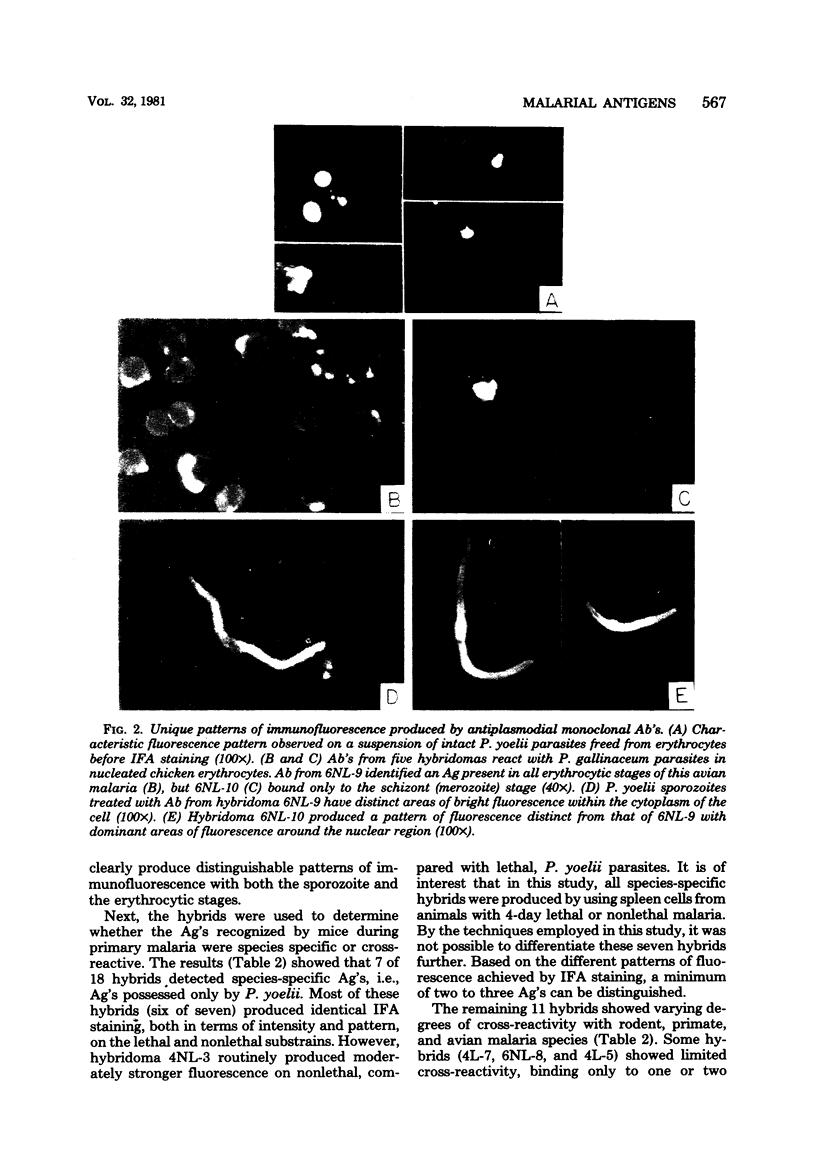
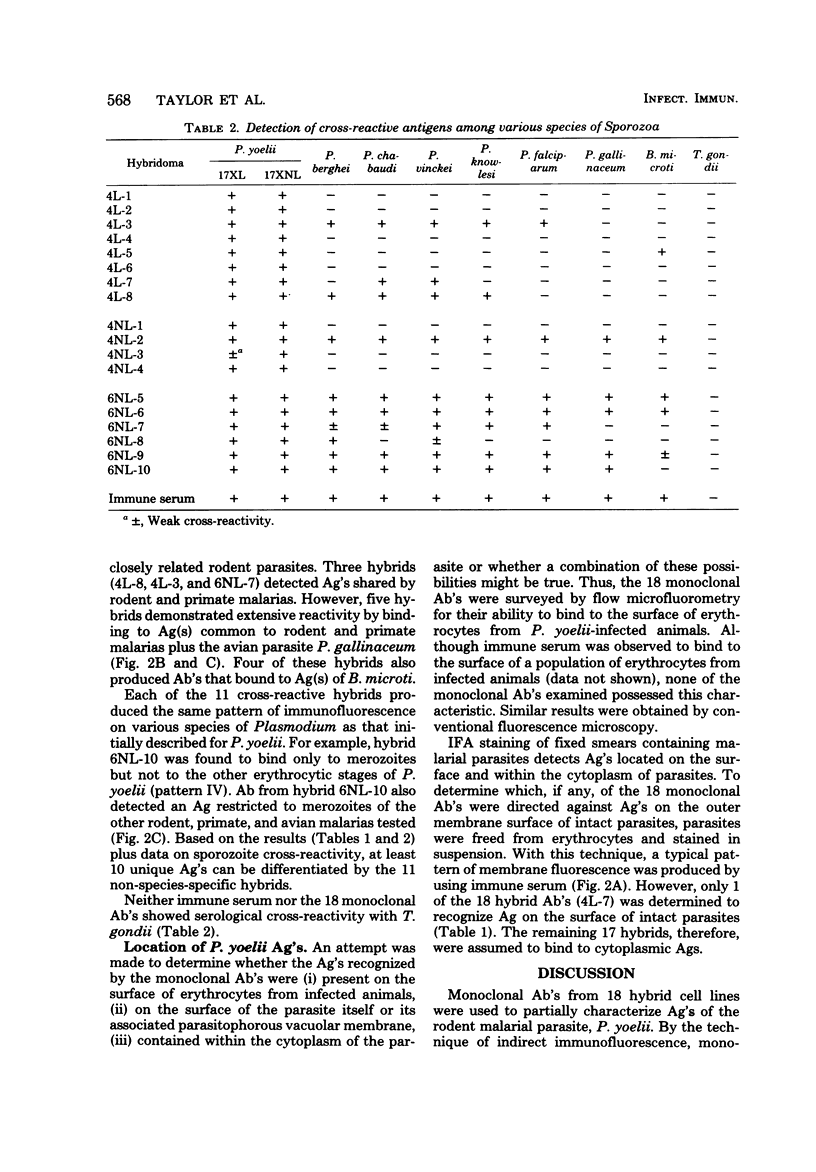
Eighteen hybridoma cell lines were used to study species-specific, stage-specific, and serological cross-reactive antigens of the rodent malarial parasite, Plasmodium yoelii. Specificity and location of plasmodial antigens were determined by indirect fluorescent-antibody analysis. Results showed that a minimum of 12 distinct plasmodial antigens could be distinguished by the 18 hybridomas. Antigens were found on the surface or within the cytoplasm of the parasite, but not on the surface of erythrocytes from infected animals. The majority (11 of 12) of antigens were present in all erythrocytic stages of the parasite, but one was stage-specific for merozoites. Additional studies showed that 6 of 18 of the monoclonal antibodies identified species-specific antigens, 2 of 18 recognized antigens confined to related rodent malarial parasites (Plasmodium berghei, Plasmodium vinckei, and Plasmodium chabaudi), whereas 8 of 18 detected cross-reactive antigens common to rodent, primate (Plasmodium knowlesi, Plasmodium falciparum), and avian (Plasmodium gallinaceum) malarias.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen S. Immunity to malaria. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Jan 15;203(1153):323–345. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins W. E., Skinner J. C., Guinn E. C. Antigenic variations in the plasmodia of lower primates as detected by immuno-fluorescence. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Jul;15(4):483–485. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox F. E. The specificity of immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M in the fluorescent-antibody test for malaria parasites in mice. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(2):341–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox F. E., Turner S. A. Antigenic relationships between the malaria parasites and piroplasms of mice as determined by the fluorescent-antibody technique. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(2):337–340. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans J. A., Dennis E. D., Cohen S. Antigenic analysis of sequential erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium knowlesi. Parasitology. 1978 Dec;77(3):333–344. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000050290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eby W. C., Kim B. S., Dray S., Young-Cooper G. O., Mage R. G. Detection of the e14 and e15 rabbit allotypic specificities by immunodiffusion in PEG agar. Immunochemistry. 1973 Jun;10(6):417–418. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. R., Trejdosiewicz A. J., Cross G. A. Protective monoclonal antibodies recognising stage-specific merozoite antigens of a rodent malaria parasite. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):366–368. doi: 10.1038/284366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Smith P. M., Mitchell G. F. Removal of leucocytes from red cells in Plasmodium berghei-infected mouse blood and purification of schizont-infected cells. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1978 Dec;72(6):573–575. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1978.11719363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBS L., LUNDE M. N. A hemagglutination test for toxoplasmosis. J Parasitol. 1957 Jun;43(3):308–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUVIN S. F., TOBIE J. E., EVANS C. B., COATNEY G. R., CONTACOS P. G. Antibody production in human malaria as determined by the fluorescent antibody technique. Science. 1962 Mar 30;135(3509):1130–1131. doi: 10.1126/science.135.3509.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielmann A., Weiss N. Plasmodium gallinaceum as antigen in immunofluorescence antibody studies. Acta Trop. 1968;25(2):185–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Taylor D. W., Evans C. B., Asofsky R. Radioimmunoassay for detecting antibodies against murine malarial parasite antigens: monoclonal antibodies recognizing Plasmodium yoelii antigens. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2565–2569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G., Jensen J. B., Reese R. T., Trager W. Fine structure of human malaria in vitro. J Protozool. 1978 Nov;25(4):443–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1978.tb04167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G., Reese R. T. Antigenicity of the infected-erythrocyte and merozoite surfaces in Falciparum malaria. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1241–1254. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies D. H., Cieplinski W., Dharmgrongartama B., Gefter M. L., Morrison S. L., Kelly T., Scharff M. D. Regulation of immunoglobulin expression in mouse myeloma cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):781–791. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Aikawa M., Dvorak J. A. Malaria (Plasmodium knowlesi) merozoites: immunity and the surface coat. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1237–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. H., Butcher G. A., Cohen S. A merozoite vaccine effective against Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. Nature. 1974 Nov 22;252(5481):311–313. doi: 10.1038/252311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W., Johnson B. M., Gershon H. E., Asofsky R. Immune responses in vitro. 3. Development of primary gamma-M, gamma-G, and gamma-A plaque-forming cell responses in mouse spleen cell cultures stimulated with heterologous erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1971 Aug 1;134(2):395–416. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Feldman H. A. Dyes as Microchemical Indicators of a New Immunity Phenomenon Affecting a Protozoon Parasite (Toxoplasma). Science. 1948 Dec 10;108(2815):660–663. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2815.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Wallach D. F., Lightholder J. Two Plasmodium knowlesi-specific antigens on the surface of schizont-infected Rhesus monkey erythrocytes induce antibody production in immune hosts. J Exp Med. 1979 Jul 1;150(1):86–99. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOBIE J. E., KUVIN S. F., CONTACOS P. G., COATNEY G. R., EVANS C. B. Fluorescent antibody studies on cross reactions between human and simian malaria in normal volunteers. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1962 Sep;11:589–596. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1962.11.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbaum F. I., Evans C. B., Tigelaar R. E. An in vitro assay for T cell immunity to malaria in mice. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1280–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbaum F. I., Weintraub J., Nkrumah F. K., Evans C. B., Tigelaar R. E., Rosenberg Y. J. Immunity to Plasmodium berghei yoelii in mice. II. Specific and nonspecific cellular and humoral responses during the course of infection. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):629–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida N., Nussenzweig R. S., Potocnjak P., Nussenzweig V., Aikawa M. Hybridoma produces protective antibodies directed against the sporozoite stage of malaria parasite. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):71–73. doi: 10.1126/science.6985745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Nahal H. M. Serological cross-reaction between rodent malaria parasites as determined by the indirect immunofluorescent technique. Bull World Health Organ. 1967;36(3):423–429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]