Abstract
When susceptible cells are exposed to diphtheria toxin (Mr, 62,000) the N-terminal 21,150-dalton A fragment of toxin reaches the cytoplasm, where it catalyzes the transfer of adenosinediphosphoribose from nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide to elongation factor 2 (EF2). Adenosinediphosphoribose-EF2 is inactive, so that protein synthesis is blocked. Using a simple, rapid assay for the amount of adenosinediphosphoribosylatable EF2 in unfractionated lysates of cultured cells we have followed the kinetics of inactivation of EF2 in CV-1 and BHK cells exposed to diphtheria toxin. With both cell lines a lag was observed between the addition of toxin to the cells and the adenosinediphosphoribosylation of EF2. The lag decreased with increasing toxin concentration until a limiting value of about 12 min was reached. The rate of adenosinediphosphoribosylation of EF2 after the lag was 10 to 20 times more rapid in CV-1 cells than in BHK cells exposed to the same toxin concentration. The concentration of fragment A active in the cytoplasm of toxin-treated cells was estimated from the rate of adenosinediphosphoribosylation observed. Comparison of these estimates with data from studies of binding of 125I-toxin to cells suggests that the fragment A of only a minor fraction of toxin molecules bound to cell surface receptors reaches the cytoplasm and participates in the inactivation of EF2. A model summarizing our current views on the process by which fragment A enters cells is presented.
Full text
PDF


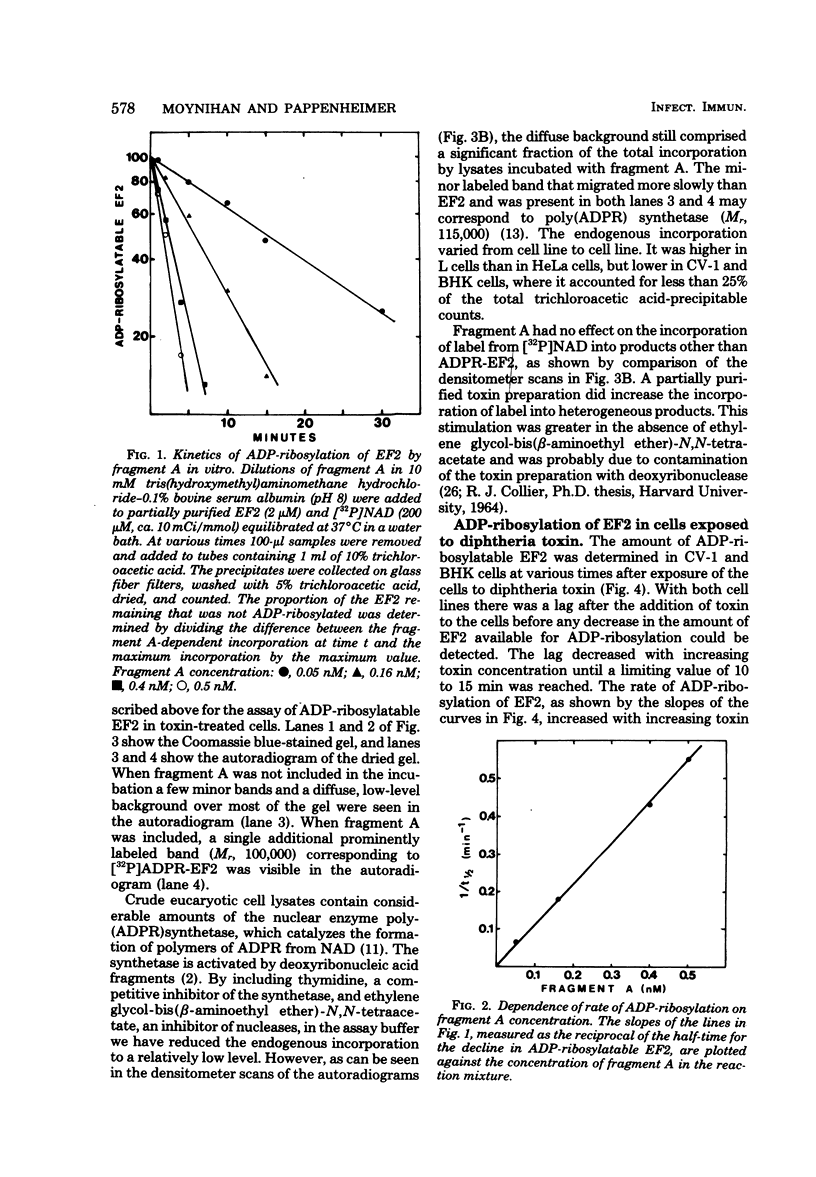
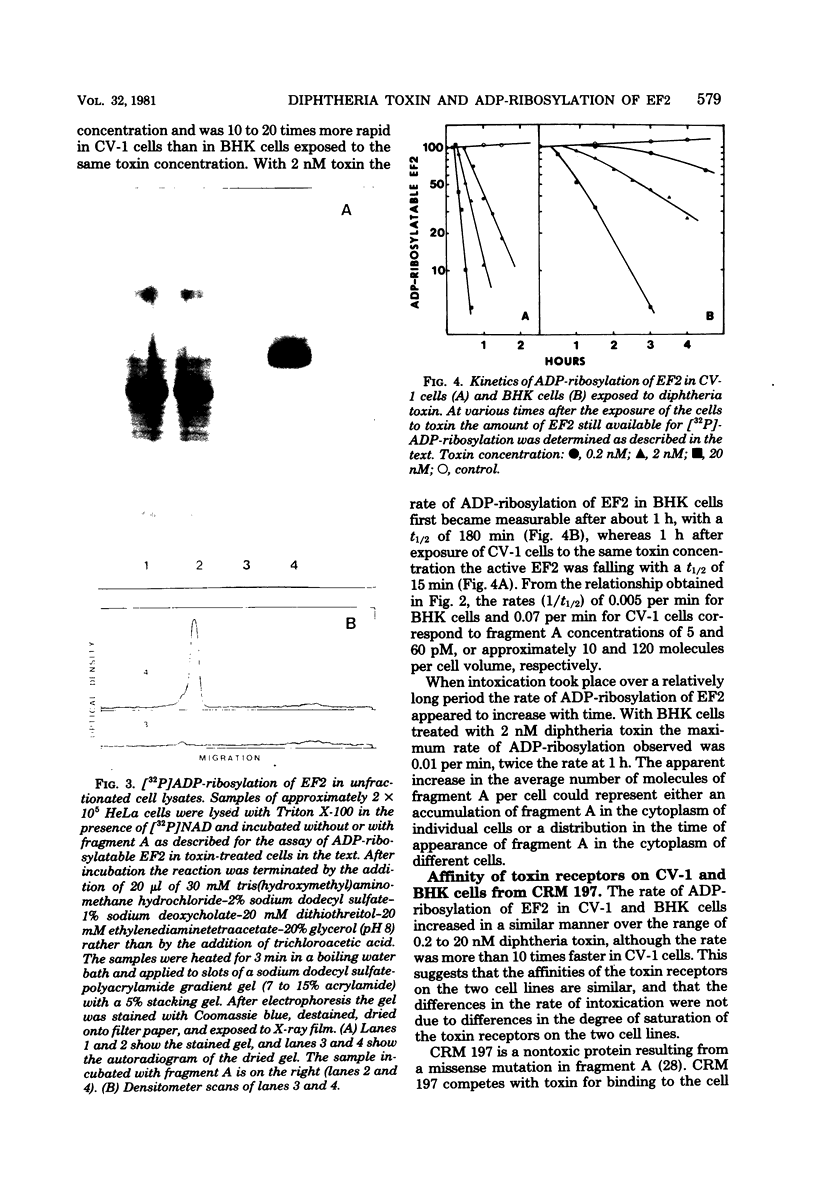
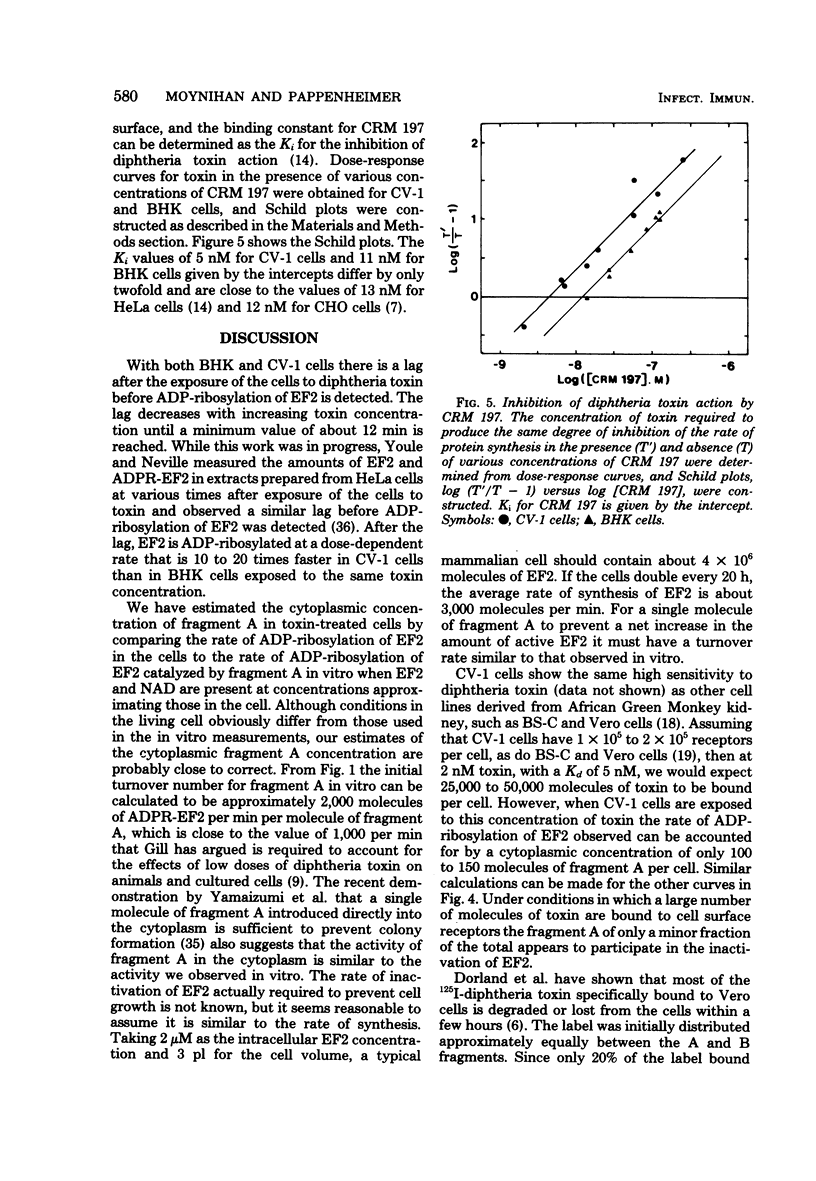


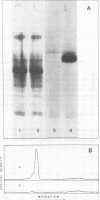
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlinghaus R., Shaeffer J., Bishop J., Schweet R. Purification of the transfer enzymes from reticulocytes and properties of the transfer reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 May;125(2):604–613. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90619-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin R. C., Gill D. M. Poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis in vitro programmed by damaged DNA. A comparison of DNA molecules containing different types of strand breaks. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10502–10508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquet P. Interaction of diphtheria toxin fragments A, B and protein crm 45 with liposomes. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;100(2):483–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquet P., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Interaction of diphtheria toxin with mammalian cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5770–5778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorland R. B., Middlebrook J. L., Leppla S. H. Receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of diphtheria toxin by monkey kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11337–11342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper R. K., Chin D., Stubbs L., Simon M. I. Studies of the diphtheria toxin receptor on Chinese hamster cells. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(1):47–55. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper R. K., Simon M. I. The entry of diphtheria toxin into the mammalian cell cytoplasm: evidence for lysosomal involvement. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):849–854. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Dinius L. L. The elongation factor 2 content of mammalian cells. Assay method and relation to ribosome number. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):654–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayaishi O., Ueda K. Poly(ADP-ribose) and ADP-ribosylation of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:95–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Kartenbeck J., Simons K., Fries E. On the entry of Semliki forest virus into BHK-21 cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):404–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Shizuta Y., Hayaishi O. Purification and characterization of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3647–3651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ittelson T. R., Gill D. M. Diphtheria toxin: specific competition for cell receptors. Nature. 1973 Mar 30;242(5396):330–332. doi: 10.1038/242330b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivins B., Saelinger C. B., Bonventre P. F., Woscinski C. Chemical modulation of diphtheria toxin action on cultured mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):665–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.665-674.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Groman N. B. In vitro inhibition of diphtheria toxin action by ammonium salts and amines. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1552–1556. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1552-1556.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S., Dorland R. B., Middlebrook J. L. Inhibition of diphtheria toxin degradation and cytotoxic action by chloroquine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2247–2250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B., Leppla S. H. Association of diphtheria toxin with Vero cells. Demonstration of a receptor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7325–7330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Response of cultured mammalian cells to the exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Corynebacterium diphtheriae: differential cytotoxicity. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Feb;23(2):183–189. doi: 10.1139/m77-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J., Danley D. E. Posttranslational modification of elongation factor 2 in diphtheria-toxin-resistant mutants of CHO-K1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1010–1014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Moehring J. M. Interaction of diphtheria toxin and its active subunit, fragment A, with toxin-sensitive and toxin-resistant cells. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1426–1432. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1426-1432.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE C. G. Observations on the diphtheria toxin-antitoxin reaction. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Apr;38(2):207–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Uchida T., Harper A. A. An immunological study of the diphtheria toxin molecule. Immunochemistry. 1972 Sep;9(9):891–906. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. A., Henriksen O., Maxwell E. S. Elongation factor 2. Amino acid sequence at the site of adenosine diphosphate ribosylation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5088–5093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Diphtheria toxin entry into cells is facilitated by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):828–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Greany R. Diphtheria toxin and related proteins. I. Isolation and properties of mutant proteins serologically related to diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3838–3844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Howard J. B., Bodley J. W. ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 by diphtheria toxin. NMR spectra and proposed structures of ribosyl-diphthamide and its hydrolysis products. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10710–10716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kartenbeck J., Helenius A. Fusion of Semliki forest virus with the plasma membrane can be induced by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):264–272. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wibo M., Poole B. Protein degradation in cultured cells. II. The uptake of chloroquine by rat fibroblasts and the inhibition of cellular protein degradation and cathepsin B1. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):430–440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Pastan I. The receptosome: an intermediate organelle of receptor mediated endocytosis in cultured fibroblasts. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90115-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Yamada S. S. A mechanism for the destruction of pinosomes in cultured fibroblasts. Piranhalysis. J Cell Biol. 1978 Aug;78(2):480–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaizumi M., Mekada E., Uchida T., Okada Y. One molecule of diphtheria toxin fragment A introduced into a cell can kill the cell. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youle R. J., Neville D. M., Jr Receptor-mediated transport of the hybrid protein ricin-diphtheria toxin fragment A with subsequent ADP-ribosylation of intracellular elongation factor II. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11089–11096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C., de Barsy T., Poole B., Trouet A., Tulkens P., Van Hoof F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 15;23(18):2495–2531. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]