Abstract
Hereditary gingival fibromatosis is a rare condition characterized by various degree of gingival overgrowth. It usually develops as an isolated disorder but can manifest with multisystem syndrome. We are here presenting a case of a 13-year-old girl who presented with severe enlargement of gingiva covering all most the entire crown involving both maxillary and mandibular arches. Differential diagnosis includes drug-induced and idiopathic gingival enlargement. Excess gingival tissue was removed by full mouth gingivectomy and sent for histopathological examination. Postoperative course was uneventful and patient's esthetics improved significantly. A 12 month postoperative period shows no recurrence.
Keywords: Hereditary gingival enlargement, gingivectomy, idiopathic enlargement, elephantiasis gingivae
Introduction
Hereditary gingival enlargement (HGF) is a rare condition with incidence of 1 in 750, 000 people.[1] It may occur isolated or as a part of multisystem syndrome. It may present itself as an autosomal dominant which has been linked to chromosome 2p21-p22 and 5q13-q22[2] or recessive mode of inheritance.[3] Although involvement of the SOS-1 gene has been suggested recently.[4] Families are affected across generations and a positive family history is always present in HGF. Hereditary gingival fibromatosis is a gradually progressive benign enlargement that affects the marginal, attached, and interdental gingiva. Histopathologically, it implies an increase in both extracellular matrix and cell numbers. Treatment consists of surgical excision of gingival tissue.
We are here presenting a rare case of a 13-year-old girl suffering from hereditary gingival fibromatosis along with surgical management to contribute the literature regarding this rare entity and moreover to emphasize the clinical significance of early management of gingival enlargement as if it is untreated timely could lead to pathological migration, abnormal jaw development, and various functional and esthetic problems.
Case Report
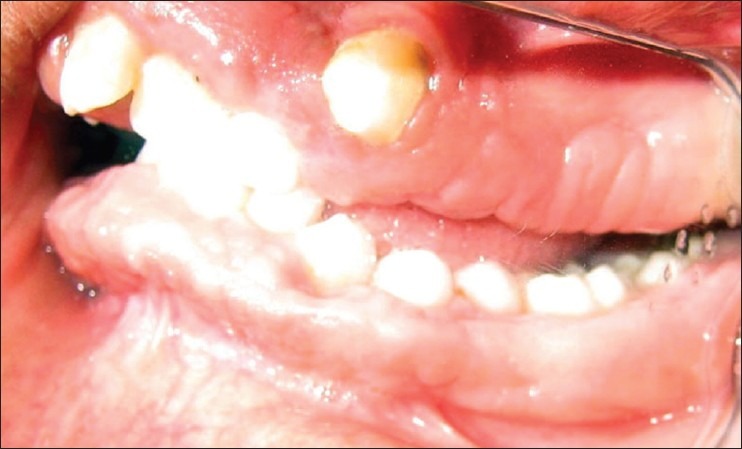
A 13-year-girl reported to Department of Periodontics, Dr. Z.A.D.C. and hospital, AMU, with a chief complaint of enlarged gums. She could not remember the duration of swelling but she said it was always present. Her medical history was non-contributory and she was not taking any medications regularly. Her family history revealed that her elder sister had also similar kind of gingival enlargement but that history can’t be confirmed. Gingival growth was painless but contributory to esthetic and masticatory difficulties. Intraoral examination revealed fibrotic gingival overgrowth both on buccal and lingual/palatal aspects with firm consistency, increased stippling, and normal pinkish color. Gingival enlargement covers most part of teeth [Figures 1–5]. Clinical examination also revealed retained deciduous canine and overlapping of maxillary central incisors and maxillary right canine placed highly in an arch. There was maxillary protrusion and anterior deep bite. Radiographic examination was done to rule out any bony enlargement and general medical examination was advised. Panoramic radiographs shows retained right primary canine, no bone loss, or any kind of bony enlargement [Figure 6].
Figure 1.
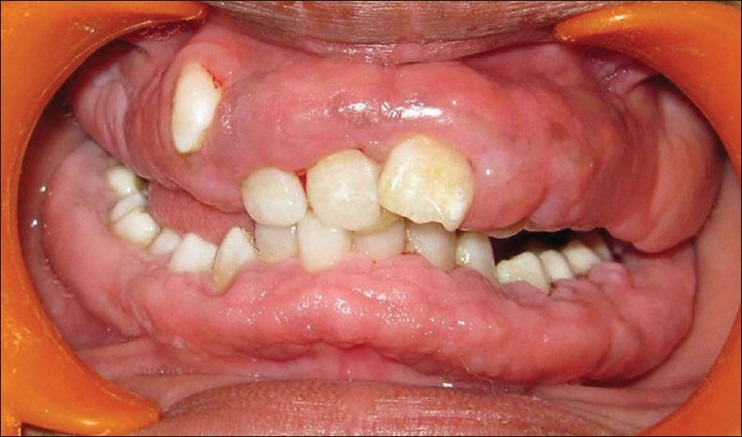
Preoperative facial view showing gingival enlargement and overlapping of central incisor
Figure 5.
Right lateral view showing the migrated right permanent canine
Figure 6.
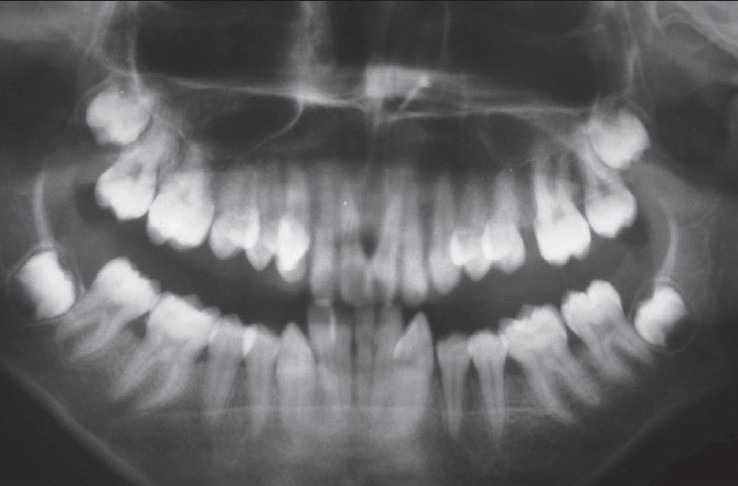
Orthopantogram showing no bone loss and the right retained deciduous canine
Figure 2.
Lingual view
Figure 3.
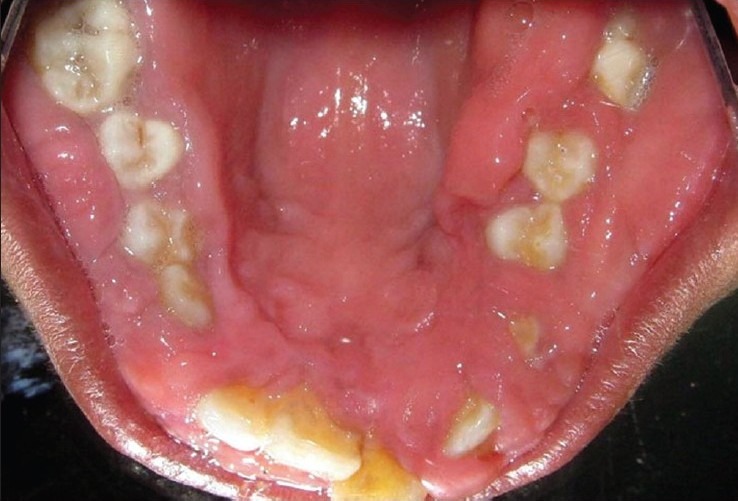
Palatal view showing right retained deciduous canine
Figure 4.
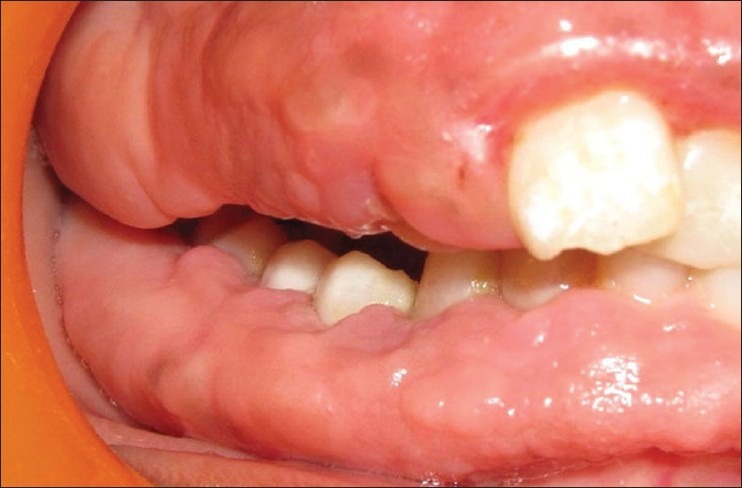
Left lateral view
Treatment
Oral hygiene instructions were given, but the plaque removal was restricted by enlarged gingiva. Therefore, internal bevel gingivectomies were performed for all quadrants in the maxillary and mandibular arches. The surgical intervention was carried out using internal bevel and crevicular incisions to remove hyperplastic tissue and retained primary canine was extracted. The patient was given a prescription for an antibiotic for 24 h before the surgery and 5 days postoperatively (Amoxicillin 500 mg, three times a day) to prevent postoperative bacteremia and an analgesic for three days postoperatively (Aceclofenac 500 mg, twice a day) to relieve postoperative pain and a periodontal dressing (Coe-Pak) were placed and removed after 1 week. The interval between surgical procedures was 2 weeks.
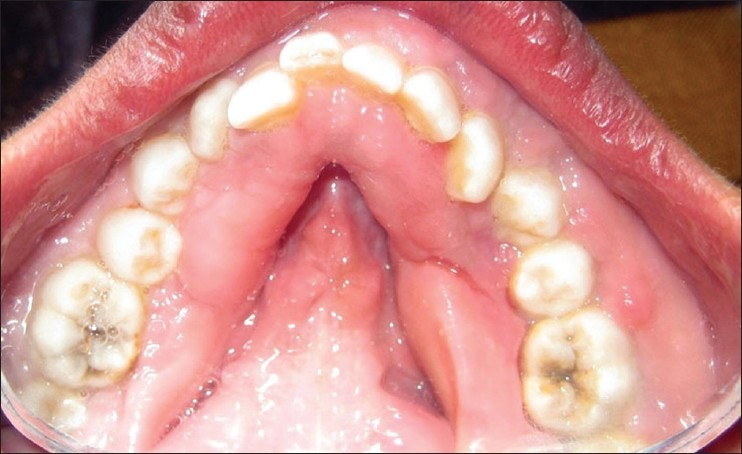
Excised tissue was sent for histopathological examination which revealed hyperkeratosis, elongated rete pegs, numerous bundles of collagen fibers, and mild inflammatory infiltrate [Figure 7]. In the light of above features and family history, diagnosis of HGF was made. Postoperative record of 12 months shows improvement in position of both central incisors and right permanent canine [Figures 8–12]. The patient was satisfied with postoperative result.
Figure 7.
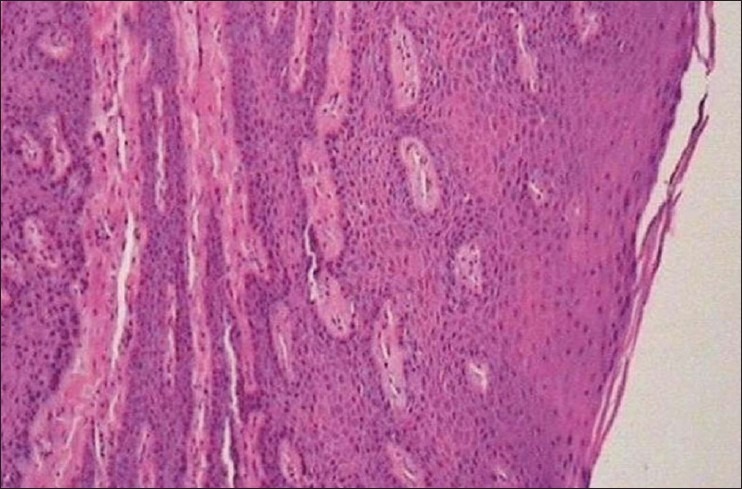
Histological picture showing collagen fibers and hyperdense connective tissue, deep rete pegs, acanthosis of epithelium
Figure 8.
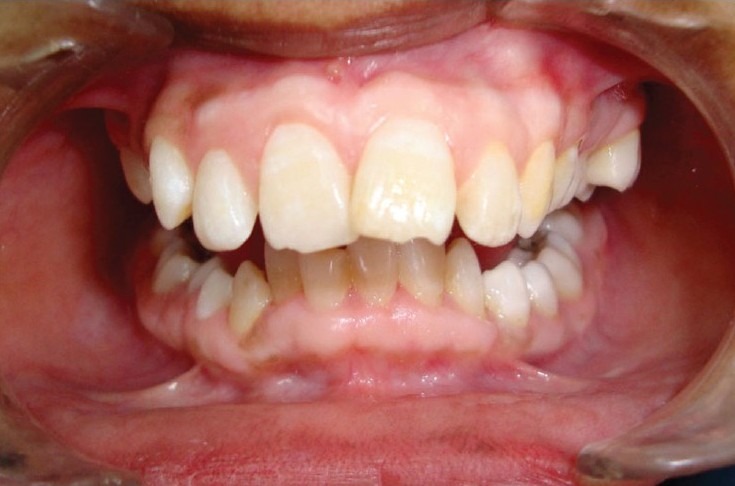
Postoperative facial view showing improvement in position of upper incisor and right maxillary canine
Figure 12.
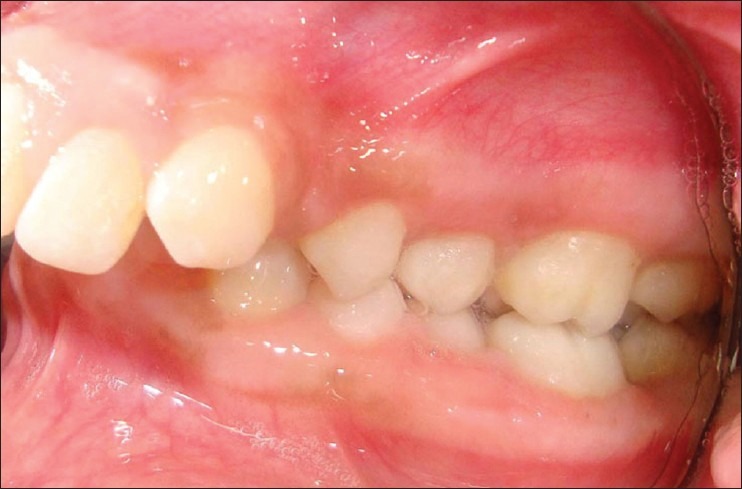
Postoperative right lateral view
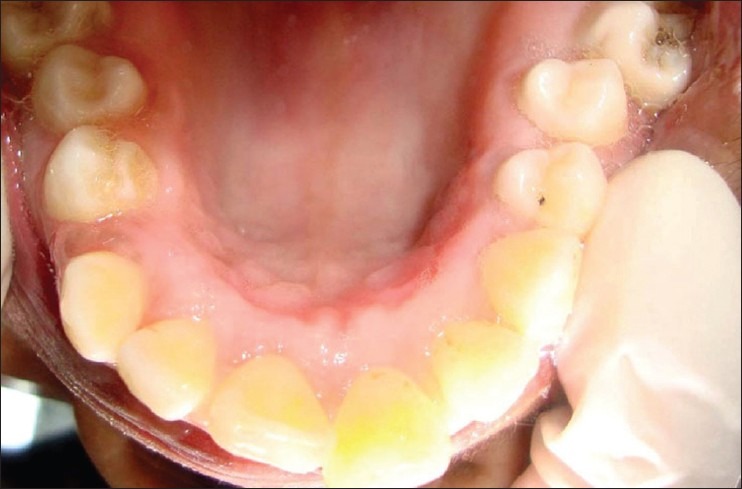
Figure 9.
Postoperative lingual view
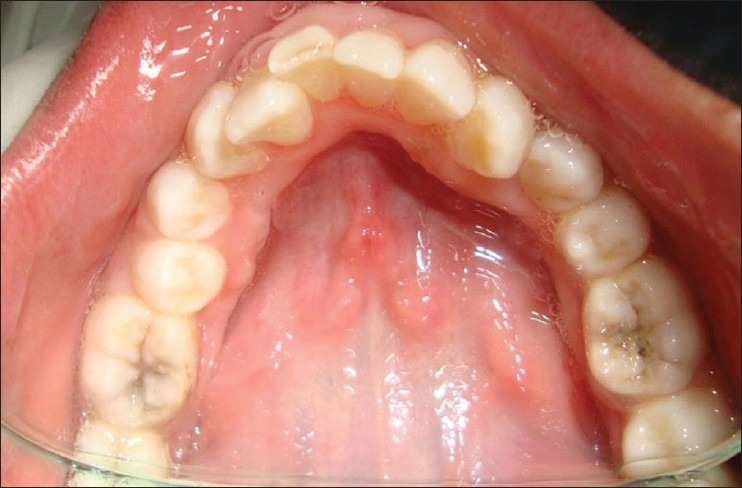
Figure 10.
Postoperative palatal view
Figure 11.
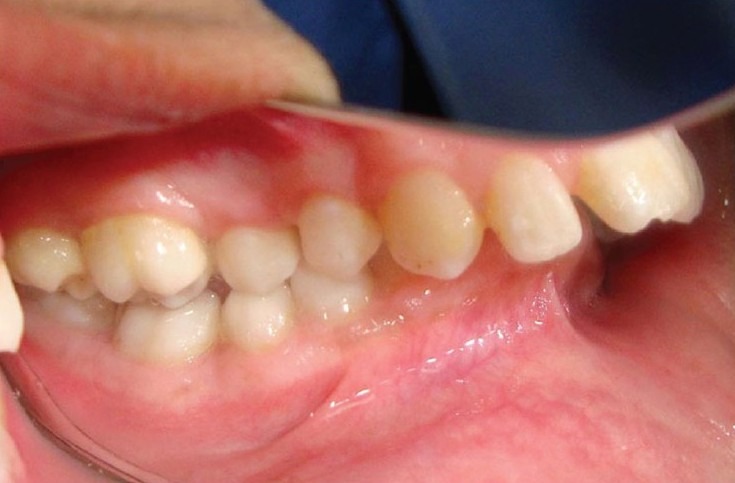
Postoperative left lateral view
Discussion
A case of hereditary gingival fibromatosis reported in this paper. It is synonyms with the conditions like elephantiasis gingivae, fibromatosis gingivae, gigantism of the gingiva, congenital macrogingivae, hereditary gingival hyperplasia, and hypertrophic gingiva.[5] Enlargement of gingiva can be due to use of medication like Phenytoin, cyclosporine, and calcium channel blockers.[6] but no drug history was present in the present case. Gingival fibromatosis can occur as an isolated nonsyndromic condition or be associated with other syndromes. The syndromes associated with GF include Jones hartsfield, Murray- Puretic-Drescher syndrome, Zimmermann-Laband, Rutherfurd, Cross, Ramon, Prune-belly syndrome associated with hearing deficiencies, hypertelorism, and supernumerary teeth.[7] She did not suffer from any skeletal deformity, epilepsy, or hypertrichosis. The laboratory investigations revealed no evidence of any systemic disorders such as leukemia, diabetes mellitus, or hormonal disorders. The histologic features observed in the present case had the typical appearance of gingival fibromatosis; hyperplasic dense fibrous connective tissue with acanthotic gingival epithelium.[8] As the family history contributes to this case with no systemic and drug history and with no clinical features fulfilling these possible syndromes, diagnosis of isolated generalized hereditary gingival fibromatosis was made.
The gingival enlargement usually begins at the time of eruption of the permanent dentition[5] or, less frequently, with the eruption of the primary dentition. This is consistent with this case. The most common effect due to enlargement was pathologic migration, diastema, and retained deciduous teeth which was present in reporting case. Due to severity of enlargement, gingival tissue covers almost entire crown causing esthetic and masticatory difficulties. After treating hyperplastic tissue, position of central incisor and upper right canine improved remarkably suggesting the need to treat excess tissue timely to prevent malocclusion.
Treatment depends upon severity of enlargement. Severe enlargement needs full mouth gingivectomy. The most preferred method for excision is external bevel gingivectomy especially when there is no bone loss and only false pockets. 20% recurrence has been reported. However, in several reported cases there was no recurrence in a period of 2 years,[5] 3 years, or even a 14-year follow-up.[9] In the present case, there was no recurrence of the gingival enlargement 12 months later. Patient's esthetics improved remarkably and she was satisfied with the postoperative result.
Conclusion
The clinical case report of a rare lesion of hereditary gingival fibromatosis presented here was managed successfully with surgical interventions with no recurrence. Gingival enlargement at this young age should be managed early to avoid pathological migration, malocclusion, esthetic, and functional complications.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
References
- 1.Fletcher J. Gingival abnormalities of genetic origin: a preliminary communication with special reference to hereditary gingival fibromatosis. J Dent Res. 1966;45:597–612. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Xiao S, Bu L, Zhu L, Zheng G, Yang M, Qian M, et al. A new locus for hereditary gingival fibromatosis (GINGF2) maps to 5q13-q22. Genomics. 2001;74:180–5. doi: 10.1006/geno.2001.6542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Singer SL, Goldblatt J, Hallam LA, Winters JC. Hereditary gingival fibromatosis with a recessive mode of inheritance. Case reports. Aust Dent J. 1993;38:427–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.1993.tb04755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hart TC, Zhang Y, Gorry MC, Hart PS, Cooper M, Marazita ML, et al. A mutation in the SOS1 gene causes hereditary gingival fibromatosis type. Am J Hum Genet. 2002;70:943–54. doi: 10.1086/339689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ramer M, Marrone J, Stahl B, Burakoff R. Hereditary gingival fibromatosis: Identification, treatment, control. J Am Dent Assoc. 1996;127:493–5. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1996.0242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rees TD, Levine RA. Systematic drugs as a risk factor for periodontal disease initiation and progression. Compendium. 1995;16:20. 22, 26 passim; quiz 42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Coletta RD, Graner E. Hereditary gingival fibromatosis: A Systematic review. J Periodontol. 2006;77:753–64. doi: 10.1902/jop.2006.050379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tipton DA, Howell KJ, Dabbous MK. Increased proliferation, collagen and fibronectin production by hereditary gingival fibromatosis fibroblasts. J Periodontol. 1997;68:524–30. doi: 10.1902/jop.1997.68.6.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Günhan O, Gardner DG, Bostanci H, Günhan M. Familial gingival fibromatosis with unusual histologic findings. J Periodontol. 1995;66:1008–11. doi: 10.1902/jop.1995.66.11.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


