Abstract
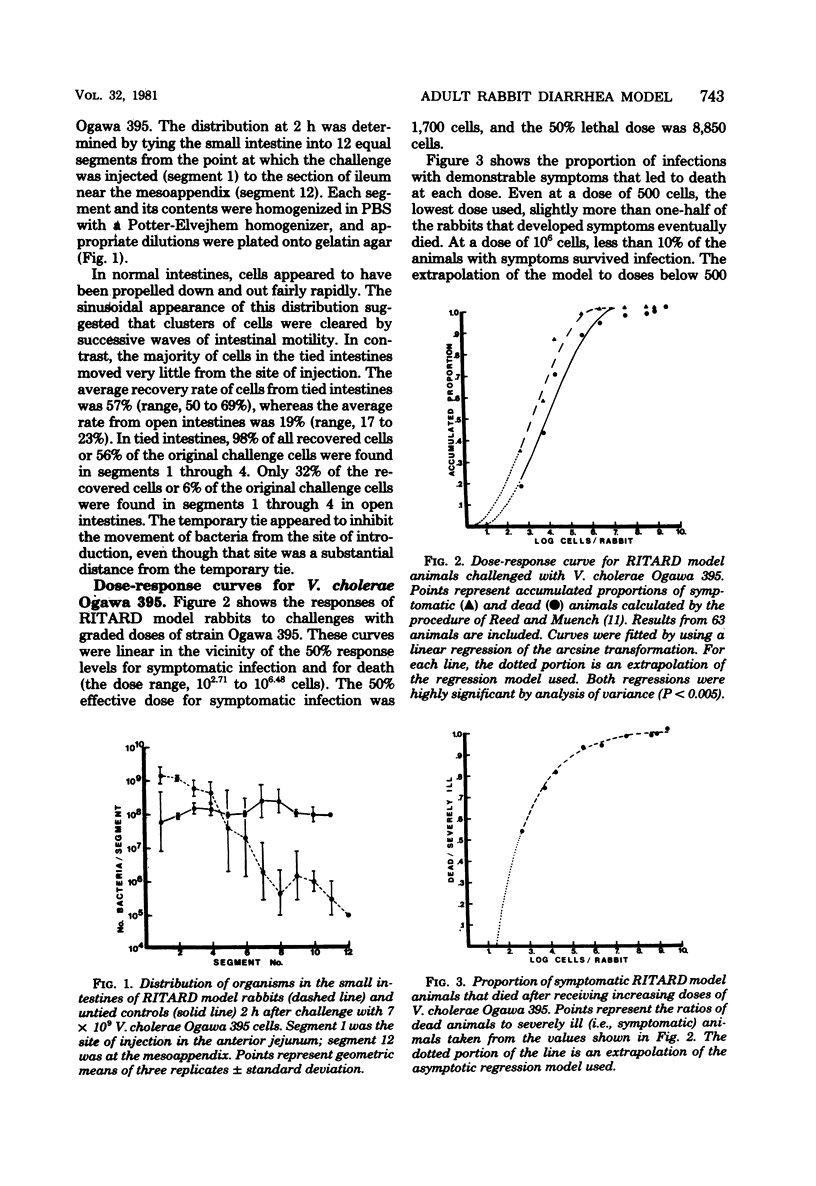
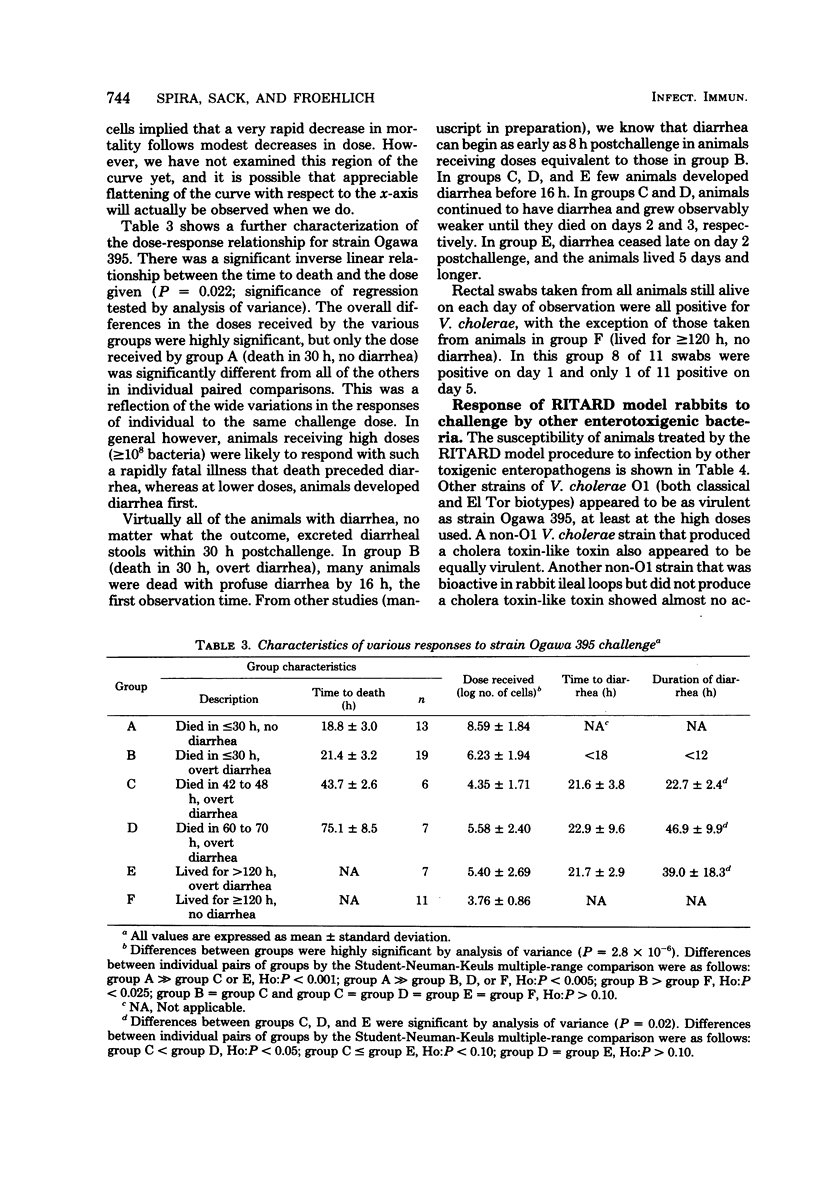
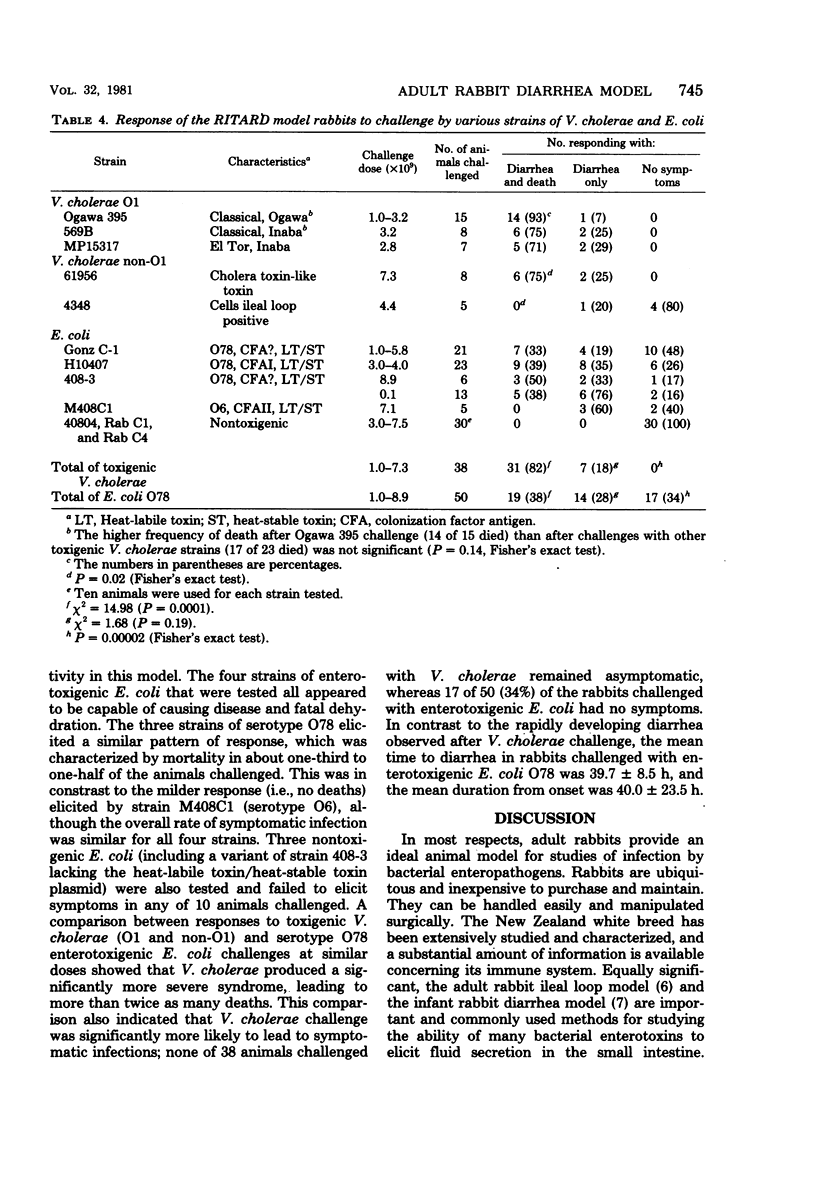
We developed an adult rabbit model for enteric infection by Vibrio cholerae and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. The cecum of each animal was first ligated to prevent it from retaining fluid secreted by the small intestine. A temporary reversible obstruction (a slip knot tie) of the small bowel was introduced at the time of challenge and removed 2 h later. With this modification, we were able to elicit a massive and usually fatal cholera-like diarrhea in adult (3.5- to 6-lb [1.6- to 2.7-kb]) animals challenged with V. cholerae. Animals challenged with enterotoxigenic E. coli also developed diarrhea which was severe and watery but less explosive and less rapidly fatal than that produced by V. cholerae. The susceptibility of animals in this model to infection by V. cholerae was similar to the susceptibility of infant rabbits challenged intraintestinally. The death rate was almost 25% when 10(3) Vibrio cells were given and 90% or more when the dose was greater than or equal to 10(6) cells per animal. We designated this procedure the RITARD (for removable intestinal tie-adult rabbit diarrhea) model.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baselski V. S., Medina R. A., Parker C. D. Survival and multiplication of Vibrio cholerae in the upper bowel of infant mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):435–440. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.435-440.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baselski V., Briggs R., Parker C. Intestinal fluid accumulation induced by oral challenge with Vibrio cholerae or cholera toxin in infant mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):704–712. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.704-712.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blachman U., Goss S. J., Pickett M. J. Experimental cholera in the chinchilla. J Infect Dis. 1974 Apr;129(4):376–384. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.4.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blachman U., Graboff S. R., Haag G. E., Gottfeld E., Pickett M. J. Experimental Cholera in Chinchillas: the Immune Response in Serum and Intestinal Secretions to Vibrio cholerae and Cholera Toxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1098–1104. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1098-1104.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., CHATTERJE D. N. An experimental study of the mechanism of action of Vibriod cholerae on the intestinal mucous membrane. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(2):559–562. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTTA N. K., HABBU M. K. Experimental cholera in infant rabbits: a method for chemotherapeutic investigation. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1955 Jun;10(2):153–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1955.tb00074.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knop J., Rowley D. Antibacterial mechanisms in the intestine. Elimination of V. cholerae from the intestines of infant mice and the role of antibody. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1975 Apr;53(2):147–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusama H., Craig J. P. Production of Biologically Active Substances by Two Strains of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1970 Jan;1(1):80–87. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.1.80-87.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Carpenter C. C. Experimental canine cholera. I. Development of the model. J Infect Dis. 1969 Feb;119(2):138–149. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.2.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Carpenter C. C. Experimental canine cholera. II. Production by cell-free culture filtrates of Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1969 Feb;119(2):150–157. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrank G. D., Verwey W. F. Distribution of cholera organisms in experimental Vibrio cholerae infections: proposed mechanisms of pathogenesis and antibacterial immunity. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):195–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.195-203.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. H., Yalow R., Berson S. A. Detection of Australia antigen and antibody by means of radioimmunoassay techniques. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):550–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



