Abstract
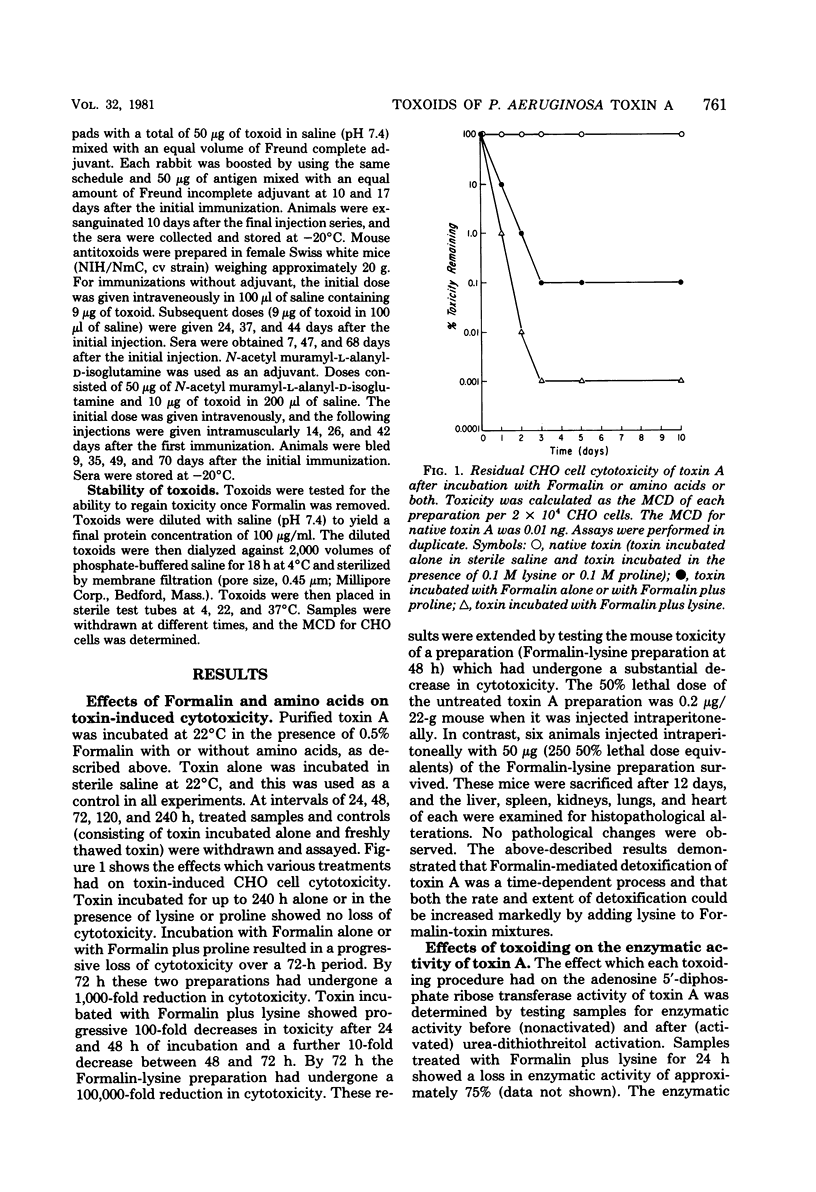
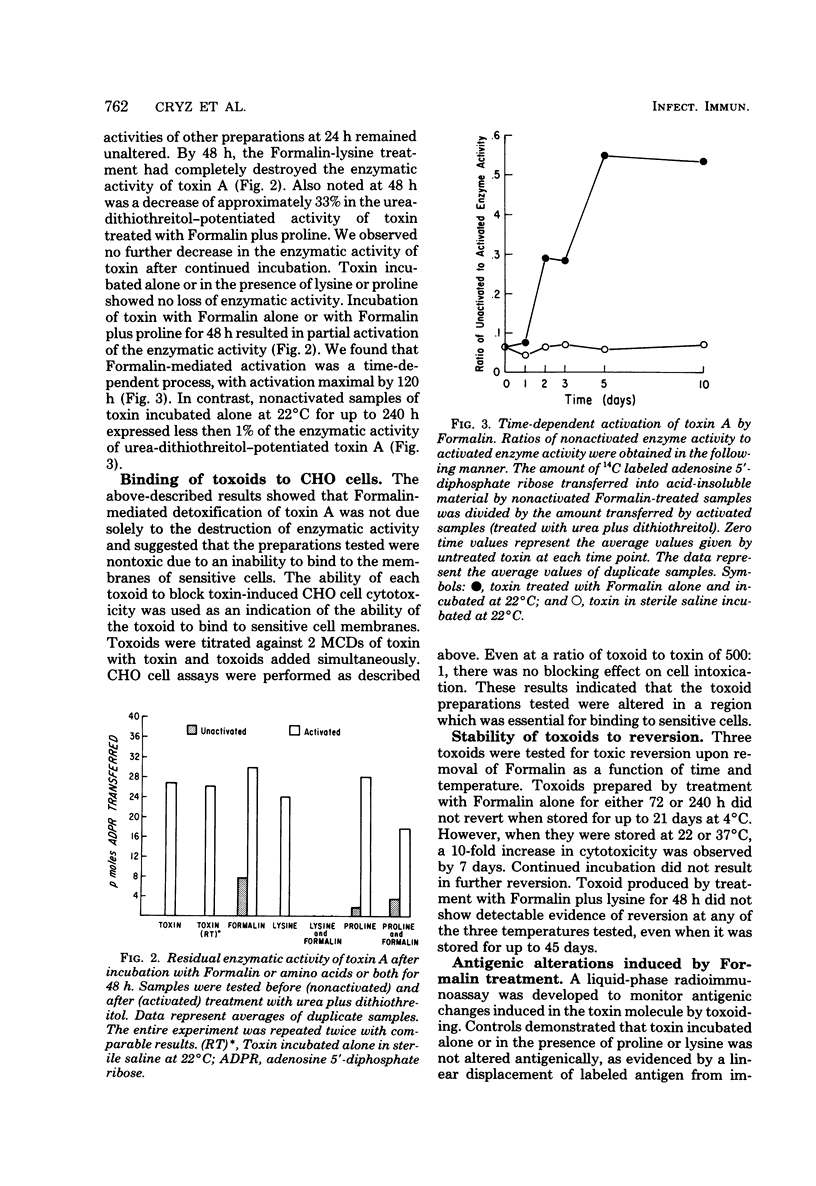
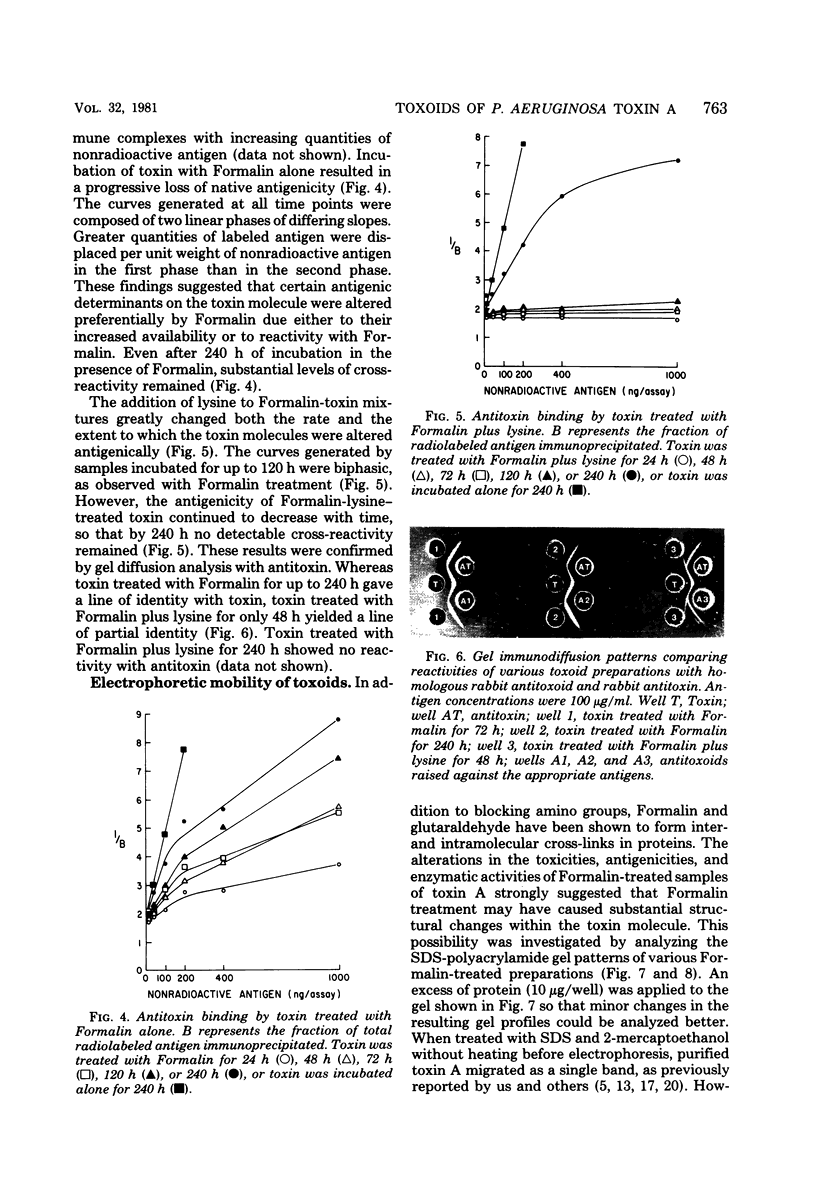
We investigated the effect of Formalin toxoiding on the biological, chemical, and immunological activities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A. Formalin treatment alone resulted in a 1,000-fold decrease in toxin-induced cell cytotoxicity and altered the antigenicity of the toxin A molecule without adversely affecting enzymatic activity. Competitive blocking experiments indicated that Formalin-mediated detoxification proceeded via alterations in a region of the toxin molecule other than the active site of the enzyme. The addition of lysine to Formalin-toxin mixtures not only increased the rate and extent of detoxification and antigenic alteration, but also completely destroyed enzymatic activity. The immunogenicities of different toxoids varied substantially. Upon dialysis and storage, Formalin-derived toxoids underwent partial toxic reversion, whereas a Formalin-lysine-derived toxoid did not. The sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel patterns of Formalin- and Formalin-lysine-treated toxins indicated that these treatments caused the formation of a heterogenous group of high-molecular-weight species and produced substantial changes in the electrophoretic mobility of toxin A.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe C., Takeshi K., Homma J. T. Studies on the detoxification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin. Jpn J Exp Med. 1978 Apr;48(2):183–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazaral M., Goscienski P. J., Hamburger R. N. Characteristics of human antibody to diphtheria toxin. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):130–136. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.130-136.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorn M. J., Vasil M. L., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H. Incidence of exotoxin production by Pseudomonas species. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):362–366. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.362-366.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J., Kandel J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. I. Thiol-dependent dissociation of a fraction of toxin into enzymically active and inactive fragments. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1496–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Welkos S. L., Holmes R. K. Immunochemical studies of diphtherial toxin and related nontoxic mutant proteins. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):835–846. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.835-846.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekins R. P. Radioimmunoassay and saturation analysis. Basic principles and theory. Br Med Bull. 1974 Jan;30(1):3–11. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd Pseudomonas in the hospital. Hosp Pract. 1976 Feb;11(2):63–70. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1976.11706501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigin R. D., Shearer W. T. Opportunistic infection in children. II. In the compromised host. J Pediatr. 1975 Nov;87(5):677–694. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80289-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Liu P. V., Kabat D. Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin Aiadenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of mammalian elongation factor 2 in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.138-144.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Sadoff J. C. Toxin inhibitors of protein synthesis: production, purification, and assay of Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:780–793. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger J. D., Straus D. C., Hilton C. B., Bass J. A. Antibodies to proteases and exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis: Demonstration by radioimmunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):49–48. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Large-scale purification and characterization of the exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1077–1086. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1077-1086.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H., Martin O. C., Muehl L. A. The exotoxin P. aeruginosa: a proenzyme having an unusual mode of activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 30;81(2):532–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91567-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Collier R. J. Expression of enzymic activity by exotoxin A from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):494–501. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.494-501.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Response of cultured mammalian cells to the exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Corynebacterium diphtheriae: differential cytotoxicity. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Feb;23(2):183–189. doi: 10.1139/m77-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyachi Y., Vaitukaitis J. L., Nieschlag E., Lipsett M. B. Enzymatic radioiodination of gonadotropins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jan;34(1):23–28. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan P., Holder I. A., MacMillan B. G. Burn wounds: microbiology, local host defenses, and current therapy. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1973 Jul;4(1):61–100. doi: 10.3109/10408367309151684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Gill D. M. Diphtheria. Science. 1973 Oct 26;182(4110):353–358. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4110.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Gordon F. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin: effect on cell cultures. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):631–636. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Iglewski B. H. Passive protection by antitoxin in experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn infections. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):596–602. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.596-602.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Shackelford A. H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in mice: localization and effect on protein synthesis. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):540–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.540-546.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Taylor N. S. Neutralizing antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in human sera: evidence for in vivo toxin production during infection. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):942–947. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.942-947.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: persisting problems and current research to find new therapies. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jun;82(6):819–831. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-6-819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skelley D. S., Brown L. P., Besch P. K. Radioimmunoassay. Clin Chem. 1973 Feb;19(2):146–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Kabat D., Iglewski B. H. Structure-activity relationships of an exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):353–361. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.353-361.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]