Abstract
In the title compound, C14H10N2O2S, the benzothiazole and quinazoline ring systems are essentially planar with maximum deviations of 0.0127 (16) and 0.1588 (15) Å, respectively, and make a dihedral angleof 3.02 (5)°, which shows that the entire molecule is almost planar. The O atoms deviate from the benzothiazole ring system by 1.2231 (14) and −1.1989 (15) Å. The crystal packing features non–classical C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and is further consolidated by π–π interactions [centroid–centroid distances = 3.7568 (8) and 3.8848 (9) Å].
Related literature
For the uses and biological importance of benzothiazole and quinazoline derivatives, see: Schwartz et al. (1992 ▶); Wolfe et al. (1990 ▶); Tereshima et al. (1995 ▶). For related structures, see: Khan et al. (2012 ▶); Grundt et al. (2010 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H10N2O2S
M r = 270.31
Orthorhombic,
a = 7.9389 (2) Å
b = 13.1460 (4) Å
c = 22.7952 (7) Å
V = 2379.02 (12) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.27 mm−1
T = 295 K
0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▶) T min = 0.922, T max = 0.947
21710 measured reflections
2328 independent reflections
1981 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.028
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.034
wR(F 2) = 0.122
S = 1.06
2328 reflections
172 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2008 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812040871/rk2382sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812040871/rk2382Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812040871/rk2382Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.43 | 3.275 (2) | 150 |
Symmetry code: (i) 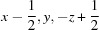 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Babu Varghese, Senior Scientific Officer, SAIF, IIT, Chennai, India, for the data collection. They also thank the University Grant Commission (UGC) for funding the minor project [Ref. No. F. MRP–3640/11 (SERO–UGC)] under which this work has been carried out.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Saccharin belongs to a class of cyclic sulfonamides and this is used as an artificial sweetener for a longtime. The benzothiazole and quinazoline derivatives form an important classes of fused heterocyclic compounds with a wide range of biological activities such as antimicrobial (Schwartz et al., 1992), anticancer (Wolfe et al., 1990), antiinflammatory (Tereshima et al., 1995). As a part of our studies in this area, the molecular and crystal structures of the title compound have been determined and the results are presented here.
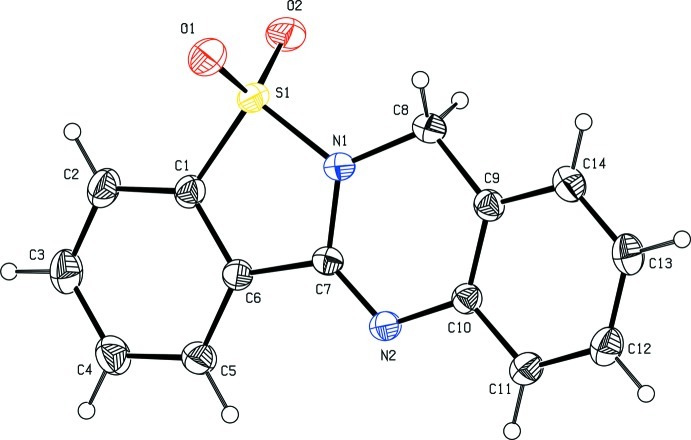
The title compound comprises a benzothiazole ring fused with quinazoline ring. X–ray analysis confirms the molecular structure and atom connectivity as illustrated in Fig. 1. The benzothiazole ring system is essentially planar with a maximum deviation of -0.0127 (16)Å for the C7 atom. The quinazoline ring system is also essentially planar with the maximum deviation of -0.1588 (15)Å for the N1 atom. The dihedral angle between the benzothiazole and quinazoline ring systems are almost coplanar with a dihedral angle of 3.02 (5)° between them.
In the benzothiazole ring system, the oxygen atoms (O1 and O2) attached to the sulfur atom are significantly deviate from the least square plane of the ring system by 1.2231 (14)Å and -1.1989 (15)Å, respectively. The thiazole ring (C1/C6/C7/N1/S1) forms a dihedral angle of 0.34 (8)° and 3.15 (6)° with the phenyl ring (C1–C6) and the quinazoline ring system, respectively. The phenyl ring (C9–C14) forms the dihedral angles of 5.01 (8)° and 5.41 (7)° with the pyrimidine ring (N1/N2/C7–C10) and the phenyl ring (C1–C6), respectively. The title compound exibits the structural similarities with already reported structures (Khan et al., 2012; Grundt et al., 2010).
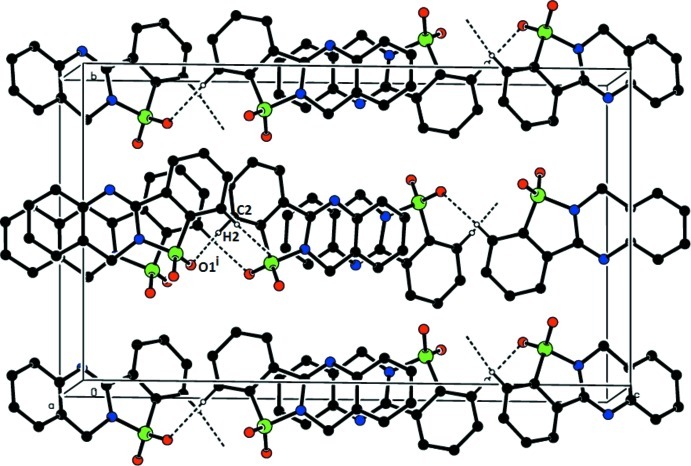
The crystal packing is stabilized by C2—H2···O1i intermolecular non–classical hydrogen bond (Table 1). The crystal packing is further stabilized by π···π interactions, with Cg1···Cg4ii and Cg3···Cg4ii distances being 3.7568 (8)Å and 3.8846 (9)Å, respectively, where Cg1 is the centre of gravity of (C1/C6/C7/N1/S1) ring; Cg3 is the centre of gravity of (C1–C6) ring; Cg4 is the centre of gravity of (C9–C14) ring. The symmetry codes: (i) -1/2+x, y, 1/2-z; (ii) -x, 1-y, 1-z. The packing view of the title compound is shown in Fig. 2.
Experimental
A solution of Saccharin (0.91 g, 5 mmol) and o–amino benzyl alcohol (0.61 g, 5 mmol) in DMF (10 ml) was irradiated with microwaves in a 800 W domestic microwave oven for 2 minutes. The reaction solution was cooled and poured over crushed ice (200 g). The precipitated product was filtered and desiccated over anhydrous CaCl2. The resulting filetered product was subjected to crystallization by slow evaporation of the solvent resulting in single crystals suitable for XRD studies.
Refinement
The positions of the hydrogen atoms were localized from the difference electron density maps and the distances were geometrically constrained. The H atoms bound to the C atoms, with d(C—H) = 0.93Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for aromatic, d(C—H) = 0.97Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for methylene.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme. The displacement ellipsoids are drawn at 30% probability level. H atoms are presented as a small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound, viewed down b–axis, showing C2—H2···O1i hydrogen bonds. The symmetry code: (i) -1/2+x, y, 1/2-z.
Crystal data
| C14H10N2O2S | F(000) = 1120 |
| Mr = 270.31 | Dx = 1.509 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 2328 reflections |
| a = 7.9389 (2) Å | θ = 3.1–26.0° |
| b = 13.1460 (4) Å | µ = 0.27 mm−1 |
| c = 22.7952 (7) Å | T = 295 K |
| V = 2379.02 (12) Å3 | Block, yellow |
| Z = 8 | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2328 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine–focus sealed tube | 1981 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.028 |
| ω– & φ–scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −9→6 |
| Tmin = 0.922, Tmax = 0.947 | k = −16→14 |
| 21710 measured reflections | l = −28→28 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.034 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.122 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0837P)2 + 0.4043P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2328 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 172 parameters | Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R–factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R–factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R–factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R–factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R–factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.0174 (2) | 0.49618 (13) | 0.32511 (7) | 0.0390 (4) | |
| C2 | −0.0613 (2) | 0.51583 (15) | 0.27215 (8) | 0.0506 (5) | |
| H2 | −0.0732 | 0.4655 | 0.2438 | 0.061* | |
| C3 | −0.1217 (3) | 0.61328 (16) | 0.26314 (9) | 0.0556 (5) | |
| H3 | −0.1767 | 0.6288 | 0.2283 | 0.067* | |
| C4 | −0.1014 (2) | 0.68776 (16) | 0.30527 (9) | 0.0532 (5) | |
| H4 | −0.1421 | 0.7529 | 0.2981 | 0.064* | |
| C5 | −0.0215 (2) | 0.66715 (14) | 0.35795 (8) | 0.0447 (4) | |
| H5 | −0.0084 | 0.7177 | 0.3861 | 0.054* | |
| C6 | 0.0382 (2) | 0.56991 (12) | 0.36773 (7) | 0.0354 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.12413 (19) | 0.53087 (11) | 0.42037 (7) | 0.0335 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.2162 (3) | 0.36384 (13) | 0.46019 (8) | 0.0457 (4) | |
| H8A | 0.3027 | 0.3170 | 0.4471 | 0.055* | |
| H8B | 0.1206 | 0.3244 | 0.4738 | 0.055* | |
| C9 | 0.2830 (2) | 0.42841 (13) | 0.50934 (7) | 0.0365 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.24723 (19) | 0.53228 (12) | 0.51127 (6) | 0.0342 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.3012 (2) | 0.58936 (14) | 0.55898 (7) | 0.0433 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.2774 | 0.6586 | 0.5605 | 0.052* | |
| C12 | 0.3900 (2) | 0.54436 (16) | 0.60411 (8) | 0.0497 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.4248 | 0.5832 | 0.6360 | 0.060* | |
| C13 | 0.4270 (2) | 0.44222 (16) | 0.60202 (8) | 0.0498 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.4872 | 0.4119 | 0.6323 | 0.060* | |
| C14 | 0.3743 (2) | 0.38476 (13) | 0.55469 (8) | 0.0449 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.4004 | 0.3158 | 0.5532 | 0.054* | |
| N1 | 0.1652 (2) | 0.42909 (10) | 0.41195 (6) | 0.0414 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.15773 (18) | 0.58305 (10) | 0.46603 (6) | 0.0371 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.24864 (17) | 0.35324 (11) | 0.31425 (6) | 0.0575 (4) | |
| O2 | −0.01803 (19) | 0.30315 (10) | 0.35705 (6) | 0.0581 (4) | |
| S1 | 0.10439 (6) | 0.38070 (3) | 0.348166 (18) | 0.04023 (19) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0408 (9) | 0.0411 (9) | 0.0352 (9) | −0.0072 (7) | 0.0019 (7) | −0.0004 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0551 (11) | 0.0603 (11) | 0.0363 (9) | −0.0090 (10) | −0.0058 (8) | −0.0043 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0545 (12) | 0.0697 (13) | 0.0425 (10) | −0.0024 (10) | −0.0114 (8) | 0.0090 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0570 (12) | 0.0512 (11) | 0.0514 (11) | 0.0031 (9) | −0.0086 (8) | 0.0096 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0487 (10) | 0.0390 (9) | 0.0464 (9) | 0.0016 (8) | −0.0060 (8) | 0.0006 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0359 (8) | 0.0360 (8) | 0.0343 (8) | −0.0053 (7) | 0.0003 (6) | 0.0003 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0338 (8) | 0.0296 (7) | 0.0373 (8) | −0.0023 (6) | 0.0014 (6) | −0.0002 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0606 (11) | 0.0329 (8) | 0.0436 (9) | 0.0040 (8) | −0.0039 (8) | 0.0006 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0351 (8) | 0.0373 (8) | 0.0370 (8) | 0.0003 (7) | 0.0051 (6) | 0.0029 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0322 (8) | 0.0360 (8) | 0.0345 (8) | −0.0005 (7) | 0.0016 (6) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0472 (10) | 0.0428 (9) | 0.0401 (9) | −0.0004 (8) | −0.0019 (7) | −0.0042 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0515 (11) | 0.0588 (12) | 0.0387 (9) | −0.0042 (9) | −0.0051 (8) | −0.0030 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0481 (10) | 0.0595 (12) | 0.0418 (9) | 0.0005 (9) | −0.0062 (8) | 0.0107 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0456 (10) | 0.0424 (10) | 0.0468 (10) | 0.0029 (8) | 0.0014 (8) | 0.0085 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0576 (9) | 0.0303 (7) | 0.0362 (7) | 0.0016 (7) | −0.0044 (6) | −0.0028 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0417 (7) | 0.0335 (7) | 0.0363 (7) | 0.0022 (6) | −0.0034 (6) | −0.0021 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0659 (9) | 0.0564 (8) | 0.0501 (8) | 0.0070 (7) | 0.0156 (6) | −0.0062 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0750 (10) | 0.0423 (7) | 0.0570 (8) | −0.0208 (7) | 0.0046 (7) | −0.0050 (6) |
| S1 | 0.0516 (3) | 0.0345 (3) | 0.0346 (3) | −0.00603 (18) | 0.00492 (17) | −0.00507 (14) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C6 | 1.382 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.384 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| C1—S1 | 1.7485 (18) | C9—C14 | 1.387 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.383 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.395 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C10—C11 | 1.389 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.381 (3) | C10—N2 | 1.419 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C11—C12 | 1.380 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.384 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C12—C13 | 1.375 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.382 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C13—C14 | 1.382 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.473 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C7—N2 | 1.275 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C7—N1 | 1.390 (2) | N1—S1 | 1.6589 (14) |
| C8—N1 | 1.452 (2) | O1—S1 | 1.4281 (13) |
| C8—C9 | 1.502 (2) | O2—S1 | 1.4230 (13) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 122.42 (17) | C14—C9—C8 | 120.43 (16) |
| C6—C1—S1 | 110.51 (12) | C10—C9—C8 | 120.31 (14) |
| C2—C1—S1 | 127.06 (14) | C11—C10—C9 | 119.36 (15) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 117.32 (18) | C11—C10—N2 | 118.00 (14) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 121.3 | C9—C10—N2 | 122.63 (14) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 121.3 | C12—C11—C10 | 120.64 (17) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.86 (18) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.7 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.6 | C10—C11—H11 | 119.7 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.6 | C13—C12—C11 | 120.12 (17) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.19 (18) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.4 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.4 | C12—C13—C14 | 119.74 (16) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 118.57 (17) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.7 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.7 | C13—C14—C9 | 120.93 (16) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.62 (15) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 112.56 (14) | C9—C14—H14 | 119.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 127.81 (15) | C7—N1—C8 | 121.96 (13) |
| N2—C7—N1 | 125.55 (14) | C7—N1—S1 | 114.95 (11) |
| N2—C7—C6 | 125.08 (14) | C8—N1—S1 | 121.22 (11) |
| N1—C7—C6 | 109.36 (13) | C7—N2—C10 | 116.43 (13) |
| N1—C8—C9 | 109.23 (14) | O2—S1—O1 | 116.34 (9) |
| N1—C8—H8A | 109.8 | O2—S1—N1 | 110.41 (8) |
| C9—C8—H8A | 109.8 | O1—S1—N1 | 109.76 (8) |
| N1—C8—H8B | 109.8 | O2—S1—C1 | 113.27 (9) |
| C9—C8—H8B | 109.8 | O1—S1—C1 | 111.92 (8) |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 108.3 | N1—S1—C1 | 92.60 (7) |
| C14—C9—C10 | 119.20 (15) | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.7 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | −0.6 (3) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | 179.80 (15) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 1.3 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.9 (3) | C8—C9—C14—C13 | −175.78 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.6 (3) | N2—C7—N1—C8 | 15.1 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.1 (3) | C6—C7—N1—C8 | −165.98 (16) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.2 (3) | N2—C7—N1—S1 | 179.66 (14) |
| S1—C1—C6—C5 | 179.80 (13) | C6—C7—N1—S1 | −1.41 (17) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 179.50 (15) | C9—C8—N1—C7 | −22.8 (2) |
| S1—C1—C6—C7 | −0.94 (18) | C9—C8—N1—S1 | 173.54 (12) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.1 (3) | N1—C7—N2—C10 | 1.1 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −179.04 (16) | C6—C7—N2—C10 | −177.62 (13) |
| C1—C6—C7—N2 | −179.58 (16) | C11—C10—N2—C7 | 173.48 (15) |
| C5—C6—C7—N2 | −0.4 (3) | C9—C10—N2—C7 | −6.2 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—N1 | 1.48 (19) | C7—N1—S1—O2 | −115.25 (13) |
| C5—C6—C7—N1 | −179.33 (16) | C8—N1—S1—O2 | 49.45 (17) |
| N1—C8—C9—C14 | −165.40 (15) | C7—N1—S1—O1 | 115.20 (13) |
| N1—C8—C9—C10 | 17.6 (2) | C8—N1—S1—O1 | −80.10 (16) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | −1.1 (2) | C7—N1—S1—C1 | 0.78 (14) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 175.98 (16) | C8—N1—S1—C1 | 165.48 (15) |
| C14—C9—C10—N2 | 178.63 (15) | C6—C1—S1—O2 | 113.68 (13) |
| C8—C9—C10—N2 | −4.3 (2) | C2—C1—S1—O2 | −66.78 (18) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.2 (3) | C6—C1—S1—O1 | −112.40 (13) |
| N2—C10—C11—C12 | −179.50 (15) | C2—C1—S1—O1 | 67.14 (18) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.5 (3) | C6—C1—S1—N1 | 0.13 (14) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.3 (3) | C2—C1—S1—N1 | 179.66 (17) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2···O1i | 0.93 | 2.43 | 3.275 (2) | 150 |
Symmetry code: (i) x−1/2, y, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: RK2382).
References
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Grundt, P., Douglas, K. A., Krivogorsky, B. & Nemykin, V. N. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1474–o1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Khan, M. H., Khan, I. U., Mughal, S. Y. & Akkurt, M. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A., Madan, P. B., Mohacsi, E., O-Brien, J. P., Todaro, L. J. & Coffen, D. L. (1992). J. Org. Chem. 57, 851–856.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tereshima, K., Shimamura, H., Kawase, A., Tanaka, Y., Tanimura, T., Ishizuka, Y. & Sato, M. (1995). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 45, 2021–2023. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, J. F., Rathman, T. L., Sleevi, M. C., Cambell, J. S. A. & Greenwood, T. D. (1990). J. Med. Chem. 33, 161–166. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812040871/rk2382sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812040871/rk2382Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812040871/rk2382Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report