Abstract
In the title molecular salt, C5H9N2 +·C7H3N2O7 −, the roughly planar anion (r.m.s. deviation = 0.120 Å) has been deprotonated at the phenol group. An intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond in the anion generates an S(6) ring. In the crystal, the components are linked by cation-to-anion N—H⋯O and N—H⋯(O,O) hydrogen bonds, generating [010] double chains. Weak C—H⋯O interactions consolidate the packing.
Related literature
For a related structure and background to hydrogen-bonding interactions, see: Jin et al. (2010 ▶). For another related structure, see: Smith et al. (2011 ▶).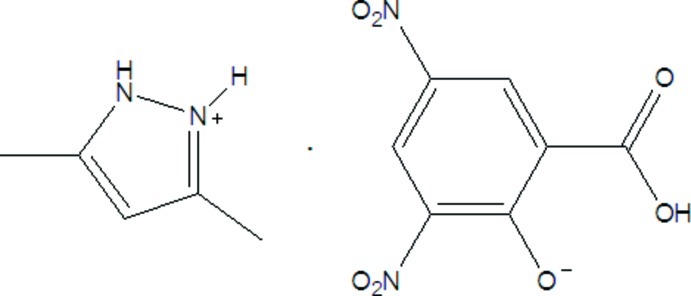
Experimental
Crystal data
C5H9N2 +·C7H3N2O7 −
M r = 324.26
Monoclinic,
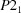
a = 8.1183 (7) Å
b = 6.0636 (5) Å
c = 14.1453 (11) Å
β = 91.904 (1)°
V = 695.93 (10) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.13 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.40 × 0.27 × 0.11 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002 ▶) T min = 0.959, T max = 0.986
3523 measured reflections
2301 independent reflections
1659 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.040
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.047
wR(F 2) = 0.105
S = 1.02
2301 reflections
208 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2002 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2002 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812041906/hb6958sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812041906/hb6958Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812041906/hb6958Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O7i | 0.86 | 2.09 | 2.859 (4) | 148 |
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.86 | 2.16 | 2.809 (4) | 132 |
| N2—H2⋯O3 | 0.86 | 1.88 | 2.684 (3) | 156 |
| O2—H2A⋯O1 | 0.82 | 1.72 | 2.481 (3) | 154 |
| C1—H1A⋯O7i | 0.96 | 2.32 | 3.166 (5) | 147 |
| C5—H5B⋯O4ii | 0.96 | 2.49 | 3.414 (5) | 160 |
| C10—H10⋯O6iii | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.379 (4) | 164 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 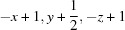 ; (ii)
; (ii) 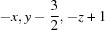 ; (iii)
; (iii) 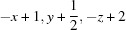 .
.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Education Office Foundation of Zhejiang Province (project No. Y201017321) and the innovation project of Zhejiang A & F University.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Organic acid-base adducts based on hydrogen bonding are a research field receiving great attention in recent years. As an extension of our study concentrating on hydrogen bonded assembly of organic acid and organic base (Jin et al., 2010), herein we report the crystal structure of 3,5-dimethylpyrazolium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate.
The crystal of the title compound of the formula C12H12N4O7 was obtained by recrystallization of the mixture of 3,5-dimethylpyrazole and 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid acid from the MeOH solution.
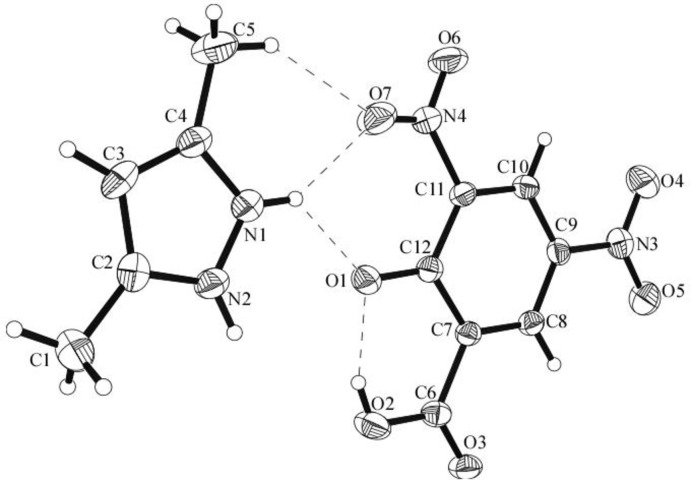
In this case (Fig. 1) it is the phenol H that has been deprotonated. The C—O distance 1.284 (4) Å concerning the phenolate is similar to the proton transfer compound bearing the 3,5-dinitrosalicylate in which only the phenol group has been deprotonated (Smith et al., 2011). The C—O distances O(2)—C(6), 1.300 (4) Å, O(3)—C(6), 1.223 (4) Å; in the COOH show characteristic C—O, and C=O distances which are also confirming the reliability of adding H atoms experimentally by different electron density onto O atoms.
One anion is bonded to one cation via N—H···O, and CH3—O associations to form a heteroadduct.
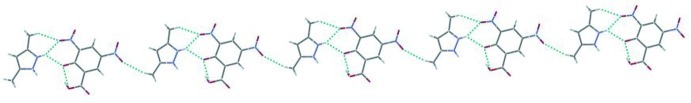
For the presence of these interactions, there are close joint motifs with descriptors of R21(6), and R12(6). The usual intramolecular hydrogen bond is found between the phenolate and the carboxyl group to exhibit a S11(6) graph. The heteroadducts were linked together by the CH3—O association between the methyl group of the pyrazole and the 5-nitro group with C—O distance of 3.415 Å to form one-dimensional chain running along the direction that made an angle of ca 60° with the a axis (Fig. 2). The chains were further stacked along the direction that is perpendicular with its extending direction via the interchain N-π interaction between the 5-nitro group and the phenyl ring of the anion with N—Cg distance of 3.236 Å to form two-dimensional sheet extending parallel to the ab plane. The sheets were further stacked along the c axis direction by the CH—O, N—H···O, and O—H···O associations to form three-dimensional ABAB layer network structure. Herein the chains at adjacent layers intersect at an angle of ca 120° with each other.
Experimental
A solution of 3,5-dimethyl pyrazole (19.2 mg, 0.2 mmol) in 5 ml of MeOH was added to a MeOH solution (6 ml) containing 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (22.8 mg, 0.1 mmol) under continuous stirring. The solution was stirred for about 1 h at room temperature, then the solution was filtered into a test tube. The solution was left standing at room temperature for several days, yellow blocks were isolated after slow evaporation of the solution in air at ambient temperature. The crystals were collected and dried in air to give the title compound.
Refinement
The absolute structure could not be determined in the present refinement. Hydrogen atoms attached to the C atoms were placed in calculated positions with d(C—H) = 0.93–0.96 Å. Positions of the hydrogen atoms at the NH, and COOH groups were located from the Fourier difference syntheses and refined independently. All Uiso values were restrained on Ueq values of the parent atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The structure of the title compound, showing displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The one-dimensional chain formed through the CH3—O interaction.
Crystal data
| C5H9N2+·C7H3N2O7− | F(000) = 336 |
| Mr = 324.26 | Dx = 1.547 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.1183 (7) Å | Cell parameters from 1025 reflections |
| b = 6.0636 (5) Å | θ = 2.5–22.6° |
| c = 14.1453 (11) Å | µ = 0.13 mm−1 |
| β = 91.904 (1)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 695.93 (10) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 2 | 0.40 × 0.27 × 0.11 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD diffractometer | 2301 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1659 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.040 |
| ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.959, Tmax = 0.986 | k = −7→7 |
| 3523 measured reflections | l = −16→12 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.047 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.105 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0405P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2301 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 208 parameters | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.2255 (4) | 0.7148 (5) | 0.2340 (2) | 0.0463 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.2726 | 0.8381 | 0.2218 | 0.056* | |
| N2 | 0.2198 (3) | 0.6193 (5) | 0.31994 (19) | 0.0469 (8) | |
| H2 | 0.2635 | 0.6724 | 0.3713 | 0.056* | |
| C6 | 0.3512 (4) | 0.7229 (6) | 0.5523 (2) | 0.0405 (8) | |
| N3 | 0.2184 (3) | 1.3159 (5) | 0.7707 (2) | 0.0487 (7) | |
| N4 | 0.5550 (4) | 0.7118 (5) | 0.8914 (2) | 0.0484 (8) | |
| O1 | 0.5414 (3) | 0.5277 (4) | 0.70183 (15) | 0.0454 (6) | |
| O2 | 0.4254 (3) | 0.5367 (4) | 0.53738 (15) | 0.0581 (7) | |
| H2A | 0.4770 | 0.4990 | 0.5855 | 0.087* | |
| O3 | 0.2657 (3) | 0.8102 (4) | 0.48999 (14) | 0.0493 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.1417 (3) | 1.4008 (4) | 0.70451 (18) | 0.0632 (7) | |
| O5 | 0.2271 (3) | 1.3968 (5) | 0.85007 (18) | 0.0689 (8) | |
| O6 | 0.5255 (4) | 0.7837 (5) | 0.96945 (17) | 0.0833 (10) | |
| O7 | 0.6547 (4) | 0.5660 (5) | 0.87978 (17) | 0.0698 (8) | |
| C1 | 0.1300 (5) | 0.6449 (8) | 0.0686 (2) | 0.0717 (13) | |
| H1A | 0.1787 | 0.7868 | 0.0584 | 0.108* | |
| H1B | 0.0155 | 0.6492 | 0.0495 | 0.108* | |
| H1C | 0.1854 | 0.5360 | 0.0320 | 0.108* | |
| C2 | 0.1462 (4) | 0.5868 (6) | 0.1713 (2) | 0.0464 (9) | |
| C3 | 0.0892 (4) | 0.4066 (7) | 0.2187 (3) | 0.0544 (10) | |
| H3 | 0.0298 | 0.2892 | 0.1925 | 0.065* | |
| C4 | 0.1370 (4) | 0.4321 (6) | 0.3134 (2) | 0.0464 (9) | |
| C5 | 0.1105 (4) | 0.2906 (7) | 0.3972 (3) | 0.0625 (11) | |
| H5A | 0.2148 | 0.2570 | 0.4278 | 0.094* | |
| H5B | 0.0572 | 0.1562 | 0.3774 | 0.094* | |
| H5C | 0.0422 | 0.3672 | 0.4406 | 0.094* | |
| C12 | 0.4688 (4) | 0.7102 (5) | 0.7195 (2) | 0.0353 (8) | |
| C7 | 0.3732 (3) | 0.8231 (6) | 0.64774 (19) | 0.0339 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.2969 (4) | 1.0188 (6) | 0.6644 (2) | 0.0376 (8) | |
| H8 | 0.2396 | 1.0905 | 0.6154 | 0.045* | |
| C9 | 0.3041 (4) | 1.1108 (6) | 0.7533 (2) | 0.0368 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.3900 (4) | 1.0088 (6) | 0.8269 (2) | 0.0396 (8) | |
| H10 | 0.3935 | 1.0711 | 0.8870 | 0.048* | |
| C11 | 0.4701 (4) | 0.8142 (6) | 0.8101 (2) | 0.0366 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0503 (17) | 0.0446 (18) | 0.0438 (17) | −0.0035 (14) | −0.0020 (13) | −0.0021 (14) |
| N2 | 0.0493 (18) | 0.051 (2) | 0.0397 (16) | −0.0042 (16) | −0.0060 (13) | −0.0055 (16) |
| C6 | 0.0382 (18) | 0.048 (2) | 0.0356 (19) | −0.0017 (17) | 0.0045 (16) | −0.0016 (17) |
| N3 | 0.0479 (17) | 0.0412 (19) | 0.057 (2) | 0.0007 (16) | 0.0029 (15) | −0.0032 (18) |
| N4 | 0.064 (2) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0372 (18) | −0.0012 (16) | −0.0046 (15) | 0.0033 (15) |
| O1 | 0.0544 (14) | 0.0412 (14) | 0.0404 (13) | 0.0081 (12) | −0.0011 (10) | −0.0056 (11) |
| O2 | 0.0701 (17) | 0.0628 (18) | 0.0408 (14) | 0.0203 (15) | −0.0077 (11) | −0.0155 (13) |
| O3 | 0.0554 (13) | 0.0590 (16) | 0.0329 (12) | 0.0050 (13) | −0.0072 (11) | 0.0004 (12) |
| O4 | 0.0679 (17) | 0.0510 (17) | 0.0699 (17) | 0.0183 (14) | −0.0112 (14) | 0.0030 (15) |
| O5 | 0.088 (2) | 0.0582 (18) | 0.0602 (17) | 0.0083 (16) | 0.0045 (14) | −0.0181 (15) |
| O6 | 0.144 (3) | 0.073 (2) | 0.0317 (15) | 0.033 (2) | −0.0088 (15) | −0.0034 (14) |
| O7 | 0.088 (2) | 0.070 (2) | 0.0509 (15) | 0.0294 (18) | −0.0100 (14) | 0.0072 (15) |
| C1 | 0.079 (3) | 0.093 (3) | 0.043 (2) | −0.017 (3) | −0.005 (2) | −0.009 (2) |
| C2 | 0.044 (2) | 0.052 (3) | 0.0424 (19) | 0.0036 (19) | −0.0059 (16) | −0.0103 (19) |
| C3 | 0.050 (2) | 0.056 (3) | 0.057 (2) | −0.006 (2) | −0.0065 (18) | −0.023 (2) |
| C4 | 0.0363 (19) | 0.042 (2) | 0.061 (2) | 0.0018 (18) | 0.0040 (16) | −0.0034 (19) |
| C5 | 0.061 (2) | 0.057 (3) | 0.069 (3) | −0.001 (2) | −0.0008 (19) | 0.010 (2) |
| C12 | 0.0346 (18) | 0.038 (2) | 0.0338 (18) | −0.0056 (16) | 0.0023 (14) | 0.0013 (16) |
| C7 | 0.0348 (16) | 0.0367 (19) | 0.0302 (16) | −0.0059 (16) | 0.0012 (13) | 0.0009 (15) |
| C8 | 0.0393 (19) | 0.039 (2) | 0.0346 (18) | −0.0019 (17) | −0.0034 (14) | 0.0036 (16) |
| C9 | 0.0394 (19) | 0.0310 (19) | 0.0399 (18) | −0.0045 (16) | 0.0016 (14) | −0.0010 (16) |
| C10 | 0.049 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.0299 (17) | −0.0064 (18) | 0.0020 (15) | −0.0014 (16) |
| C11 | 0.0403 (18) | 0.0381 (19) | 0.0312 (17) | −0.0023 (18) | −0.0024 (13) | 0.0046 (16) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—C2 | 1.329 (4) | C1—H1B | 0.9600 |
| N1—N2 | 1.348 (4) | C1—H1C | 0.9600 |
| N1—H1 | 0.8600 | C2—C3 | 1.371 (5) |
| N2—C4 | 1.321 (4) | C3—C4 | 1.391 (5) |
| N2—H2 | 0.8600 | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| C6—O3 | 1.224 (4) | C4—C5 | 1.484 (5) |
| C6—O2 | 1.301 (4) | C5—H5A | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.486 (4) | C5—H5B | 0.9600 |
| N3—O4 | 1.221 (3) | C5—H5C | 0.9600 |
| N3—O5 | 1.226 (3) | C12—C11 | 1.427 (4) |
| N3—C9 | 1.449 (4) | C12—C7 | 1.431 (4) |
| N4—O7 | 1.213 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.363 (4) |
| N4—O6 | 1.218 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.375 (4) |
| N4—C11 | 1.460 (4) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C12 | 1.283 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.379 (4) |
| O2—H2A | 0.8200 | C10—C11 | 1.372 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.496 (5) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9600 | ||
| C2—N1—N2 | 108.7 (3) | N2—C4—C3 | 106.7 (3) |
| C2—N1—H1 | 125.6 | N2—C4—C5 | 121.9 (3) |
| N2—N1—H1 | 125.6 | C3—C4—C5 | 131.4 (3) |
| C4—N2—N1 | 109.8 (3) | C4—C5—H5A | 109.5 |
| C4—N2—H2 | 125.1 | C4—C5—H5B | 109.5 |
| N1—N2—H2 | 125.1 | H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 |
| O3—C6—O2 | 120.9 (3) | C4—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| O3—C6—C7 | 121.7 (3) | H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| O2—C6—C7 | 117.4 (3) | H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| O4—N3—O5 | 123.1 (3) | O1—C12—C11 | 124.5 (3) |
| O4—N3—C9 | 117.9 (3) | O1—C12—C7 | 121.0 (3) |
| O5—N3—C9 | 119.0 (3) | C11—C12—C7 | 114.4 (3) |
| O7—N4—O6 | 122.4 (3) | C8—C7—C12 | 122.2 (3) |
| O7—N4—C11 | 120.2 (3) | C8—C7—C6 | 118.1 (3) |
| O6—N4—C11 | 117.4 (3) | C12—C7—C6 | 119.7 (3) |
| C6—O2—H2A | 109.5 | C7—C8—C9 | 120.4 (3) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C7—C8—H8 | 119.8 |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C9—C8—H8 | 119.8 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C8—C9—C10 | 120.8 (3) |
| C2—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C8—C9—N3 | 119.8 (3) |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C10—C9—N3 | 119.4 (3) |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C11—C10—C9 | 119.1 (3) |
| N1—C2—C3 | 107.6 (3) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.5 |
| N1—C2—C1 | 122.4 (4) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 130.0 (3) | C10—C11—C12 | 123.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 107.2 (3) | C10—C11—N4 | 116.3 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 126.4 | C12—C11—N4 | 120.6 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 126.4 | ||
| C2—N1—N2—C4 | −0.4 (4) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.8 (5) |
| N2—N1—C2—C3 | 0.0 (4) | C7—C8—C9—N3 | −178.3 (3) |
| N2—N1—C2—C1 | −179.8 (3) | O4—N3—C9—C8 | 0.0 (4) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.3 (4) | O5—N3—C9—C8 | −179.4 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.9 (4) | O4—N3—C9—C10 | −179.1 (3) |
| N1—N2—C4—C3 | 0.6 (3) | O5—N3—C9—C10 | 1.5 (4) |
| N1—N2—C4—C5 | −179.9 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.6 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—N2 | −0.6 (4) | N3—C9—C10—C11 | 179.7 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 180.0 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.2 (4) |
| O1—C12—C7—C8 | −179.0 (3) | C9—C10—C11—N4 | −178.4 (3) |
| C11—C12—C7—C8 | 2.9 (4) | O1—C12—C11—C10 | −179.5 (3) |
| O1—C12—C7—C6 | 2.8 (4) | C7—C12—C11—C10 | −1.4 (4) |
| C11—C12—C7—C6 | −175.3 (3) | O1—C12—C11—N4 | −1.3 (5) |
| O3—C6—C7—C8 | −0.9 (4) | C7—C12—C11—N4 | 176.7 (3) |
| O2—C6—C7—C8 | 179.7 (3) | O7—N4—C11—C10 | −165.3 (3) |
| O3—C6—C7—C12 | 177.4 (3) | O6—N4—C11—C10 | 12.4 (4) |
| O2—C6—C7—C12 | −2.1 (4) | O7—N4—C11—C12 | 16.5 (5) |
| C12—C7—C8—C9 | −2.7 (5) | O6—N4—C11—C12 | −165.9 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 175.5 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O7i | 0.86 | 2.09 | 2.859 (4) | 148 |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.86 | 2.16 | 2.809 (4) | 132 |
| N2—H2···O3 | 0.86 | 1.88 | 2.684 (3) | 156 |
| O2—H2A···O1 | 0.82 | 1.72 | 2.481 (3) | 154 |
| C1—H1A···O7i | 0.96 | 2.32 | 3.166 (5) | 147 |
| C5—H5B···O4ii | 0.96 | 2.49 | 3.414 (5) | 160 |
| C10—H10···O6iii | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.379 (4) | 164 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1; (ii) −x, y−3/2, −z+1; (iii) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB6958).
References
- Bruker (2002). SADABS, SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Jin, S. W., Zhang, W. B., Liu, L., Gao, H. F., Wang, D. Q., Chen, R. P. & Xu, X. L. (2010). J. Mol. Struct. 975, 128–136.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D., Healy, P. C. & White, J. M. (2011). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 41, 1649–1662.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812041906/hb6958sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812041906/hb6958Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812041906/hb6958Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report