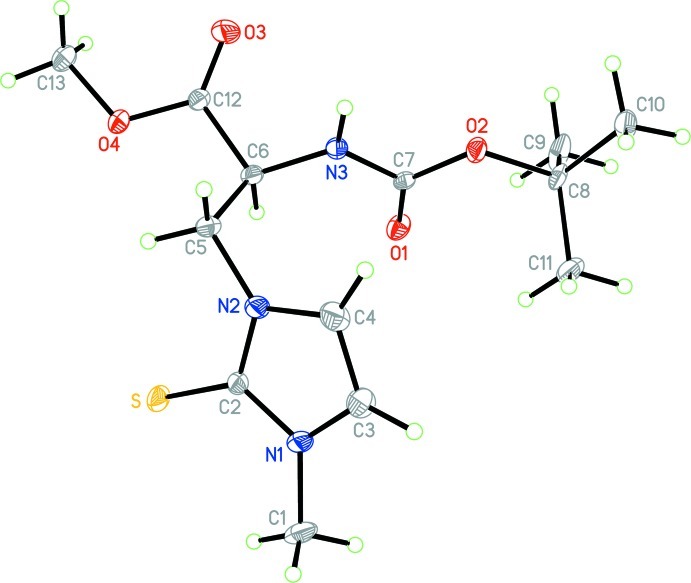
Abstract
In the title compound, C13H21N3O4S, the mean plane of the –N(H)—C(=O)—O– group of the carbamate unit forms a dihedral angle of 64.7 (2)° with the mean plane of the –C—C(=O)—O– group of the ester unit. In the crystal, molecules are linked by N—H⋯O=C hydrogen bonds, forming chains along the c-axis direction.
Related literature
The title compound is a mercaptoimidazole derivative. For applications of mercaptoimidazole derivatives in the treatment of hyperpigmentation, see: Kasraee (2002 ▶); Kasraee et al. (2005 ▶) and for inhibiting tyrosinase, see: Liao et al. (2012 ▶). For typical bond lengths of intermolecular N—H⋯O=C hydrogen bonds, see: Taylor et al. (1984 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H21N3O4S
M r = 315.39
Monoclinic,
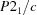
a = 8.7636 (1) Å
b = 19.1184 (2) Å
c = 9.6735 (2) Å
β = 98.485 (1)°
V = 1603.02 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 1.97 mm−1
T = 110 K
0.60 × 0.50 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Agilent Xcalibur (Sapphire3, Gemini) diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2010 ▶) T min = 0.550, T max = 1.000
12262 measured reflections
3093 independent reflections
2923 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.019
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.036
wR(F 2) = 0.137
S = 1.05
3093 reflections
190 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.39 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.53 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812043486/lh5544sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812043486/lh5544Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812043486/lh5544Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H3A⋯O1i | 0.88 | 2.25 | 2.9819 (14) | 140 |
Symmetry code: (i) 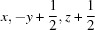 .
.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support in part from the National Science Council, Taiwan (NSC 99–2119-M-241-001-MY2). Helpful comments from the reviewers are also greatly appreciated.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Methimazole causes hypopigmentation in some patients during the clinical oral antithyroid medication (Kasraee, 2002; Kasraee et al., 2005). Ergothioneine has a potent inhibition effect on inhibiting tyrosinase enzyme activity, resulting from the presence of the sulfur substituted imidazole ring (Liao et al., 2012). It shows that molecules with a mercaptoimidazole group have potential as depigmenting agents. The title compound (I) is the key intermediate for the synthesis of the amino acid derivatives containing methimazole moiety. Methimazole exists between the 2-thiol and 2-thione forms and has been observed to react in both guizes, depending upon the reaction conditions. Compound (I) is the nitrogen-substituted product from the 2-thione form.
Herein we report the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound. The molecular structure of (I) is shown in Fig. 1. The essentially planar carbamate group (N3/C7/O1/O2) forms a dihedral angle of 64.7 (2)° with the mean plane of the carboxylate group (C6/C12/O3/O4). In the crystal, molecules are linked by N—H···O═C hydrogen bonds involving the amino and carbamate group forming chains along the c-axis direction. Intermolecular N—H···O═C hydrogen bonds are are highlighted in the literature by Taylor et al. (1984).
Experimental
To a mixture of 1-methyl-2-mercaptoimidazole (390 mg, 3.4 mmole) and methyl 3-bromo-2-[(tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino]propanoate (970 mg, 3.4 mmol) in 17 ml of N,N-dimethylformamide was added potassium carbonate (940 mg, 6.8 mmole). The reaction mixture was stirred at 343 K for 1.5 h under N2 atmosphere. The resulting mixture was partitioned between dichloromethane (70 ml) and H2O (35 ml). The organic layer was dried over MgSO4 and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was separated by chromatography over silica gel and eluted with hexane/ethyl acetate (3/7) to afford 776 mg of the title compound (I) in 72% yield. Single crystals suitable for X-ray measurements were obtained by recrystallization from a dichloromethane/hexane solution of the title compound at room temperature.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with C—H = 0.95 - 1.00 Å, N—H = 0.88 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C,N).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) with ellipsoids for non-H atoms shown at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C13H21N3O4S | - |
| Mr = 315.39 | Dx = 1.307 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point: 379 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| a = 8.7636 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 9755 reflections |
| b = 19.1184 (2) Å | θ = 4.6–71.5° |
| c = 9.6735 (2) Å | µ = 1.97 mm−1 |
| β = 98.485 (1)° | T = 110 K |
| V = 1603.02 (4) Å3 | Cube, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.60 × 0.50 × 0.30 mm |
| F(000) = 672 |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur (Sapphire3, Gemini) diffractometer | 3093 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2923 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.019 |
| Detector resolution: 16.0690 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 71.6°, θmin = 4.6° |
| ω scans | h = −10→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2010) | k = −23→23 |
| Tmin = 0.550, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −10→11 |
| 12262 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.137 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.120P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3093 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 190 parameters | Δρmax = 0.39 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.53 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. CrysAlis PRO, Oxford Diffraction Ltd., Version 1.171.33.66 (release 28–04-2010 CrysAlis171. NET) (compiled Apr 28 2010,14:27:37) Empirical absorption correction using spherical harmonics, implemented in SCALE3 ABSPACK scaling algorithm. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S | 0.73233 (4) | 0.397097 (16) | 0.68939 (3) | 0.01934 (17) | |
| O1 | 1.13487 (11) | 0.21854 (5) | 0.76481 (9) | 0.0166 (2) | |
| O2 | 1.21653 (11) | 0.16902 (5) | 0.97808 (10) | 0.0159 (2) | |
| O3 | 1.39031 (11) | 0.39024 (5) | 0.96950 (12) | 0.0242 (3) | |
| O4 | 1.20097 (10) | 0.46673 (5) | 0.89321 (11) | 0.0185 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.65404 (12) | 0.27506 (6) | 0.81002 (12) | 0.0173 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.85617 (12) | 0.32536 (6) | 0.92269 (12) | 0.0154 (3) | |
| N3 | 1.18007 (12) | 0.28264 (5) | 0.96527 (11) | 0.0128 (3) | |
| H3A | 1.2174 | 0.2816 | 1.0548 | 0.015* | |
| C1 | 0.51211 (16) | 0.26296 (8) | 0.71401 (16) | 0.0257 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.5002 | 0.2993 | 0.6417 | 0.039* | |
| H1B | 0.4240 | 0.2645 | 0.7656 | 0.039* | |
| H1C | 0.5167 | 0.2170 | 0.6701 | 0.039* | |
| C2 | 0.74673 (14) | 0.33203 (7) | 0.80813 (13) | 0.0133 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.70687 (16) | 0.23359 (8) | 0.92408 (16) | 0.0237 (3) | |
| H3B | 0.6621 | 0.1909 | 0.9484 | 0.028* | |
| C4 | 0.83277 (16) | 0.26432 (8) | 0.99458 (15) | 0.0222 (3) | |
| H4A | 0.8938 | 0.2476 | 1.0773 | 0.027* | |
| C5 | 0.98306 (14) | 0.37429 (7) | 0.95850 (14) | 0.0150 (3) | |
| H5A | 1.0054 | 0.3794 | 1.0613 | 0.018* | |
| H5B | 0.9531 | 0.4207 | 0.9180 | 0.018* | |
| C6 | 1.12846 (13) | 0.34846 (6) | 0.90267 (13) | 0.0124 (3) | |
| H6A | 1.1017 | 0.3412 | 0.7996 | 0.015* | |
| C7 | 1.17322 (13) | 0.22218 (6) | 0.89111 (13) | 0.0117 (3) | |
| C8 | 1.21603 (16) | 0.09602 (6) | 0.92637 (15) | 0.0155 (3) | |
| C9 | 1.32792 (18) | 0.08866 (7) | 0.82123 (18) | 0.0255 (4) | |
| H9A | 1.4312 | 0.1032 | 0.8646 | 0.038* | |
| H9B | 1.2938 | 0.1183 | 0.7399 | 0.038* | |
| H9C | 1.3309 | 0.0398 | 0.7914 | 0.038* | |
| C10 | 1.27314 (18) | 0.05494 (7) | 1.05848 (16) | 0.0228 (3) | |
| H10A | 1.1998 | 0.0602 | 1.1251 | 0.034* | |
| H10B | 1.3743 | 0.0728 | 1.1004 | 0.034* | |
| H10C | 1.2821 | 0.0054 | 1.0351 | 0.034* | |
| C11 | 1.05181 (16) | 0.07481 (7) | 0.86891 (15) | 0.0215 (3) | |
| H11A | 0.9859 | 0.0809 | 0.9415 | 0.032* | |
| H11B | 1.0502 | 0.0257 | 0.8399 | 0.032* | |
| H11C | 1.0135 | 0.1042 | 0.7882 | 0.032* | |
| C12 | 1.25754 (15) | 0.40293 (6) | 0.92748 (14) | 0.0131 (3) | |
| C13 | 1.31275 (16) | 0.52315 (7) | 0.90481 (17) | 0.0236 (3) | |
| H13A | 1.2600 | 0.5673 | 0.8774 | 0.035* | |
| H13B | 1.3897 | 0.5137 | 0.8432 | 0.035* | |
| H13C | 1.3641 | 0.5266 | 1.0017 | 0.035* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S | 0.0231 (3) | 0.0120 (2) | 0.0207 (3) | −0.00343 (11) | −0.00411 (17) | 0.00477 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0231 (5) | 0.0148 (5) | 0.0116 (5) | −0.0038 (3) | 0.0021 (4) | −0.0014 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0216 (5) | 0.0103 (5) | 0.0145 (5) | −0.0009 (3) | −0.0014 (4) | −0.0014 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0128 (5) | 0.0217 (5) | 0.0364 (6) | −0.0026 (4) | −0.0020 (4) | 0.0038 (4) |
| O4 | 0.0153 (5) | 0.0110 (5) | 0.0281 (6) | −0.0027 (3) | −0.0001 (4) | −0.0003 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0109 (5) | 0.0163 (6) | 0.0243 (6) | −0.0033 (4) | 0.0010 (4) | 0.0038 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0115 (5) | 0.0145 (6) | 0.0198 (6) | −0.0016 (4) | 0.0011 (4) | 0.0042 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0147 (5) | 0.0121 (5) | 0.0108 (5) | 0.0002 (4) | −0.0008 (4) | −0.0005 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0149 (7) | 0.0260 (8) | 0.0345 (9) | −0.0096 (5) | −0.0017 (6) | 0.0024 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0113 (6) | 0.0110 (6) | 0.0178 (7) | 0.0000 (4) | 0.0031 (5) | −0.0004 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0182 (7) | 0.0200 (7) | 0.0335 (8) | −0.0042 (5) | 0.0055 (6) | 0.0119 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0175 (7) | 0.0226 (7) | 0.0264 (8) | −0.0010 (5) | 0.0031 (5) | 0.0125 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0114 (6) | 0.0156 (7) | 0.0173 (7) | −0.0015 (5) | 0.0002 (5) | −0.0019 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0116 (6) | 0.0129 (6) | 0.0122 (6) | −0.0015 (4) | −0.0002 (5) | −0.0007 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0078 (5) | 0.0122 (6) | 0.0155 (6) | −0.0027 (4) | 0.0022 (4) | 0.0004 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0208 (7) | 0.0078 (6) | 0.0179 (7) | −0.0042 (5) | 0.0028 (6) | −0.0017 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0321 (8) | 0.0118 (6) | 0.0366 (9) | −0.0032 (6) | 0.0184 (7) | −0.0024 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0297 (7) | 0.0129 (6) | 0.0242 (7) | −0.0019 (5) | −0.0014 (6) | 0.0028 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0231 (7) | 0.0198 (7) | 0.0200 (7) | −0.0105 (5) | −0.0019 (5) | 0.0023 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0139 (6) | 0.0127 (6) | 0.0126 (6) | −0.0018 (4) | 0.0010 (5) | −0.0008 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0189 (7) | 0.0137 (6) | 0.0369 (9) | −0.0064 (5) | −0.0004 (6) | 0.0010 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S—C2 | 1.6852 (13) | C4—H4A | 0.9500 |
| O1—C7 | 1.2204 (16) | C5—C6 | 1.5370 (16) |
| O2—C7 | 1.3380 (16) | C5—H5A | 0.9900 |
| O2—C8 | 1.4825 (14) | C5—H5B | 0.9900 |
| O3—C12 | 1.1993 (17) | C6—C12 | 1.5301 (16) |
| O4—C12 | 1.3398 (15) | C6—H6A | 1.0000 |
| O4—C13 | 1.4502 (16) | C8—C11 | 1.5193 (18) |
| N1—C2 | 1.3605 (16) | C8—C9 | 1.5199 (19) |
| N1—C3 | 1.3819 (18) | C8—C10 | 1.5204 (19) |
| N1—C1 | 1.4567 (17) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| N2—C2 | 1.3604 (17) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| N2—C4 | 1.3890 (17) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| N2—C5 | 1.4553 (16) | C10—H10A | 0.9800 |
| N3—C7 | 1.3571 (16) | C10—H10B | 0.9800 |
| N3—C6 | 1.4402 (16) | C10—H10C | 0.9800 |
| N3—H3A | 0.8800 | C11—H11A | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9800 | C11—H11B | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9800 | C11—H11C | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1C | 0.9800 | C13—H13A | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.344 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3B | 0.9500 | C13—H13C | 0.9800 |
| C7—O2—C8 | 121.10 (10) | C5—C6—H6A | 108.1 |
| C12—O4—C13 | 115.91 (10) | O1—C7—O2 | 126.64 (11) |
| C2—N1—C3 | 109.86 (11) | O1—C7—N3 | 124.20 (11) |
| C2—N1—C1 | 125.02 (12) | O2—C7—N3 | 109.16 (11) |
| C3—N1—C1 | 124.88 (12) | O2—C8—C11 | 109.28 (11) |
| C2—N2—C4 | 110.38 (11) | O2—C8—C9 | 110.05 (10) |
| C2—N2—C5 | 123.76 (11) | C11—C8—C9 | 113.60 (12) |
| C4—N2—C5 | 125.80 (11) | O2—C8—C10 | 102.62 (11) |
| C7—N3—C6 | 122.36 (10) | C11—C8—C10 | 110.26 (11) |
| C7—N3—H3A | 118.8 | C9—C8—C10 | 110.47 (12) |
| C6—N3—H3A | 118.8 | C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1B | 109.5 | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1C | 109.5 | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C8—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| N2—C2—N1 | 105.34 (11) | C8—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| N2—C2—S | 126.68 (10) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—S | 127.98 (10) | C8—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—N1 | 107.92 (13) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3B | 126.0 | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| N1—C3—H3B | 126.0 | C8—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—N2 | 106.51 (12) | C8—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 126.7 | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| N2—C4—H4A | 126.7 | C8—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| N2—C5—C6 | 110.72 (10) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| N2—C5—H5A | 109.5 | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 109.5 | O3—C12—O4 | 124.96 (12) |
| N2—C5—H5B | 109.5 | O3—C12—C6 | 124.98 (11) |
| C6—C5—H5B | 109.5 | O4—C12—C6 | 110.05 (10) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 108.1 | O4—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| N3—C6—C12 | 110.47 (10) | O4—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| N3—C6—C5 | 110.99 (10) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C12—C6—C5 | 110.99 (10) | O4—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| N3—C6—H6A | 108.1 | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C12—C6—H6A | 108.1 | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3A···O1i | 0.88 | 2.25 | 2.9819 (14) | 140 |
Symmetry code: (i) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH5544).
References
- Agilent (2010). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Kasraee, B. (2002). J. Invest. Dermatol. 118, 205–207. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kasraee, B., Handjani, F., Parhizgar, A., Omrani, G. R., Fallahi, M. R., Amini, M., Nikbakhsh, M., Tran, C., Hügin, A., Sorg, O. & Saurat, J.-H. (2005). Dermatology, 211, 360–362. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Liao, W. C., Wu, W. H., Tsai, P.-C., Wang, H.-F., Liu, Y.-H. & Chan, C.-F. (2012). Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 166, 259–267. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R., Kennard, O. & Versichel, W. (1984). Acta Cryst. B40, 280–288.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812043486/lh5544sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812043486/lh5544Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812043486/lh5544Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report