Abstract
In the title compound, C21H15F2N3O2, a pyrazole derivative bearing three aromatic substituents, the central five-membered heterocyclic ring makes dihedral angles of 1.77 (14), 3.68 (13) and 72.15 (14)° with the three benzene rings. In the crystal, C—H⋯O and C—H⋯F interactions connect the molecules into double layers parallel to the bc plane.
Related literature
For general information about the pharmacological properties and medical applications of pyrazole derivatives, see: Kumar et al. (2009 ▶); Sarojini et al. (2010 ▶); Samshuddin et al. (2012 ▶). For the crystal structures of other pyrazole derivatives, see: Baktır et al. (2011 ▶); Jasinski et al. (2012 ▶). For the puckering analysis of cyclic motifs, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶). For graph-set analysis of hydrogen bonds, see: Etter et al. (1990 ▶); Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).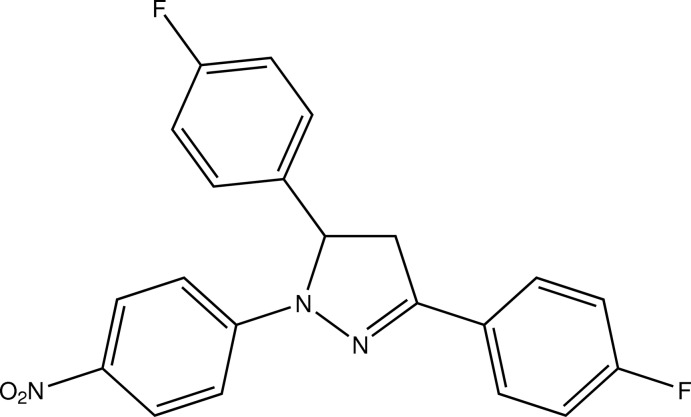
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H15F2N3O2
M r = 379.36
Monoclinic,
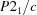
a = 13.2884 (13) Å
b = 12.7364 (10) Å
c = 11.4656 (9) Å
β = 115.324 (3)°
V = 1754.0 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 200 K
0.57 × 0.33 × 0.27 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▶) T min = 0.692, T max = 0.971
15973 measured reflections
4301 independent reflections
3066 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.052
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.067
wR(F 2) = 0.221
S = 1.06
4301 reflections
253 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.39 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2010 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681204370X/is5210sup1.cif
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681204370X/is5210Isup2.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681204370X/is5210Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681204370X/is5210Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12—H12⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.41 | 3.305 (3) | 157 |
| C16—H16⋯F2ii | 0.95 | 2.55 | 3.427 (3) | 154 |
| C26—H26⋯F1iii | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.494 (3) | 169 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 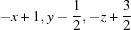 ; (ii)
; (ii) 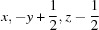 ; (iii)
; (iii) 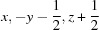 .
.
Acknowledgments
BN thanks the UGC for financial assistance through a BSR one-time grant for the purchase of chemicals. SS thanks Mangalore University for the research facilities.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Pyrazole derivatives are well known for their broad spectrum of pharmacological properties and have been found – among others – to exhibit antimicrobial, antioxidant, antiamoebic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antidepressant and anticancer activity (Kumar et al., 2009; Sarojini et al., 2010; Samshuddin et al., 2012). Because of these various interesting fields of application as well as their fairly assessable path of synthesis, the pyrazoline ring became a center of attraction for organic chemists. The crystal structures of some pyrazolines derived from 4,4'-difluoro chalcone have been reported (Baktır et al., 2011; Jasinski et al., 2012). Fuelled by our ongoing interest in pharmacological active compounds, the title compound was synthesized.
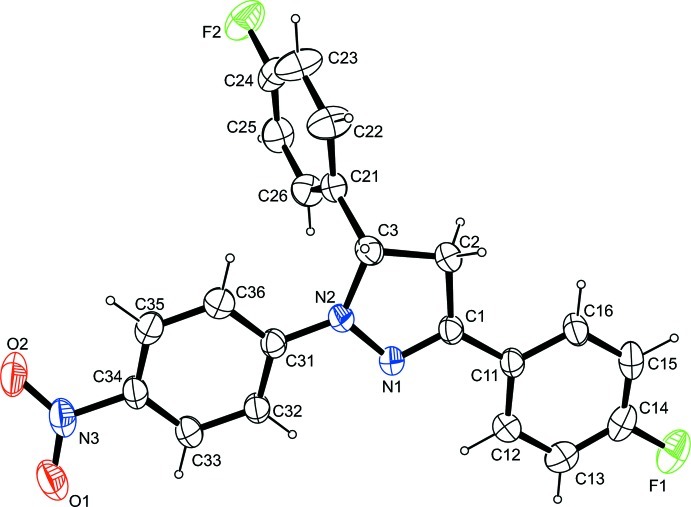
Three phenyl-derived substituents are bonded to a central 4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole moiety. The least-squares planes defined by the C11–C16, C31–C36 and C21–C26 benzene rings enclose dihedral angles of 1.77 (14), 3.68 (13) and 72.15 (14)°, respectively, with the least-squares plane defined by the intracyclic atoms of the central five-membered heterocycle with the largest angle formed by one of the two para-fluoro phenyl groups. A conformational analysis of the 4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole moiety is precluded due to its low puckering amplitude (Cremer & Pople, 1975). The nitro group is slightly tilted out of plane of the least-square plane defined by the carbon atoms of the aromatic moiety it is bonded to, the corresponding O2—N3—C34—C35 torsion angle being 17.0 (3)° (Fig. 1).
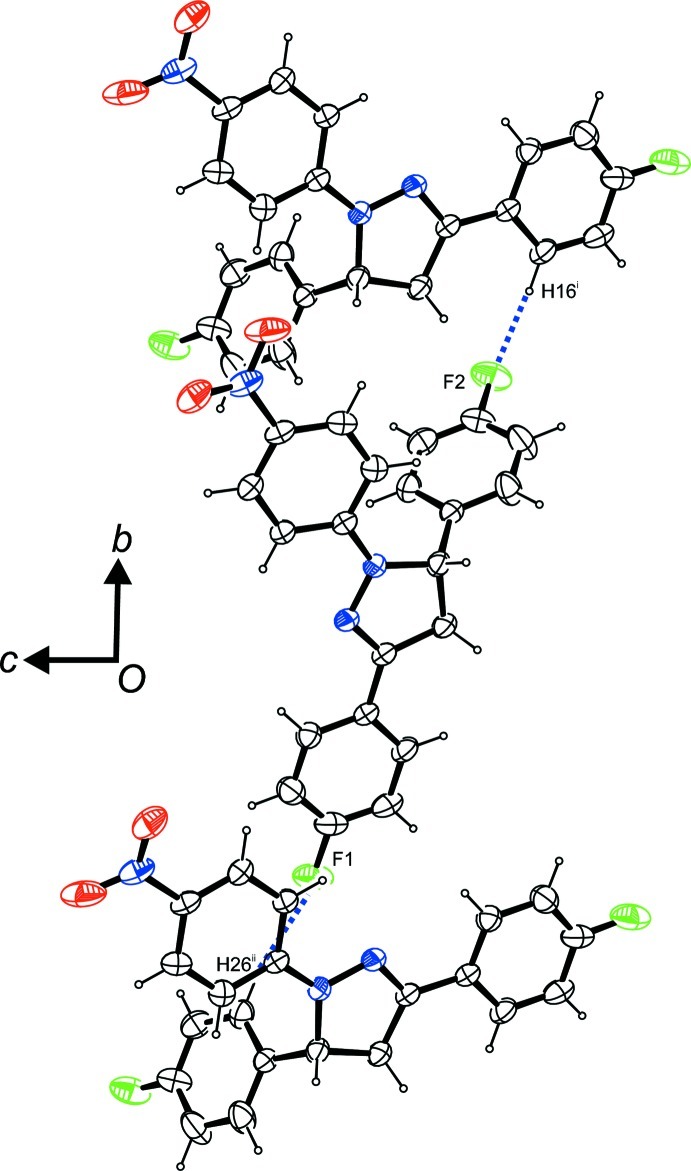
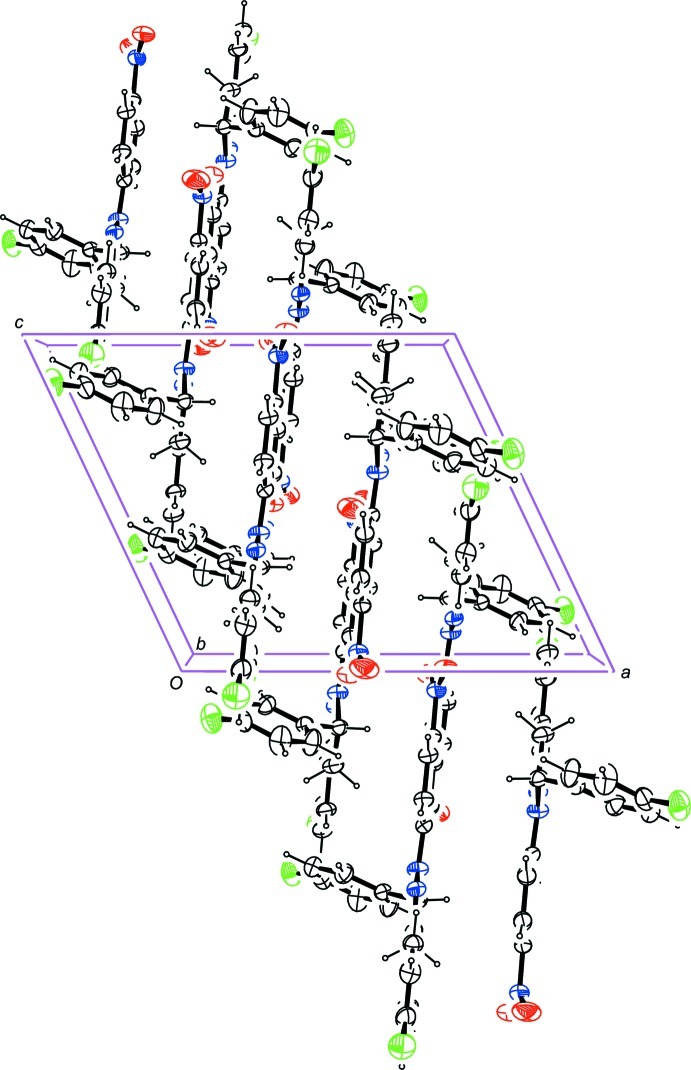
In the crystal, C—H···O and C—H···F contacts can be observed whose range falls by more than 0.1 Å below the sum of van-der-Waals radii of the atoms participating in them. These are exclusively supported by hydrogen atoms bonded to para-fluoro phenyl groups. Metrical parameters as well as information about the symmetry of these contacts are summarized in Table 1. In terms of graph-set analysis (Etter et al., 1990; Bernstein et al., 1995), the descriptor for the C—H···O contacts is C(12) on the unary level, while the C—H···F contacts necessitate a C(11)C(11) descriptor on the same level. In total, the molecules are connected to double layers parallel to the bc plane. The shortest intercentroid distance between two aromatic systems was measured at 4.8923 (17) Å and is observed between the two different fluorinated phenyl groups in neighbouring molecules. Taking into account the centroid of the 4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole moiety as well, the shortest intercentroid distance is found at 3.5918 (15) Å between this pyrazole unit and the nitrated phenyl group (Fig. 2). The packing of the title compound in the crystal structure is shown in Figure 3.
Experimental
A mixture of 4,4'-difluoro chalcone (2.68 g, 0.01 mol) and 4-nitrophenyl hydrazine (1.53 g, 0.01 mol) was refluxed in glacial acetic acid (50 ml) for 6 h. The reaction mixture was cooled and pourred into ice-cold water (50 ml). The precipitate was collected by filtration and purified by recrystallization from ethanol (yield: 74%). Yellow blocks, suitable for the X-ray diffraction study, were grown from a DMF solution by slow evaporation at room temperature.
Refinement
H atoms were placed in calculated positions (C—H 0.95 Å for aromatic carbon atoms, C—H 0.99 Å for the methylene group and C—H 1.00 Å for the methine group) and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with U(H) set to 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labels and anisotropic displacement ellipsoids (drawn at 50% probability level).
Fig. 2.
Intermolecular contacts, viewed along [-1 0 0]. For clarity, only an arbitrary selection of intermolecular contacts is shown. [Symmetry codes: (i) x, -y + 1/2, z + 1/2; (ii) x, -y - 1/2, z - 1/2].
Fig. 3.
Molecular packing of the title compound, viewed along [0 1 0] (anisotropic displacement ellipsoids drawn at 50% probability level).
Crystal data
| C21H15F2N3O2 | F(000) = 784 |
| Mr = 379.36 | Dx = 1.437 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point: 443 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 13.2884 (13) Å | Cell parameters from 6702 reflections |
| b = 12.7364 (10) Å | θ = 2.3–27.9° |
| c = 11.4656 (9) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| β = 115.324 (3)° | T = 200 K |
| V = 1754.0 (3) Å3 | Block, orange |
| Z = 4 | 0.57 × 0.33 × 0.27 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 4301 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3066 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.052 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 2.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −17→17 |
| Tmin = 0.692, Tmax = 0.971 | k = −15→16 |
| 15973 measured reflections | l = −15→14 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.067 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.221 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1331P)2 + 0.5062P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4301 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 253 parameters | Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.39 e Å−3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| F1 | 0.11689 (15) | −0.42461 (13) | −0.04507 (17) | 0.0638 (5) | |
| F2 | 0.01460 (13) | 0.43563 (13) | 0.35591 (18) | 0.0611 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.61528 (16) | 0.02802 (17) | 1.00769 (16) | 0.0536 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.57223 (18) | 0.19339 (18) | 0.98021 (18) | 0.0663 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.30617 (15) | −0.05788 (13) | 0.36124 (16) | 0.0305 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.32892 (15) | 0.04326 (14) | 0.40815 (16) | 0.0327 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.56940 (16) | 0.10368 (18) | 0.93869 (18) | 0.0428 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.25491 (17) | −0.05414 (16) | 0.23711 (18) | 0.0297 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.2351 (2) | 0.05569 (17) | 0.1837 (2) | 0.0368 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.1545 | 0.0717 | 0.1396 | 0.044* | |
| H2B | 0.2688 | 0.0663 | 0.1225 | 0.044* | |
| C3 | 0.29364 (18) | 0.12390 (17) | 0.30617 (19) | 0.0322 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.3607 | 0.1583 | 0.3047 | 0.039* | |
| C11 | 0.21963 (17) | −0.15094 (17) | 0.16168 (18) | 0.0298 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.24429 (19) | −0.24829 (18) | 0.2240 (2) | 0.0354 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.2849 | −0.2511 | 0.3151 | 0.042* | |
| C13 | 0.2103 (2) | −0.34014 (19) | 0.1545 (3) | 0.0426 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.2270 | −0.4063 | 0.1968 | 0.051* | |
| C14 | 0.1515 (2) | −0.3339 (2) | 0.0222 (2) | 0.0431 (6) | |
| C15 | 0.1269 (2) | −0.2404 (2) | −0.0425 (2) | 0.0437 (6) | |
| H15 | 0.0871 | −0.2385 | −0.1338 | 0.052* | |
| C16 | 0.16125 (19) | −0.14838 (19) | 0.0279 (2) | 0.0375 (5) | |
| H16 | 0.1448 | −0.0827 | −0.0156 | 0.045* | |
| C21 | 0.21828 (17) | 0.20653 (17) | 0.32160 (18) | 0.0303 (4) | |
| C22 | 0.2177 (2) | 0.30641 (19) | 0.2750 (3) | 0.0495 (6) | |
| H22 | 0.2653 | 0.3225 | 0.2350 | 0.059* | |
| C23 | 0.1486 (3) | 0.3840 (2) | 0.2857 (3) | 0.0570 (7) | |
| H23 | 0.1479 | 0.4525 | 0.2528 | 0.068* | |
| C24 | 0.08164 (19) | 0.35925 (19) | 0.3447 (3) | 0.0422 (6) | |
| C25 | 0.0790 (2) | 0.2616 (2) | 0.3912 (2) | 0.0431 (6) | |
| H25 | 0.0308 | 0.2464 | 0.4309 | 0.052* | |
| C26 | 0.14779 (19) | 0.18489 (19) | 0.3796 (2) | 0.0390 (5) | |
| H26 | 0.1468 | 0.1163 | 0.4117 | 0.047* | |
| C31 | 0.39135 (16) | 0.05788 (16) | 0.53770 (18) | 0.0289 (4) | |
| C32 | 0.42036 (18) | −0.02827 (17) | 0.62266 (19) | 0.0321 (4) | |
| H32 | 0.3995 | −0.0972 | 0.5896 | 0.039* | |
| C33 | 0.47889 (18) | −0.01300 (18) | 0.7534 (2) | 0.0344 (5) | |
| H33 | 0.4983 | −0.0711 | 0.8108 | 0.041* | |
| C34 | 0.50939 (17) | 0.08796 (18) | 0.80077 (19) | 0.0331 (5) | |
| C35 | 0.48391 (18) | 0.17349 (18) | 0.7191 (2) | 0.0348 (5) | |
| H35 | 0.5063 | 0.2419 | 0.7534 | 0.042* | |
| C36 | 0.42597 (18) | 0.15954 (18) | 0.5877 (2) | 0.0346 (5) | |
| H36 | 0.4095 | 0.2181 | 0.5311 | 0.042* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| F1 | 0.0698 (11) | 0.0542 (10) | 0.0696 (11) | −0.0138 (8) | 0.0319 (9) | −0.0309 (8) |
| F2 | 0.0490 (9) | 0.0516 (10) | 0.0853 (12) | 0.0049 (7) | 0.0312 (9) | −0.0195 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0509 (10) | 0.0741 (14) | 0.0274 (8) | 0.0024 (9) | 0.0089 (7) | −0.0019 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0681 (13) | 0.0731 (14) | 0.0428 (10) | 0.0056 (11) | 0.0096 (9) | −0.0301 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0346 (9) | 0.0314 (9) | 0.0248 (8) | 0.0006 (7) | 0.0119 (7) | −0.0021 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0425 (10) | 0.0293 (9) | 0.0234 (8) | 0.0018 (7) | 0.0113 (7) | 0.0009 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0354 (10) | 0.0617 (14) | 0.0292 (9) | −0.0014 (9) | 0.0117 (8) | −0.0124 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0316 (10) | 0.0352 (11) | 0.0239 (9) | 0.0015 (8) | 0.0133 (8) | −0.0014 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0474 (13) | 0.0379 (12) | 0.0248 (9) | 0.0063 (10) | 0.0151 (9) | 0.0025 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0356 (11) | 0.0350 (11) | 0.0267 (9) | 0.0027 (8) | 0.0139 (8) | 0.0035 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0301 (10) | 0.0366 (11) | 0.0233 (9) | 0.0008 (8) | 0.0121 (8) | −0.0025 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0364 (11) | 0.0373 (11) | 0.0308 (10) | 0.0015 (9) | 0.0127 (9) | 0.0014 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0449 (13) | 0.0362 (12) | 0.0505 (14) | 0.0009 (10) | 0.0240 (11) | −0.0002 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0418 (13) | 0.0435 (13) | 0.0490 (13) | −0.0072 (10) | 0.0243 (11) | −0.0179 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0465 (14) | 0.0559 (15) | 0.0288 (10) | −0.0052 (11) | 0.0162 (10) | −0.0114 (10) |
| C16 | 0.0428 (12) | 0.0456 (13) | 0.0233 (9) | 0.0011 (10) | 0.0132 (9) | −0.0011 (9) |
| C21 | 0.0319 (10) | 0.0334 (11) | 0.0261 (9) | −0.0009 (8) | 0.0128 (8) | −0.0010 (8) |
| C22 | 0.0518 (15) | 0.0375 (13) | 0.0737 (18) | 0.0024 (11) | 0.0408 (14) | 0.0105 (12) |
| C23 | 0.0619 (17) | 0.0300 (13) | 0.091 (2) | 0.0033 (12) | 0.0439 (16) | 0.0080 (13) |
| C24 | 0.0311 (11) | 0.0396 (13) | 0.0511 (14) | 0.0004 (9) | 0.0132 (10) | −0.0151 (10) |
| C25 | 0.0375 (12) | 0.0548 (15) | 0.0420 (12) | 0.0000 (10) | 0.0217 (10) | −0.0030 (11) |
| C26 | 0.0415 (12) | 0.0412 (12) | 0.0392 (11) | −0.0023 (10) | 0.0221 (10) | 0.0042 (9) |
| C31 | 0.0287 (10) | 0.0344 (11) | 0.0251 (9) | 0.0009 (8) | 0.0128 (8) | −0.0020 (8) |
| C32 | 0.0363 (11) | 0.0330 (11) | 0.0255 (9) | −0.0020 (8) | 0.0118 (8) | −0.0023 (8) |
| C33 | 0.0369 (11) | 0.0404 (12) | 0.0256 (9) | −0.0004 (9) | 0.0132 (8) | 0.0004 (8) |
| C34 | 0.0273 (10) | 0.0460 (12) | 0.0244 (9) | 0.0007 (9) | 0.0094 (8) | −0.0073 (9) |
| C35 | 0.0317 (11) | 0.0355 (11) | 0.0376 (11) | −0.0023 (9) | 0.0151 (9) | −0.0097 (9) |
| C36 | 0.0332 (11) | 0.0354 (11) | 0.0355 (11) | −0.0003 (9) | 0.0150 (9) | −0.0007 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| F1—C14 | 1.356 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.385 (3) |
| F2—C24 | 1.362 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| O1—N3 | 1.230 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| O2—N3 | 1.232 (3) | C21—C22 | 1.378 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.289 (2) | C21—C26 | 1.388 (3) |
| N1—N2 | 1.379 (2) | C22—C23 | 1.389 (4) |
| N2—C31 | 1.369 (2) | C22—H22 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C3 | 1.474 (3) | C23—C24 | 1.364 (4) |
| N3—C34 | 1.448 (3) | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C11 | 1.463 (3) | C24—C25 | 1.360 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.504 (3) | C25—C26 | 1.383 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.548 (3) | C25—H25 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C26—H26 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C31—C32 | 1.407 (3) |
| C3—C21 | 1.514 (3) | C31—C36 | 1.411 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 1.0000 | C32—C33 | 1.376 (3) |
| C11—C16 | 1.392 (3) | C32—H32 | 0.9500 |
| C11—C12 | 1.398 (3) | C33—C34 | 1.387 (3) |
| C12—C13 | 1.378 (3) | C33—H33 | 0.9500 |
| C12—H12 | 0.9500 | C34—C35 | 1.381 (3) |
| C13—C14 | 1.380 (4) | C35—C36 | 1.379 (3) |
| C13—H13 | 0.9500 | C35—H35 | 0.9500 |
| C14—C15 | 1.367 (4) | C36—H36 | 0.9500 |
| C1—N1—N2 | 108.68 (16) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| C31—N2—N1 | 118.70 (16) | C11—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| C31—N2—C3 | 127.24 (18) | C22—C21—C26 | 118.4 (2) |
| N1—N2—C3 | 113.53 (16) | C22—C21—C3 | 119.40 (18) |
| O1—N3—O2 | 123.6 (2) | C26—C21—C3 | 122.22 (19) |
| O1—N3—C34 | 118.9 (2) | C21—C22—C23 | 121.1 (2) |
| O2—N3—C34 | 117.5 (2) | C21—C22—H22 | 119.4 |
| N1—C1—C11 | 120.38 (18) | C23—C22—H22 | 119.4 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 113.68 (18) | C24—C23—C22 | 118.4 (2) |
| C11—C1—C2 | 125.93 (17) | C24—C23—H23 | 120.8 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 102.70 (16) | C22—C23—H23 | 120.8 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 111.2 | C25—C24—F2 | 119.2 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 111.2 | C25—C24—C23 | 122.5 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 111.2 | F2—C24—C23 | 118.3 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2B | 111.2 | C24—C25—C26 | 118.6 (2) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 109.1 | C24—C25—H25 | 120.7 |
| N2—C3—C21 | 113.17 (16) | C26—C25—H25 | 120.7 |
| N2—C3—C2 | 101.21 (16) | C25—C26—C21 | 121.0 (2) |
| C21—C3—C2 | 113.27 (18) | C25—C26—H26 | 119.5 |
| N2—C3—H3 | 109.6 | C21—C26—H26 | 119.5 |
| C21—C3—H3 | 109.6 | N2—C31—C32 | 120.28 (18) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 109.6 | N2—C31—C36 | 120.42 (19) |
| C16—C11—C12 | 118.82 (19) | C32—C31—C36 | 119.30 (19) |
| C16—C11—C1 | 121.22 (19) | C33—C32—C31 | 120.3 (2) |
| C12—C11—C1 | 119.97 (18) | C33—C32—H32 | 119.9 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 120.7 (2) | C31—C32—H32 | 119.9 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.7 | C32—C33—C34 | 119.5 (2) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.7 | C32—C33—H33 | 120.3 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 118.5 (2) | C34—C33—H33 | 120.3 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 120.7 | C35—C34—C33 | 121.33 (19) |
| C14—C13—H13 | 120.7 | C35—C34—N3 | 119.5 (2) |
| F1—C14—C15 | 119.3 (2) | C33—C34—N3 | 119.2 (2) |
| F1—C14—C13 | 118.1 (2) | C36—C35—C34 | 120.0 (2) |
| C15—C14—C13 | 122.6 (2) | C36—C35—H35 | 120.0 |
| C14—C15—C16 | 118.6 (2) | C34—C35—H35 | 120.0 |
| C14—C15—H15 | 120.7 | C35—C36—C31 | 119.6 (2) |
| C16—C15—H15 | 120.7 | C35—C36—H36 | 120.2 |
| C15—C16—C11 | 120.8 (2) | C31—C36—H36 | 120.2 |
| C1—N1—N2—C31 | −174.73 (17) | C2—C3—C21—C26 | 85.0 (2) |
| C1—N1—N2—C3 | −2.4 (2) | C26—C21—C22—C23 | 0.1 (4) |
| N2—N1—C1—C11 | −179.48 (17) | C3—C21—C22—C23 | 179.1 (3) |
| N2—N1—C1—C2 | −0.7 (2) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | 0.6 (5) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 3.2 (2) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | −1.0 (4) |
| C11—C1—C2—C3 | −178.07 (19) | C22—C23—C24—F2 | 179.5 (3) |
| C31—N2—C3—C21 | −62.7 (3) | F2—C24—C25—C26 | −179.8 (2) |
| N1—N2—C3—C21 | 125.73 (19) | C23—C24—C25—C26 | 0.8 (4) |
| C31—N2—C3—C2 | 175.7 (2) | C24—C25—C26—C21 | 0.0 (4) |
| N1—N2—C3—C2 | 4.2 (2) | C22—C21—C26—C25 | −0.4 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—N2 | −4.1 (2) | C3—C21—C26—C25 | −179.3 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C21 | −125.55 (18) | N1—N2—C31—C32 | −7.3 (3) |
| N1—C1—C11—C16 | 178.05 (19) | C3—N2—C31—C32 | −178.48 (19) |
| C2—C1—C11—C16 | −0.6 (3) | N1—N2—C31—C36 | 173.54 (18) |
| N1—C1—C11—C12 | −1.8 (3) | C3—N2—C31—C36 | 2.4 (3) |
| C2—C1—C11—C12 | 179.6 (2) | N2—C31—C32—C33 | −177.13 (19) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | −0.8 (3) | C36—C31—C32—C33 | 2.0 (3) |
| C1—C11—C12—C13 | 179.1 (2) | C31—C32—C33—C34 | −0.2 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.0 (3) | C32—C33—C34—C35 | −1.2 (3) |
| C12—C13—C14—F1 | −179.0 (2) | C32—C33—C34—N3 | 178.99 (18) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.8 (4) | O1—N3—C34—C35 | −162.4 (2) |
| F1—C14—C15—C16 | 178.9 (2) | O2—N3—C34—C35 | 17.0 (3) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.9 (4) | O1—N3—C34—C33 | 17.4 (3) |
| C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.1 (3) | O2—N3—C34—C33 | −163.2 (2) |
| C12—C11—C16—C15 | 0.7 (3) | C33—C34—C35—C36 | 0.7 (3) |
| C1—C11—C16—C15 | −179.1 (2) | N3—C34—C35—C36 | −179.45 (18) |
| N2—C3—C21—C22 | 151.6 (2) | C34—C35—C36—C31 | 1.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C21—C22 | −94.0 (3) | N2—C31—C36—C35 | 176.68 (18) |
| N2—C3—C21—C26 | −29.5 (3) | C32—C31—C36—C35 | −2.4 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C12—H12···O2i | 0.95 | 2.41 | 3.305 (3) | 157 |
| C16—H16···F2ii | 0.95 | 2.55 | 3.427 (3) | 154 |
| C26—H26···F1iii | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.494 (3) | 169 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iii) x, −y−1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: IS5210).
References
- Baktır, Z., Akkurt, M., Samshuddin, S., Narayana, B. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1292–o1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2008). SADABS Bruker Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2010). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, USA.
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Etter, M. C., MacDonald, J. C. & Bernstein, J. (1990). Acta Cryst. B46, 256–262. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Jasinski, J. P., Golen, J. A., Samshuddin, S., Narayana, B. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2012). Crystals, 2, 1108–1115.
- Kumar, S., Bawa, S., Drabu, S., Kumar, R. & Gupta, H. (2009). Recent Pat. Anti-infect. Drug Discov 4, 154–163. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Samshuddin, S., Narayana, B., Sarojini, B. K., Khan, M. T. H., Yathirajan, H. S., Raj, C. G. D. & Raghavendra, R. (2012). Med. Chem. Res. 21, 2012–2022.
- Sarojini, B. K., Vidyagayatri, M., Darshanraj, C. G., Bharath, B. R. & Manjunatha, H. (2010). Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 7, 214–224.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681204370X/is5210sup1.cif
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681204370X/is5210Isup2.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681204370X/is5210Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681204370X/is5210Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report