Abstract
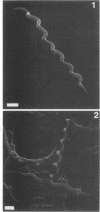
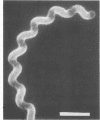
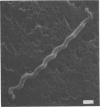
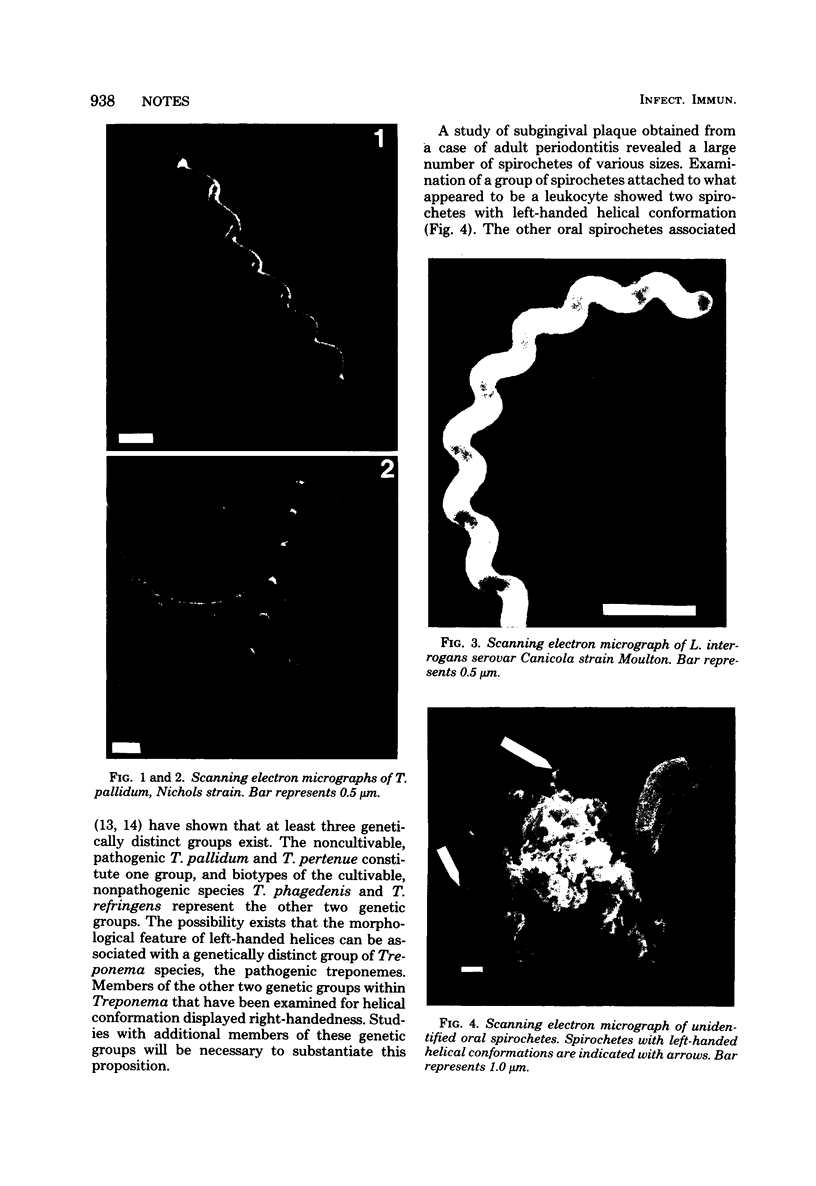
Borrelia turicatae (mouse virulent) and Treponema denticola, a small oral treponeme, formed right-handed helices as determined by scanning electron microscopy. Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain), Treponema paraluis-cuniculi, and two unidentified oral spirochetes displayed left-handed helices.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bey R. F., Johnson R. C., Fitzgerald T. J. Suppression of lymphocyte response to concanavalin A by mucopolysaccharide material from Treponema pallidum-infected rabbits. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):64–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.64-69.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carleton O., Charon N. W., Allender P., O'Brien S. Helix handedness of Leptospira interrogans as determined by scanning electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1413–1416. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1413-1416.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D. Shape of Treponema pallidum. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):943–944. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.943-944.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Cleveland P., Johnson R. C., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Scanning electron microscopy of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) attached to cultured mammalian cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1333–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1333-1344.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes N. S., Muse K. E., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Parasitism by virulent Treponema pallidum of host cell surfaces. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):174–186. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.174-186.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Harris V. G. Differentiation of pathogenic and saprophytic letospires. I. Growth at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):27–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.27-31.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayser A., Adrian M. Les spirochètes: sens de l'enroulement. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1978 Apr;129(3):351–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg N. R. Biology of the chemoheterotrophic spirilla. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):55–115. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.55-115.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao R. M., Fieldsteel A. H. Genetic relationship between Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue, two noncultivable human pathogens. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):427–429. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.427-429.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao R., Fieldsteel A. H. Genetics of Treponema: relationship between Treponema pallidum and five cultivable treponemes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):101–107. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.101-107.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEQUEIRA P. J. The morphology of Treponema pallidum. Lancet. 1956 Oct 13;271(6946):749–749. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)90959-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemper E. D., Black S. H. Morphology of freeze-etched Treponema refringens (Nichols). Arch Microbiol. 1978 Jun 26;117(3):227–238. doi: 10.1007/BF00738540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]