Abstract
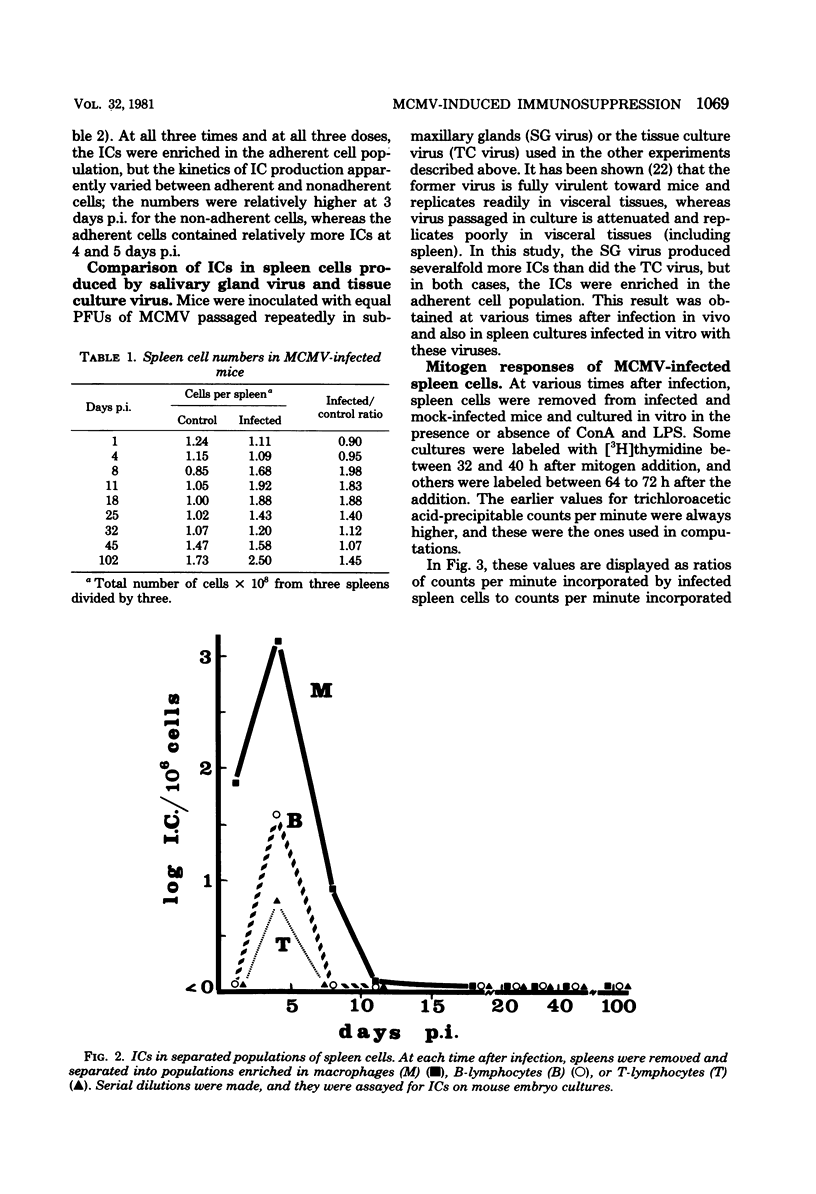
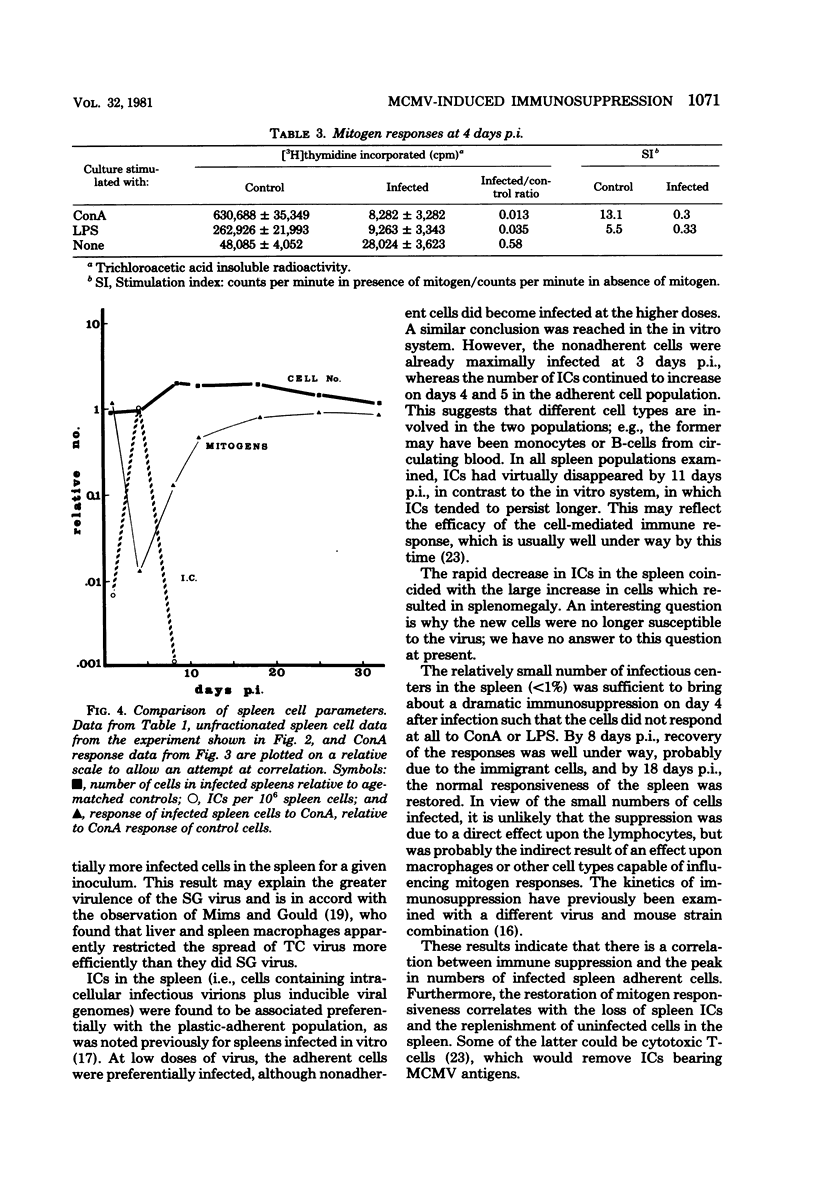
An attempt was made to correlate murine cytomegalovirus-induced immuno-suppression with the presence of virus-infected cells in the spleen. For this purpose, SWR/J mice were infected with murine cytomegalovirus, and spleens were removed periodically and assayed for the presence of infectious centers in different cell populations and for their capacity to respond to mitogens. The maximal degree of immunosuppression correlated with the peak in adherent cell infectious centers. This was followed by a rapid rise in the number of cells per spleen (splenomegaly), a more gradual return to normal responsiveness to mitogens, and a rapid disappearance of infectious centers. These results add more support to the hypothesis that murine cytomegalovirus-induced immunosuppression is caused indirectly by infection of adherent spleen cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araullo-Cruz T. P., Ho M., Armstrong J. A. Protective effect of early serum from mice after cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):840–842. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.840-842.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booss J., Wheelock E. F. Correlation of survival from murine cytomegalovirus infection with spleen cell responsiveness to Concanavallin A. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jun;149(2):443–445. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booss J., Wheelock E. F. Progressive inhibition of T-cell function preceding clinical signs of cytomegalovirus infection in mice. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):478–481. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmer J. E., Mackenzie J. S., Stanley N. F. Resistance to murine cytomegalovirus linked to the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):107–114. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee S. N., Fiala M., Weiner J., Stewart J. A., Stacey B., Warmer N. Primary cytomegalovirus and opportunistic infections. Incidence in renal transplant recipients. JAMA. 1978 Nov 24;240(22):2446–2449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. R., Overall J. C., Glasgow L. A. Synergistic effect on mortality in mice with murine cytomegalovirus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, or Candida albicans infections. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):982–989. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.982-989.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. R., Overall J. C., Jr Synergistic infection with murine cytomegalovirus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jun;137(6):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.6.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann H., Frisch-Niggemeyer W., Heinz F. Rapid diagnosis of tick-borne encephalitis by means of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. J Gen Virol. 1979 Mar;42(3):505–511. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-3-505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Mattsson D. M., Seidel M. V., Balfour H. H., Jr Cell-mediated immunity to murine cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1978 Nov;138(5):567–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Miller J., Najarian J. S. Cytomegalovirus-induced immune suppression. II. Cell-mediated immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):119–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Najarian J. S. Cytomegalovirus-induced immune suppression. I. Humoral immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):109–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B., Loh L., Misra V., Judd B., Suzuki J. Multiple interactions between murine cytomegalovirus and lymphoid cells in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jan;38(1):149–159. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B., Misra V., Mosmann T. R. Cytomegalovirus infectivity: analysis of the phenomenon of centrifugal enhancement of infectivity. Virology. 1976 Jul 1;72(1):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B. The murine cytomegalovirus as a model for the study of viral pathogenesis and persistent infections. Arch Virol. 1979;62(1):1–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01314900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey D. K., Olsen G. A., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Alteration of host defense mechanisms by murine cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):754–760. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.754-760.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey D. K., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Correlation of the suppression of mitogen responsiveness and the mixed lymphocyte reaction with the proliferative response to viral antigen of splenic lymphocytes from cytomegalovirus-infected mice. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):464–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh L., Hudson J. B. Immunosuppressive effect of murine cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):54–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.54-60.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh L., Hudson J. B. Interaction of murine cytomegalovirus with separated populations of spleen cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):853–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.853-860.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims C. A., Gould J. The role of macrophages in mice infected with murine cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Oct;41(1):143–153. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-1-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Hudson J. B. Some properties of the genome of murine cytomegalovirus (MCV). Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):135–149. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Blazkovec A. A., Walker D. L. Immunosuppression during acute murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):835–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Walker D. L. Virulence and attenuation of murine cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):228–236. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.228-236.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Manischewitz J. E., Ennis F. A. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to murine cytomegalovirus infection. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):541–543. doi: 10.1038/273541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selgrade M. K., Ahmed A., Sell K. W., Gershwin M. E., Steinberg A. D. Effect of murine cytomegalovirus on the in vitro responses of T and B cells to mitogens. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1459–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr S. E., Allison A. C. Role of T lymphocytes in recovery from murine cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):458–462. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.458-462.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



