Abstract
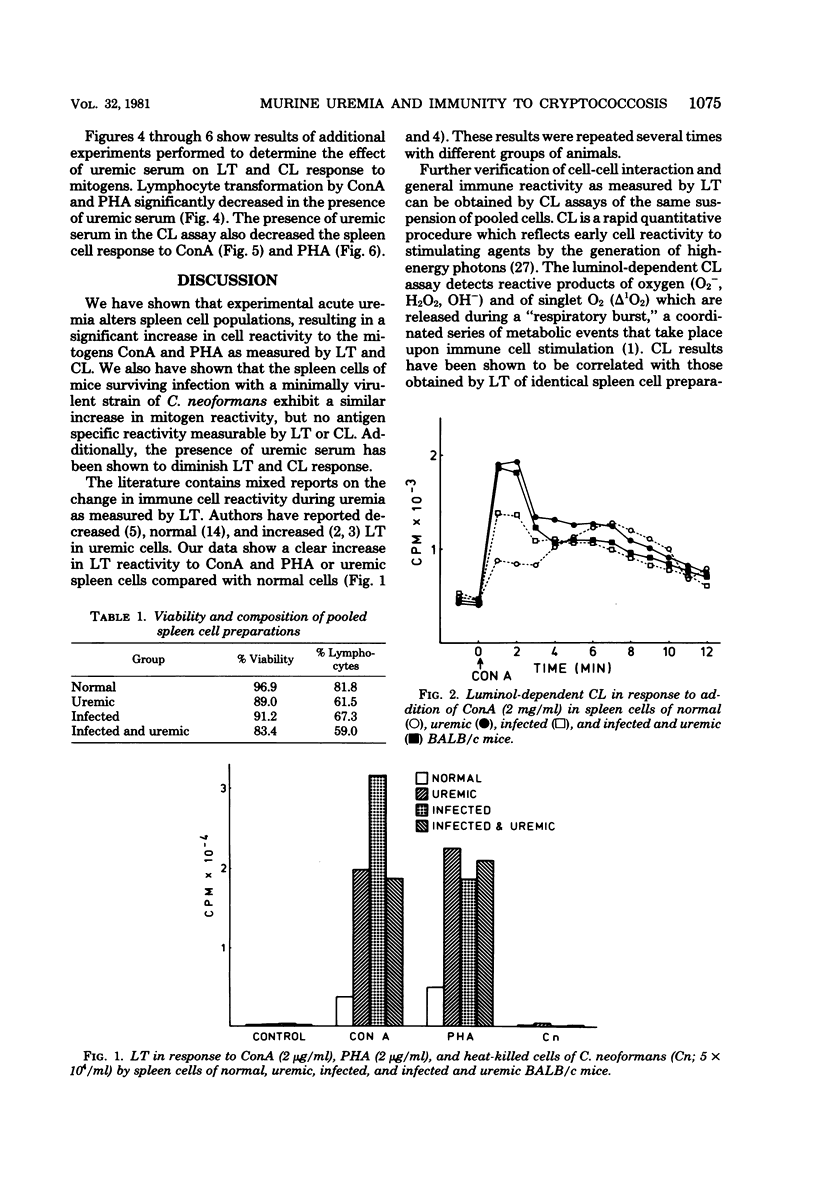
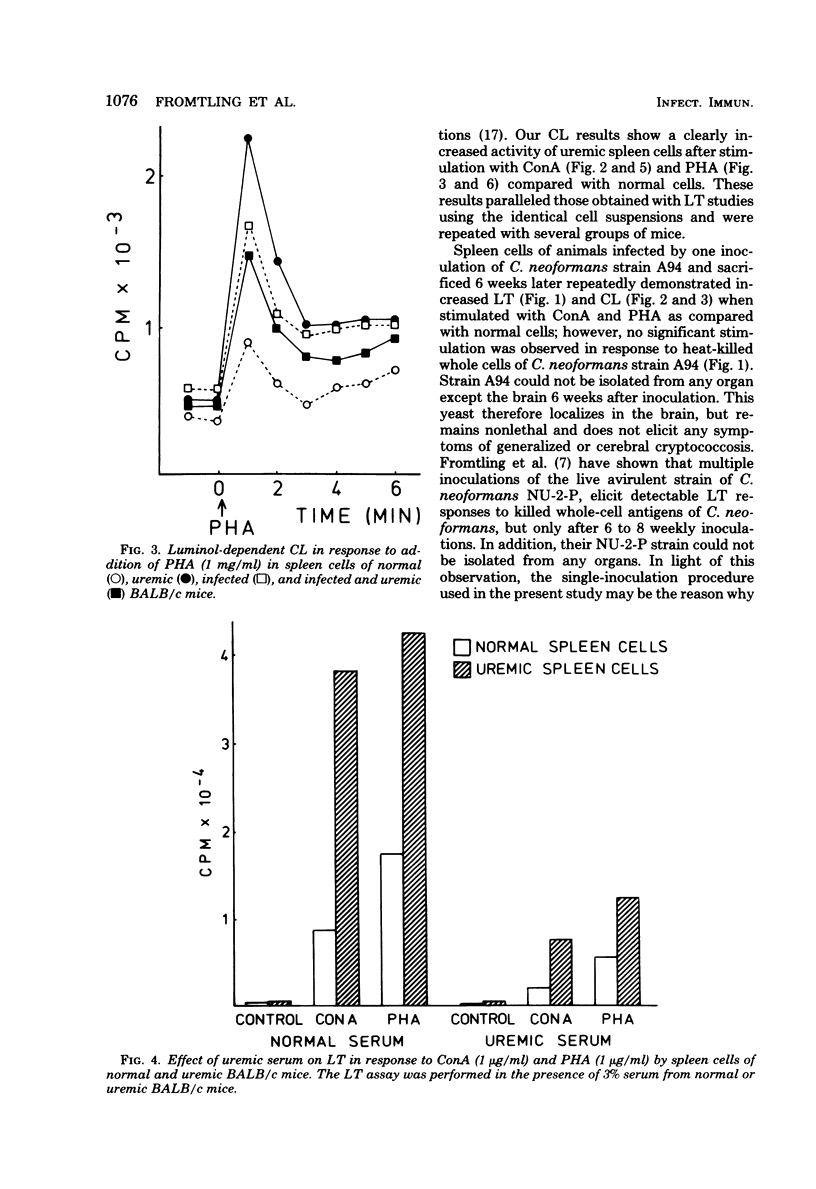
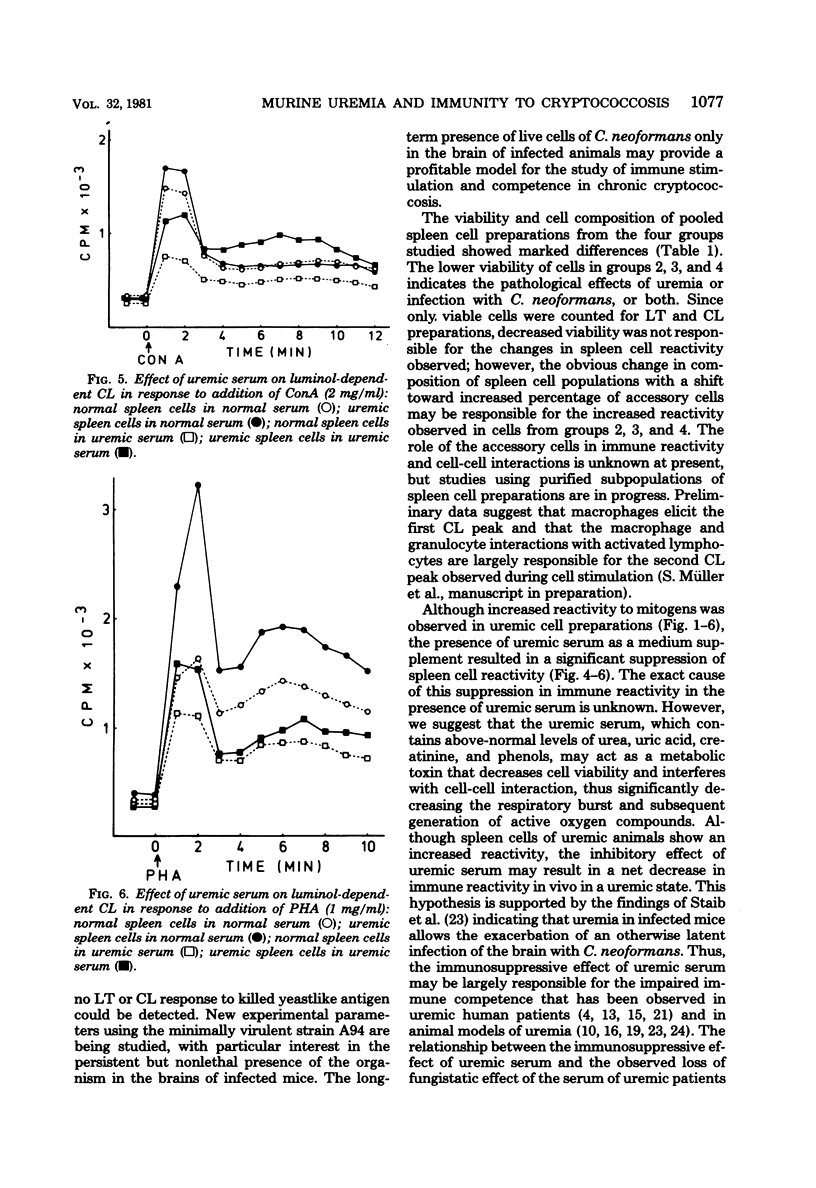
The effect of uremia on immune incompetence was studied. BALB/c mice were infected with a minimally virulent strain of Cryptococcus neoformans 6 weeks before immune assay. Uremia was induced by intramuscular injection of 0.15 ml of glycerol. Pooled spleen cells from four experimental groups (normal, uremic, infected, and infected and uremic) were assayed by lymphocyte transformation (LT) and luminol-dependent chemiluminescence (CL) 24 h after induction of uremia. A greater response to phytohemagglutinin and concanavalin A stimulation in tests of LT and CL was exhibited by uremic cells than by nonuremic cells; however, the presence of BALB/c uremic serum resulted in lower responses by both LT and CL. Infected mice showed a greater response to mitogens than did noninfected mice, but no significant stimulation in response to heat-killed whole cells of C. neoformans. Spleen cell populations of uremic mice had a lower viability and a different composition of spleen cell subpopulations than did cell preparations from nonuremic mice.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):659–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byron P. R., Mallick N. P., Taylor G. Immune potential in human uraemia. 1. Relationship of glomerular filtration rate to depression of immune potential. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Sep;29(9):765–769. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.9.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels J. C., Remmers A. R., Jr, Sarles H. E., Fish J. C., Cobb E. K., Levin W. C., Ritzmann S. E. Interpretation of nucleic acid synthesis. Studies in renal-failure lymphocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Sep;8(3):240–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhorn J., Grosse G., Staib F., Wollensak J. Intraokulare Cryptococcose. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1976 Apr;168(4):577–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elves M. W., Israëls M. C., Collinge M. An assessment of the mixed leucocyte reaction in renal failure. Lancet. 1966 Mar 26;1(7439):682–685. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91628-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromtling R. A., Blackstock R., Hall N. K., Bulmer G. S. Kinetics of lymphocyte transformation in mice immunized with viable avirulent forms of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):449–453. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.449-453.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromtling R. A., Fromtling A. M., Staib F. Auxanographic detection of experimental murine uremia with Cryptococcus neoformans. Zentralbl Bakteriol A. 1980 Nov;248(2):268–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOWLAND G., SMIDDY F. G. The effect of acute experimental uraemia on the immunological responses of the rabbit to bovine serum albumin. Br J Urol. 1962 Sep;34:274–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1962.tb09456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Alford R. H. Cell-mediated immunity in Cryptococcosis. Cell Immunol. 1974 Oct;14(1):12–21. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUME D. M., MERRILL J. P., MILLER B. F., THORN G. W. Experiences with renal homotransplantation in the human: report of nine cases. J Clin Invest. 1955 Feb;34(2):327–382. doi: 10.1172/JCI103085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRKPATRICK C. H., WILSON W. E., TALMAGE D. W. IMMUNOLOGIC STUDIES IN HUMAN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION. I. OBSERVATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF SUPPRESSED CUTANEOUS REACTIVITY IN UREMIA. J Exp Med. 1964 May 1;119:727–742. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.5.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroe D. J., Vazquez J. J. Hypersensitivity reactions in experimental uremia. Am J Pathol. 1967 Mar;50(3):401–419. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff S. C., Bennett J. E. Abnormalities in cell-mediated immunity in patients with Cryptococcus neoformans infection. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Jun;55(6):430–441. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staib F. Das Serum-Reststickstoff-Auxanogramm (mit Spross- und Schimmelpilzen) Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1964 Nov;194(3):379–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staib F., Grosse G., Schoon A., Berger R., Abel T. Cryptococcose, Zufallsdiagnose post mortem--neue Gesichtspunkte zur Pathogenese. Mykosen. 1977 Sep;20(9):319–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staib F., Mishra S. K., Grosse G., Abel T. Ocular cryptococcosis - experimental and clinical observations. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1977;237(2-3):378–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staib F., Mishra S. K. Selective involvement of the brain in experimental murine cryptococcosis. I. Microbiological observations. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975 Jul;232(2-3):355–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel G., Wilson D. R., Arce M. L., Oken D. E. Glycerol induced hemoglobinuric acute renal failure in the rat. II. The experimental model, predisposing factors, and pathophysiologic features. Nephron. 1967;4(5):276–297. doi: 10.1159/000179588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter J. E., Atchison R. W. Epidemiological and immunological studies of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.82-87.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrogemann K., Weidemann M. J., Ketelsen U. P., Wekerle H., Fischer H. Chemiluminescence and immune cell activation. II. Enhancement of concanavalin A-induced chemiluminescence following in vitro preincubation of rat thymocytes; dependency on macrophage-lymphocyte interaction. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Jan;10(1):36–40. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrogemann K., Weidemann M. J., Peskar B. A., Staudinger H., Rietschel E. T., Fischer H. Chemiluminescence and immune cell activation. I. Early activation of rat thymocytes can be monitored by chemiluminescence measurements. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Oct;8(10):749–752. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830081014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



