Abstract
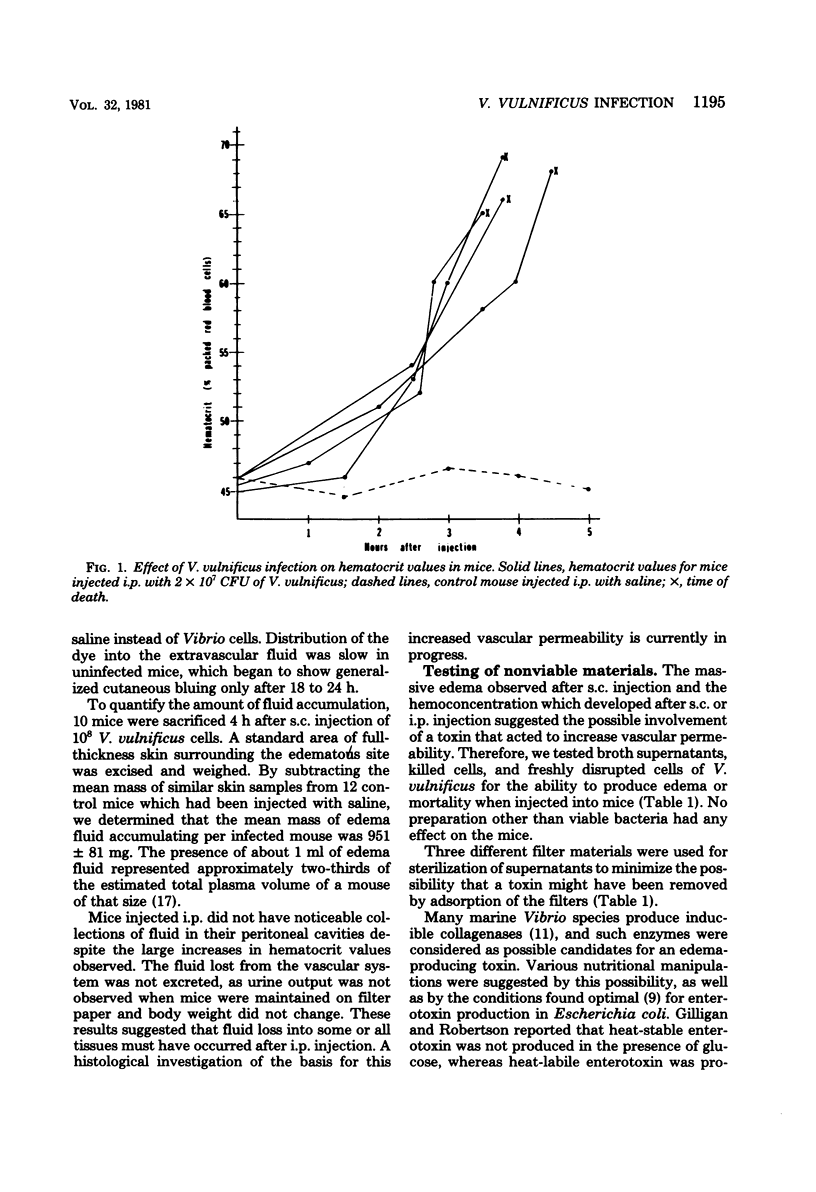
Vibrio vulnificus (lactose-positive Vibrio), a recently recognized pathogenic marine species, produced extreme hemoconcentration and death within 3 to 6 h after subcutaneous or intraperitoneal injection of 10(8) viable cells into mice; hemotocrit values approached 70% (normal, 45%). About 1 ml of edema fluid accumulated at the site of each subcutaneous injection, and locally increased vascular permeability was demonstrated by a skin bluing assay, using Evans blue dye. A corresponding fluid accumulation did not occur in the peritoneal cavity after an intraperitoneal injection. Filter-sterilized supernatants of cultures grown under a variety of conditions did not produce local edema or lethality, nor did whole Vibrio cells killed by a variety of methods or disrupted by sonic oscillation. Edema fluids collected from infected mice and sterilized by filtration had no effect when they were injected subcutaneously or intraperitoneally into mice. Inocula of 10(9) viable cells of V. vulnificus contained within a diffusion chamber implanted subcutaneously did not produce skin bluing, edema, or lethality; Vibrio cells remained viable and virulent within these chambers for at least 2 weeks. These experiments suggested that vascular permeability changes in V. vulnificus infections may not be attributable to a diffusible toxin and may require direct contact between host cells and viable Vibrio cells.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arko R. J. Implantation and use of a subcutaneous culture chamber in laboratory animals. Lab Anim Sci. 1973 Feb;23(1):105–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L., Reichelt J. L. Taxonomy of marine bacteria: Beneckea parahaemolytica and Beneckea alginolytica. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1144–1155. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1144-1155.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. C. More pathogenic vibrios. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 4;300(1):39–41. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901043000111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drzeniek R., Scharmann W., Balke E. Neuraminidase and N-acetylneuraminate pyruvate-lyase of Pasteurella multocida. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):357–368. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd Vibrio ("Beneckea") vulnificus, the bacterium associated with sepsis, septicaemia, and the sea. Lancet. 1979 Oct 27;2(8148):903–903. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92715-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan P. H., Robertson D. C. Nutritional requirements for synthesis of heat-labile enterotoxin by enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):99–107. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.99-107.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Baker C. N., Thornsberry C. Halophilic Vibrio species isolated from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Apr;3(4):425–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.4.425-431.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel J. R., Dreisbach J. H., Ziegler H. B. Collagenolytic activity of some marine bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):145–151. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.145-151.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W., Sandefur P. D. Evidence of a role for permeability factors in the pathogenesis of salmonellosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):197–209. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole M. D., Oliver J. D. Experimental pathogenicity and mortality in ligated ileal loop studies of the newly reported halophilic lactose-positive Vibrio sp. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):126–129. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.126-129.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt J. L., Baumann P., Baumann L. Study of genetic relationships among marine species of the genera Beneckea and Photobacterium by means of in vitro DNA/DNA hybridization. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Oct 11;110(1):101–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00416975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland F. P. Leg gangrene and endotoxin shock due to vibrio parahaemolyticus--an infection acquired in New England coastal waters. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jun 4;282(23):1306–1306. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197006042822306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISH L., FURTH J., STOREY R. H. Direct determinations of plasma, cell, and organ-blood volumes in normal and hypervolemic mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Jul;74(3):644–648. doi: 10.3181/00379727-74-18003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



