Abstract
Recordings of blood velocity profiles and their behavior in the time domain in some peripheral human vessels (carotid arteries and limb vessels) are reported.
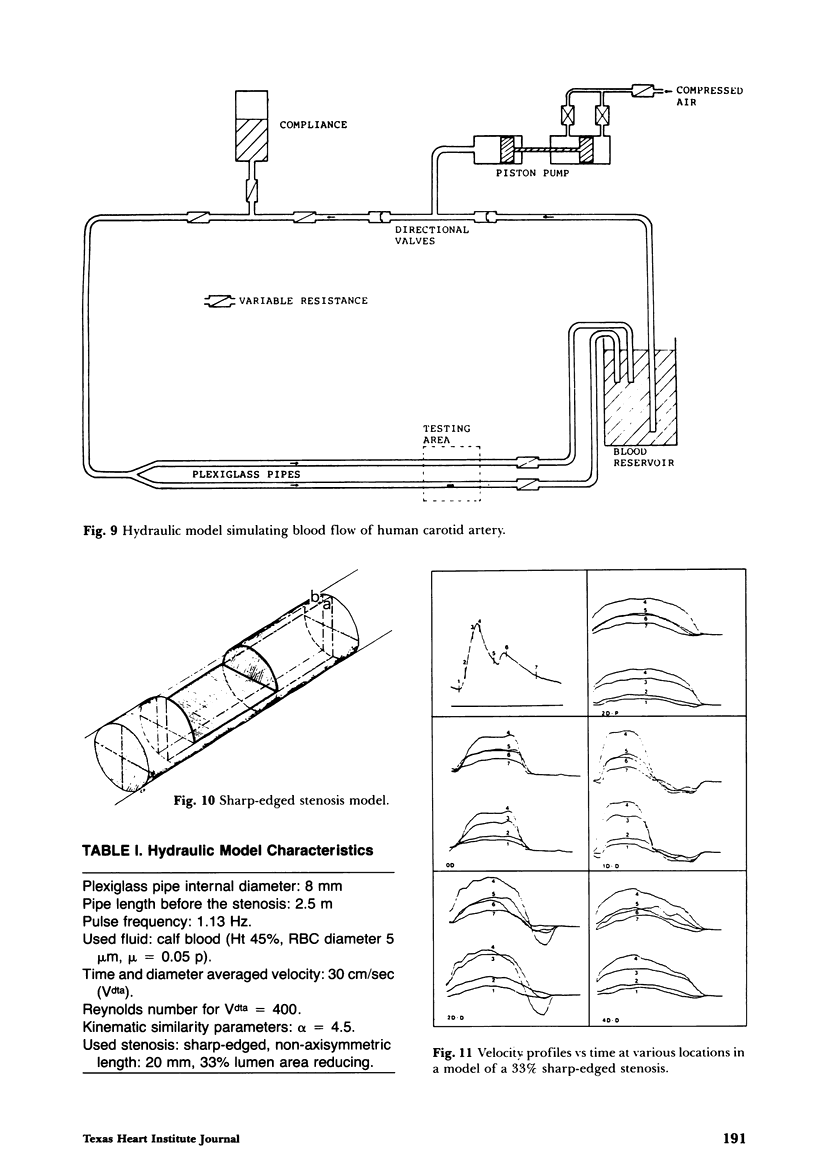
Measurements have been obtained with a pulsed ultrasonic instrument based on the analysis of the cross-correlation function of blood-diffused echoes. The alterations of blood velocity profiles and of the velocity in the time domain, induced by known stenosis, have been studied in vitro as a function of the distance between stenosis and measuring point, and the position of the sample volume along the diameter. These studies may be useful for a better comprehension of blood velocity measurements made with ultrasound equipment for clinical noninvasive diagnostic purposes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atabek H. B., Ling S. C., Patel D. J. Analysis of coronary flow fields in thoracotomized dogs. Circ Res. 1975 Dec;37(6):752–761. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.6.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berguer R., Hwang N. H. Critical arterial stenosis: a theoretical and experimental solution. Ann Surg. 1974 Jul;180(1):39–50. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197407000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear W. M., Jr, Phillips D. J., Thiele B. L., Hirsch J. H., Chikos P. M., Marinelli M. R., Ward K. J., Strandness D. E., Jr Detection of carotid occlusive disease by ultrasonic imaging and pulsed Doppler spectrum analysis. Surgery. 1979 Nov;86(5):698–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C., Schultz D. L. Velocity distribution in aortic flow. Cardiovasc Res. 1973 Sep;7(5):601–613. doi: 10.1093/cvr/7.5.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. S., Taenzer J. C., Ramsey S. D., Jr, Holzemer J. F., Suarez J. R., Marich K. W., Evans T. C., Sandok B. A., Greenleaf J. F. A real-time ultrasonic imaging system for carotid arteriography. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1977;3(2-3):129–142. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(77)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALE J. F., McDONALD D. A., WOMERSLEY J. R. Velocity profiles of oscillating arterial flow, with some calculations of viscous drag and the Reynolds numbers. J Physiol. 1955 Jun 28;128(3):629–640. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson R. W., 2nd, Berry S. M., Katocs A. S., Jr, O'Donnell J. A., Jamil Z., Savitsky J. P. Comparison of pulsed Doppler and real-time B-mode echo arteriography for noninvasive imaging of the extracranial carotid arteries. Surgery. 1980 Mar;87(3):286–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H. M., Meier W. E., Anliker M., Kumpe D. A. Noninvasive measurement of velocity profiles and blood flow in the common carotid artery by pulsed Doppler ultrasound. Stroke. 1976 Jul-Aug;7(4):370–377. doi: 10.1161/01.str.7.4.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. S., Hall A. D. Importance of emboli from carotid bifurcation in pathogenesis of cerebral ischemic attacks. Arch Surg. 1970 Dec;101(6):708–passim. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1970.01340300064012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozersky D. J., Hokanson D. E., Baker D. W., Sumner D. S., Strandness D. E., Jr Ultrasonic arteriography. Arch Surg. 1971 Dec;103(6):663–667. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1971.01350120023003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M. P., Reid J. M., Davis D. L., Paulson P. S. Cervical carotid imaging with a continuous-wave Doppler flowmeter. Stroke. 1974 Mar-Apr;5(2):145–154. doi: 10.1161/01.str.5.2.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wissler R. W., Vesselinovitch D. Studies of regression of advanced atherosclerosis in experimental animals and man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;275:363–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb43368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. F., Tsai F. Y. Flow characteristics in models of arterial stenoses. II. Unsteady flow. J Biomech. 1973 Sep;6(5):547–559. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(73)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


