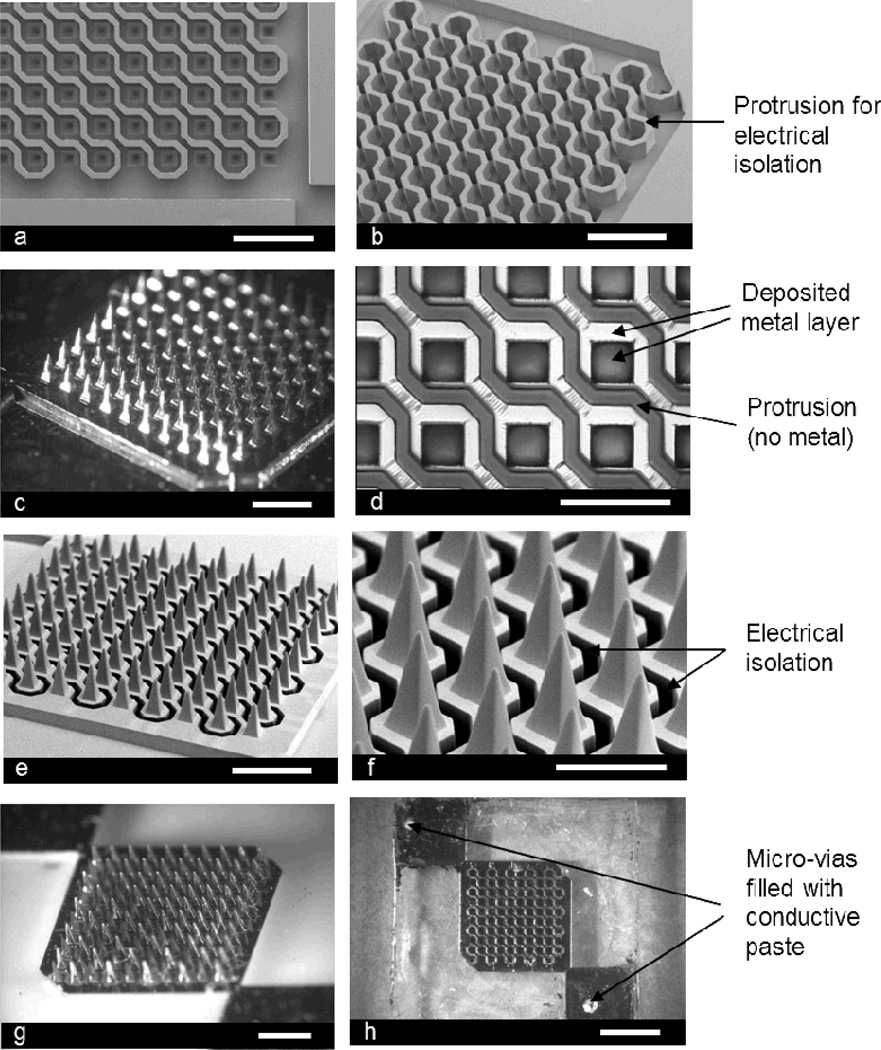
Figure 1.
Fabricated microneedle array for electroporation: (a) top view of the fabricated SU-8 mold (scale bar: 1 mm), (b) angled view of the SU-8 mold showing the protrusions (scale bar: 1 mm), (c) Ni master structure formed by electroplating (scale bar: 1 mm), (d) further magnified view of the PDMS mold replicated from the Ni master after selective removal of metal layer on the protrusions (scale bar: 500 µm), (e) angled view of the microneedle array, which is formed from the PDMS mold by micromolding, before electroplating (scale bar: 1 mm), (f) further magnified view of the microneedle array showing electrical isolation (dark region) (scale bar: 500 µm), (g) Ni plated microneedle array (scale bar: 1 mm), and (h) backside of the device showing micro-vias filled with conductive polymer (scale bar: 2 mm).