Abstract
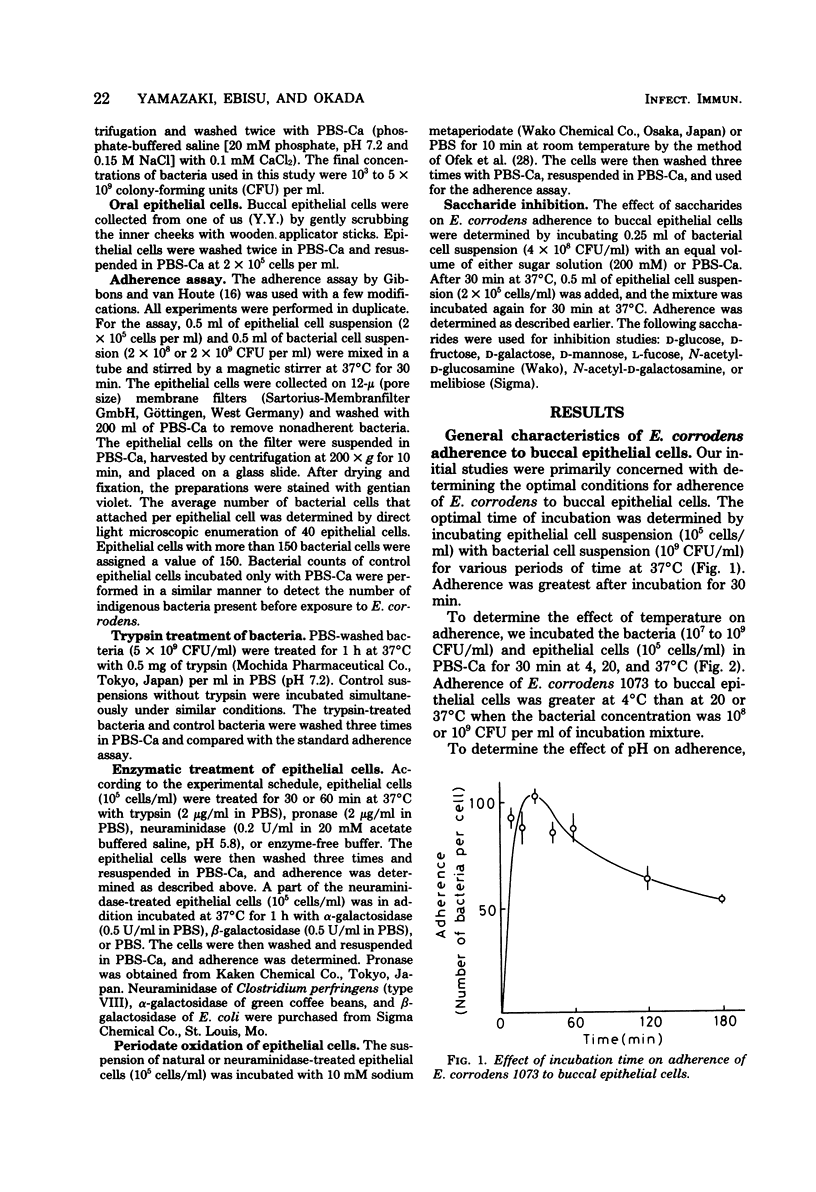
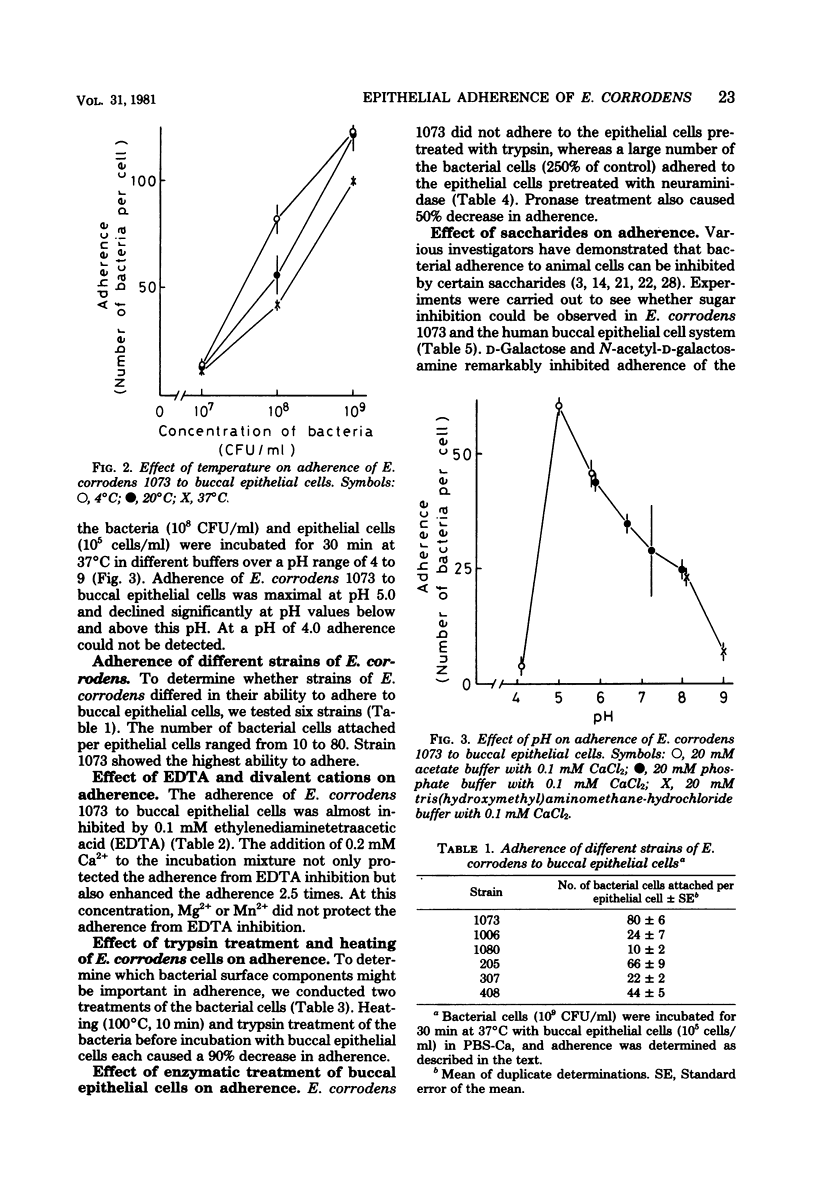
The mechanism of Eikenella corrodens adherence to human buccal epithelial cells in vitro was studied. Initial experiments to determine the optimal conditions for adherence of E. corrodens to buccal epithelial cells showed that adherence was dependent on time, temperature, bacterial concentration, and pH. Different strains of E. corrodens varied in their ability to adhere, and strain 1073 showed the greatest ability in adherence. Strain 1073 was selected for studies of adherence mechanisms. Trypsin treatment or heating (100 degrees C, 10 min) of the bacterial cells abolished their capacity to adhere to buccal epithelial cells. Treatment of buccal epithelial cells with trypsin also abolished adherence of E. corrodens 1073, whereas neuraminidase treatment of buccal epithelial cells enhanced the adherence. The adherence was inhibited by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and restored by adding Ca2+. The adherence was remarkably inhibited by sugars containing D-galactose and n-acetyl-D-galactosamine. Treatment of neuraminidase-treated epithelial cells with sodium metaperiodate or alpha- and beta-galactosidase did not decrease the adherence. These data suggest that adherence of E. corrodens 1073 to human buccal epithelial cells may require the interaction of lectin-like proteins on the bacterial surface with galactose-like receptors on the surface of epithelial cells.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkan M., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Adherence pharyngeal and skin strains of group A streptococci to human skin and oral epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):555–557. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.555-557.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit Z., Ofek I., Goldman R., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Mannose residues on phagocytes as receptors for the attachment of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhi. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):455–460. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartelt M. A., Duncan J. L. Adherence of group A streptococci to human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):200–208. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.200-208.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Ofek I. Epithelial cell binding of group A streptococci by lipoteichoic acid on fimbriae denuded of M protein. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):759–771. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello A. H., Cisar J. O., Kolenbrander P. E., Gabriel O. Neuraminidase-dependent hamagglutination of human erythrocytes by human strains of Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):563–572. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.563-572.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. P., Anderson E. S., Campbell I. Fimbriae and adhesive properties in Salmonellae. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):107–138. doi: 10.1002/path.1700920113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebisu S., Garegg P. J., Iversen T., Goldstein I. J. An attempt to raise antibodies against 2-O-alpha-D-galactopyranose, the disaccharide unit of collagen. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2137–2143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Fillery E. D., Chan K. H., Grove D. A. Sialidase-enhanced lectin-like mechanism for Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):335–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.335-343.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. M protein-associated adherence of Streptococcus pyogenes to epithelial surfaces: prerequisite for virulence. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):826–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.826-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. Parameters affecting the adherence and tissue tropisms of Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):85–91. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.85-91.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshdat Y., Ofek I., Yashouv-Gan Y., Sharon N., Mirelman D. Isolation of a mannose-specific lectin from Escherichia coli and its role in the adherence of the bacteria to epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 29;85(4):1551–1559. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91179-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fader R. C., Avots-Avotins A. E., Davis C. P. Evidence for pili-mediated adherence of Klebsiella pneumoniae to rat bladder epithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):729–737. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.729-737.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabridge M. G., Taylor-Robinson D. Interaction of Mycoplasma pneumoniae with human lung fibroblasts: role of receptor sites. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):455–459. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.455-459.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Selective bacterial adherence to oral epithelial surfaces and its role as an ecological determinant. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):567–573. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.567-573.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes C. E., Goldstein I. J. Equilibrium dialysis and cell binding studies on Bandeiraea simplicifolia lectin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6837–6840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving J. T., Socransky S. S., Tanner A. C. Histological changes in experimental periodontal disease in rats monoinfected with gram-negative organisms. J Periodontal Res. 1978 Jul;13(4):326–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1978.tb00187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Behling U. H., Lai C. H., Listgarten M., Socransky S., Nowotny A. Role of bacterial products in periodontitis: immune response in gnotobiotic rats monoinfected with Eikenella corrodens. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):246–253. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.246-253.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: nature of the interaction with isolated rabbit brush border membranes and human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):240–245. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.240-245.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Listgarten M. A., Johnson D., Nowotny A., Tanner A. C., Socransky S. S. Histopathology of periodontal disease in gnotobiotic rats monoinfected with Eikenella corrodens. J Periodontal Res. 1978 Mar;13(2):134–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1978.tb00162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loontiens F. G., Van Wauwe J. P., De Gussem R., De Bruyne C. K. Binding of para-substituted phenyl glycosides to concanavalin A. Carbohydr Res. 1973 Sep;30(1):51–62. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)82172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomerie J. Z. Factors affecting virulence in Escherichia coli urinary tract infections. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137(5):645–647. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.5.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Moon H. W., Isaacson R. E. Colonization of porcine intestine by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: selection of piliated forms in vivo, adhesion of piliated forms to epithelial cells in vitro, and incidence of a pilus antigen among porcine enteropathogenic E. coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):344–352. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.344-352.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Jefferson W., Campbell G. L. Cell membrane-binding properties of group A streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):990–1003. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F. Virulence factors of the bacterial cell surface. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137(5):630–633. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.5.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C. Ecology, physiology, and genetics of fimbriae and pili. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:79–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Gotschlich E. C. Type I Escherichia coli pili: characterization of binding to monkey kidney cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1182–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Gibbons R. J. Attachment of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subsp. asaccharolyticus to oral surfaces and its possible role in colonization of the mouth and of periodontal pockets. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):254–264. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.254-264.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. The predominant cultivable microflora of advanced periodontitis. Scand J Dent Res. 1977 Jan-Feb;85(2):114–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1977.tb00541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S. Microbiology of periodontal disease -- present status and future considerations. J Periodontol. 1977 Sep;48(9):497–504. doi: 10.1902/jop.1977.48.9.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawaneh S. M., Ayoub E. M., Baer H., Cruz A. C., Spellacy W. N. Factors influencing adherence of group B streptococci to human vaginal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):441–447. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.441-447.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



