Abstract
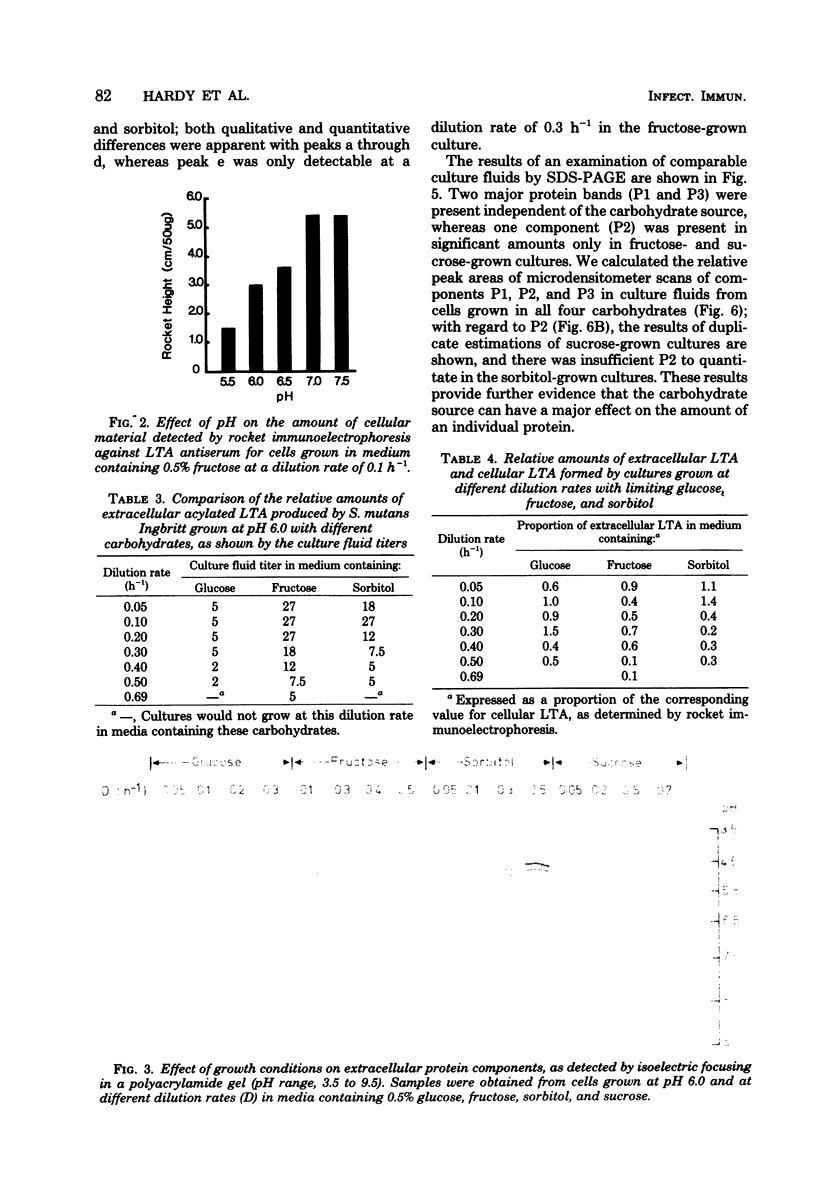
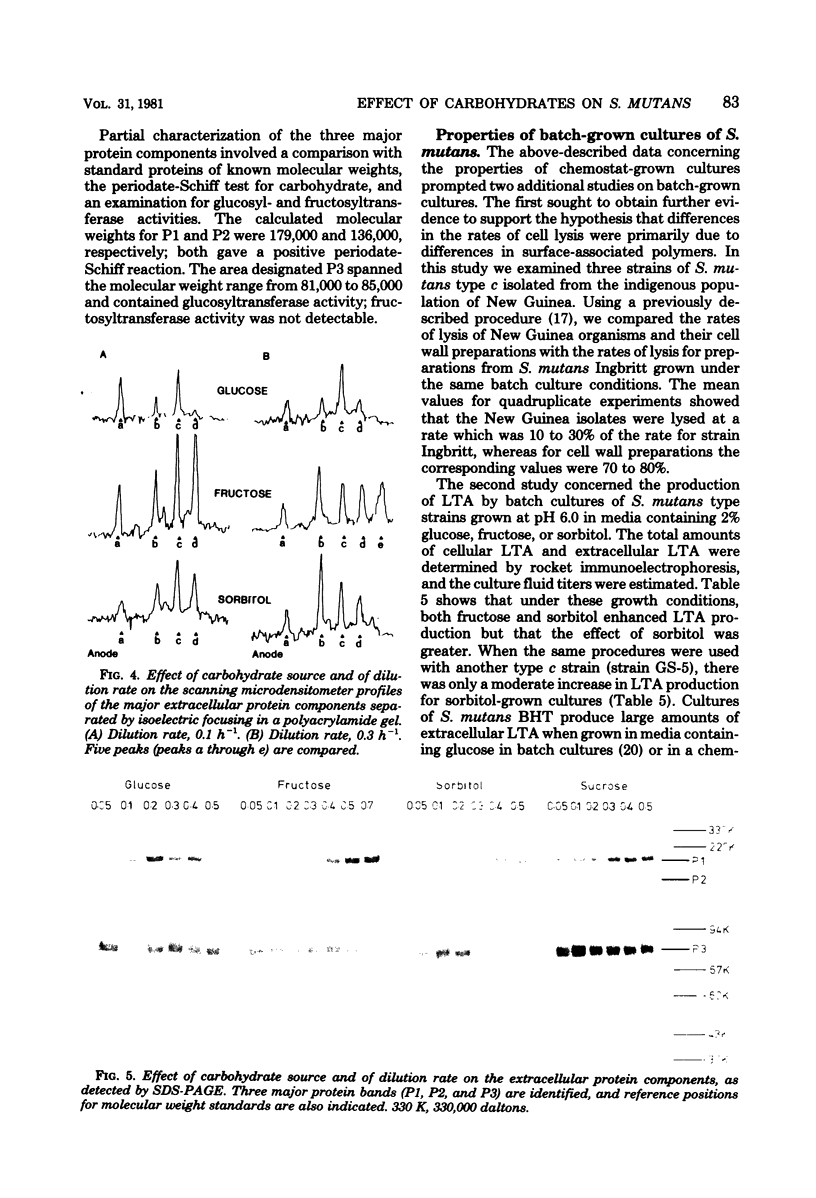
Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt was grown in a chemostat at destined dilution rates in either 0.5% fructose or 0.5% sorbitol and at destined pH values in 0.5% fructose. The yield of cells was affected by the carbohydrate source, as well as by the pH, with the lowest yield being at pH 5.5 in 0.5% fructose. Fructose-grown cells showed greater susceptibility to lysis by a muramidase than the corresponding glucose-grown cells, but there were no marked differences in the lytic susceptibilities of the corresponding cell wall preparations or in the serological reactivities of wall lysates with antiserum to S. mutans Ingbritt. The greatest amounts of cellular lipoteichoic acid were obtained at high dilution rates in both fructose and sorbitol, as well as at high pH values in fructose. The greatest amounts of extracellular lipoteichoic acid were found at low dilution rates, as estimated by rocket immunoelectrophoresis and also by hemagglutination. Three major extracellular protein components were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and the effects of growth conditions on these components were determined. Results for batch-grown cultures showed that there was genotypic variation in the susceptibility of cells to lysis by a muramidase. The enhancement of lipoteichoic acid production by fructose and sorbitol in batch cultures was not identical in representative strains of S. mutans serotype c, nor was the effect of fructose found uniformly in representative strains of the different S. mutans serotypes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. T., Patterson C. E. Ethanol production and alcohol dehydrogenase activity in Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Jan;18(1):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. K., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Extractability of cell wall polysaccharide from lactobacilli and streptococci by autoclaving and by dilue acid. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):842–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.842-851.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C., Baird J. K., Hunter J. R., Longyear V. M. Variations in surface polymers of Streptococcus mutans. J Dent Res. 1976 Apr;55(Spec No):C42–C49. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500323011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C., Phipps P. J., Hamilton I. R. Effect of growth rate and glucose concentration on the activity of the phosphoenolpyruvate phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt grown in continuous culture. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):224–231. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.224-231.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B., Newbrun E. Extracellular glucosyltransferase activity of an HS strain of Streptococcus mutans. Helv Odontol Acta. 1969 Oct;13(2):84–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Torii M., Kotani S., Masuda N., Ooshima T., Yokogawa K., Kawata S. Lysis of Streptococcus mutans cells with mutanolysin, a lytic enzyme prepared from a culture liquor of Streptomyces globisporus 1829. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(7):543–549. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton I. R., Phipps P. J., Ellwood D. C. Effect of growth rate and glucose concentration on the biochemical properties of Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt in continuous culture. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.861-869.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M., Machardy S. M., Sheppard A. J., Woods N. C. Evidence for an immunological relationship between Streptococcus mutans and human cardiac tissue. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):576–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.576-588.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques N. A., Hardy L., Campbell L. K., Knox K. W., Evans J. D., Wicken A. J. Effect of carbohydrate source and growth conditions on the production of lipoteichoic acid by Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1079–1087. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1079-1087.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques N. A., Hardy L., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Effect of growth conditions on the formation of extracellular lipoteichoic acid by Streptococcus mutans BHT. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):75–84. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.75-84.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Jacques N. A., Campbell L. K., Wicken A. J., Hurst S. F., Bleiweis A. S. Phenotypic stability of the cell wall of Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt grown under various conditions. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1071–1078. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1071-1078.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham J. L., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J., Hewett M. J. Formation of extracellular lipoteichoic acid by oral streptococci and lactobacilli. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):378–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.378-386.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Staat R. H., Rosan B., Taylor K. G., Doyle R. J. Association of protein with the cell wall of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):118–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.118-126.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., Reeves M. W. Regulation of the synthesis of M protein by sugars, Todd Hewitt broth, and horse serum, in growing cells of Streptococcus pyogenes. Microbios. 1978;21(85-86):185–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Bergmeier L. A., Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans: purification and properties of a double antigen and its protease-resistant component. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.486-493.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Distribution of cross-reactive antigens A and B in Streptococcus mutans and other oral streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jun;118(2):383–388. doi: 10.1099/00221287-118-2-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Use of triton X-100 to overcome the inhibition of fructosyltransferase by SDS. Anal Biochem. 1979 Aug;97(1):173–175. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):109–115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rølla G., Oppermann R. V., Bowen W. H., Ciardi J. E., Knox K. W. High amounts of lipoteichoic acid in sucrose-induced plaque in vivo. Caries Res. 1980;14(4):235–238. doi: 10.1159/000260459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slee A. M., Tanzer J. M. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase activity in Streptococcus mutans NCTC 10449. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):821–828. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.821-828.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Martin E. J., Wittenberger C. L. Characterization of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):865–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.865-868.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staat R. H., Langley S. D., Doyle R. J. Streptococcus mutans adherence: presumptive evidence for protein-mediated attachment followed by glucan-dependent cellular accumulation. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):675–681. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.675-681.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergren G., Freedman M. Comparative study of two variants of the mouth Streptococcus sanguis with different colonial morphologies and abilities to adhere. Arch Oral Biol. 1979;24(9):667–672. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(79)90116-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




