Abstract
Intravenous injection of a small dose of lipopolysaccharide 24 h before infection with Listeria monocytogenes enhanced the resistance of mice to this organism. This protective effect of lipopolysaccharide related to the ability of nonimmune macrophages to inhibit bacterial proliferation in livers and spleens. Surprisingly, lipopolysaccharide-treated mice exhibited inferior acquired immunity, as measured by adoptive transfer of immunity to normal mice, delayed-type hypersensitivity to Listeria antigens, and uptake of tritiated thymidine by lymphocytes in the spleen. These results support the view that lipopolysaccharide stimulates a highly effective anti-Listeria immunity via the macrophage component, despite interference with the lymphocyte component.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AL-ASKARI S., ZWEIMAN B., LAWRENCE H. S., THOMAS L. THE EFFECT OF ENDOTOXIN ON SKIN HOMOGRAFTS IN RABBITS. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:742–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., SEBESTYEN M. M. Effect of bacterial endotoxins on the reticuloendothelial system. Fed Proc. 1957 Sep;16(3):860–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Waller R. Activated macrophages in congenitally athymic "nude mice" and in lethally irradiate mice. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):844–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
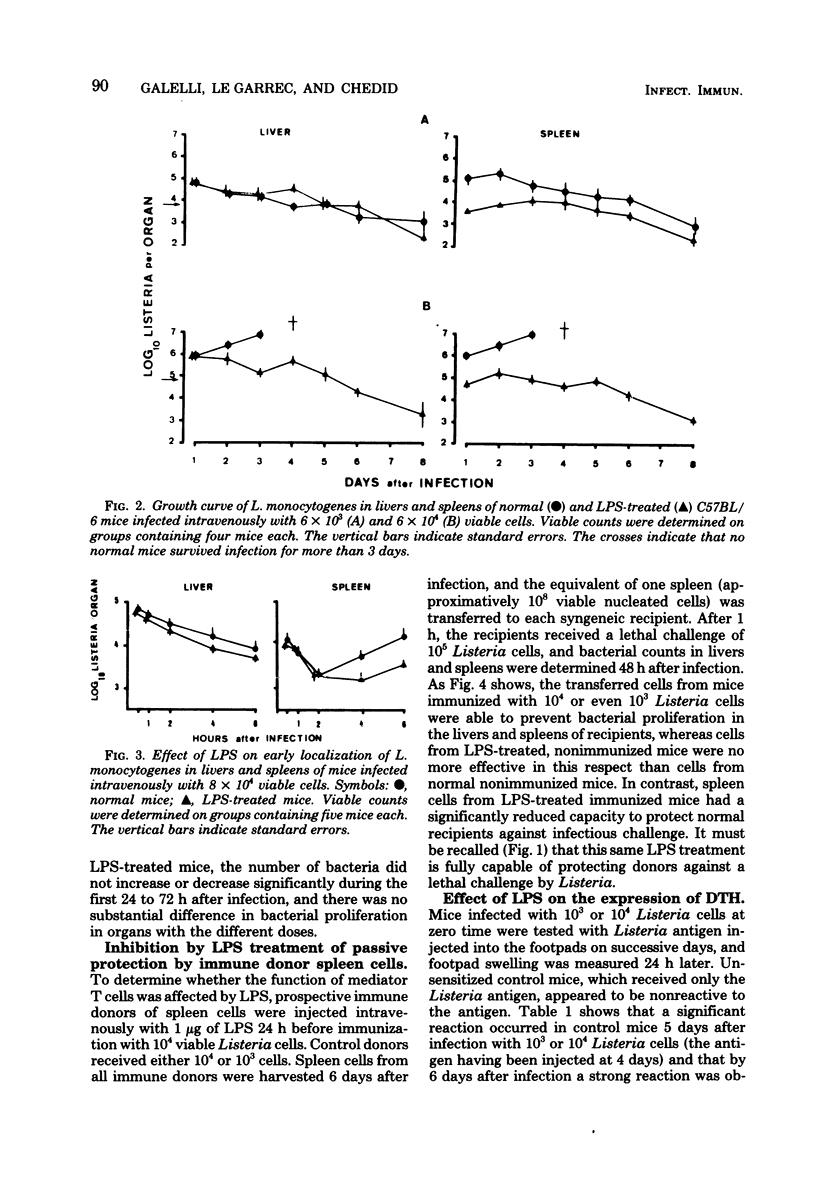
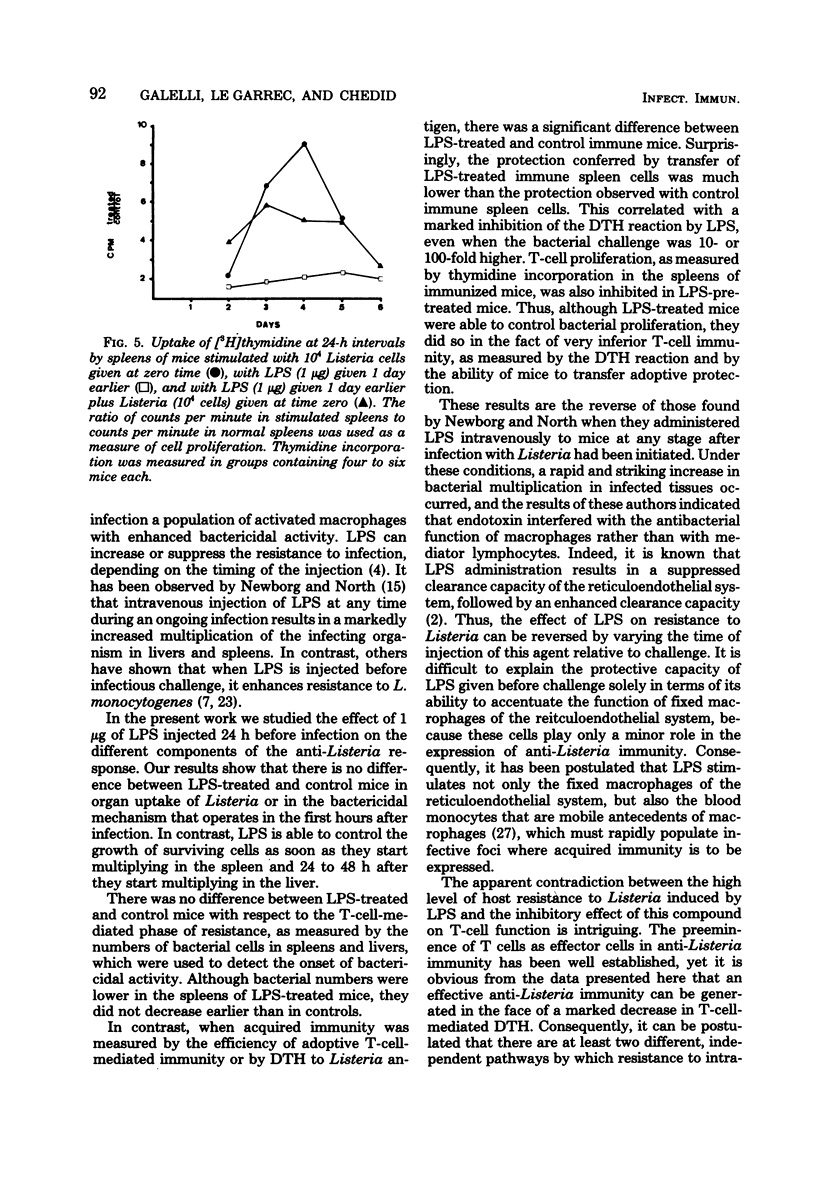
- Cluff L. E. Effects of endotoxins on susceptibility to infections. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):205–215. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerling P., Finger H., Bockemühl J. Listeria monocytogenes infection in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):437–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.437-439.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerling P., Finger H., Hof H. Cell-mediated resistance to infection with Listeria monocytogenes in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):382–385. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.382-385.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauve R. M., Delaunay A. Résistance cellulaire à l'infection bactérienne. 3. Modifications de la résistance de souris NCS à l'infection par Listeria monocytogenes après injection d'endotoxine. Effets comparés d'une injection d'endotoxine et d'une immunisation active sur l'aspect morphologique et la résistance cellulaire à l'infection des macrophages de souris NCS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Mar;110(3 Suppl):95–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzl R. E., McMaster P. D. The primary immune response in mice. I. The enhancement and suppression of hemolysin production by a bacterial endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1968 Jun 1;127(6):1087–1107. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.6.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING N. R. The attachment of proteins to aldehyde-tanned cells. Br J Haematol. 1961 Jul;7:299–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1961.tb00340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrange P. H., Mackaness G. B., Miller T. E., Pardon P. Effects of bacterial lipopolysaccharide on the induction and expression of cell-mediated immunity. I. Depression of the afferent arc. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):442–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newborg M. F., North R. J. On the mechanism of T cell-independent anti-Listeria resistance in nude mice. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):571–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newborg M. F., North R. J. Suppressive effect of bacterial endotoxin on the expression of cell-mediated anti-Listeria immunity. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):667–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.667-672.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Cellular kinetics associated with the development of acquired cellular resistance. J Exp Med. 1969 Aug 1;130(2):299–314. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Cellular mediators of anti-Listeria immunity as an enlarged population of short lived, replicating T cells. Kinetics of their production. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):342–355. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The action of cortisone acetate on cell-mediated immunity to infection. Suppression of host cell proliferation and alteration of cellular composition of infective foci. J Exp Med. 1971 Dec 1;134(6):1485–1500. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.6.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The action of cortisone acetate on cell-mediated immunity to infection: histogenesis of the lymphoid cell response and selective elimination of committed lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Mar;3(3):501–515. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90255-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The mitotic potential of fixed phagocytes in the liver as revealed during the development of cellular immunity. J Exp Med. 1969 Aug 1;130(2):315–326. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARANT M., BOYER F., CHEDID L. AUGMENTATION DE LA R'ESISTANCE AUX INFECTIONS CONS'ECUTIVE 'A UNE INJECTION D'ENDOTOXINE. MISE EN 'EVIDENCE DU M'ECANISME PAR L'ASSOCIATION DE SULFAMIDE. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 1;260:2630–2633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parant M. A., Parant F. J., Chedid L. A. Enhancement of resistance to infections by endotoxin-induced serum factor from Mycobacterium bovis BCG-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):654–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.654-659.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson U. Lipopolysaccharide-induced suppression of the primary immune response to a thymus-dependent antigen. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):789–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skopińska E. Some effects of Escherichia coli endotoxin on the graft-versus-host reaction in mice. Transplantation. 1972 Oct;14(4):432–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Jacobs D. M. Modulation of immune response by bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS): cellular basis of stimulatory and inhibitory effects of LPS on the in vitro IgM antibody response to a T-dependent antigen. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2347–2351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C., Nowotny A. Effect of endotoxin on tumor resistance in mice. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):95–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.95-100.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Blanden R. V. Macrophage activation in mice lacking thymus-derived (T) cells. Experientia. 1975 May 15;31(5):591–593. doi: 10.1007/BF01932477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Cohn Z. A. The origin and kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):415–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


