Abstract
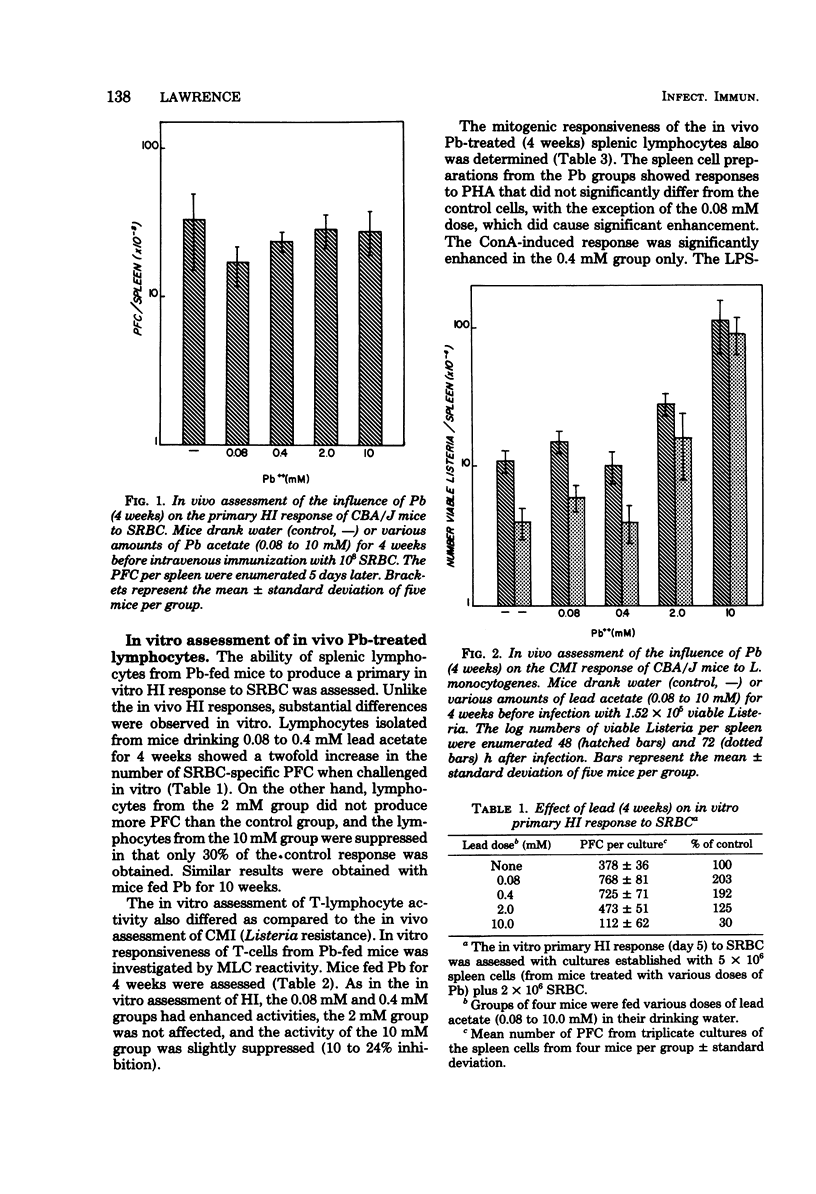
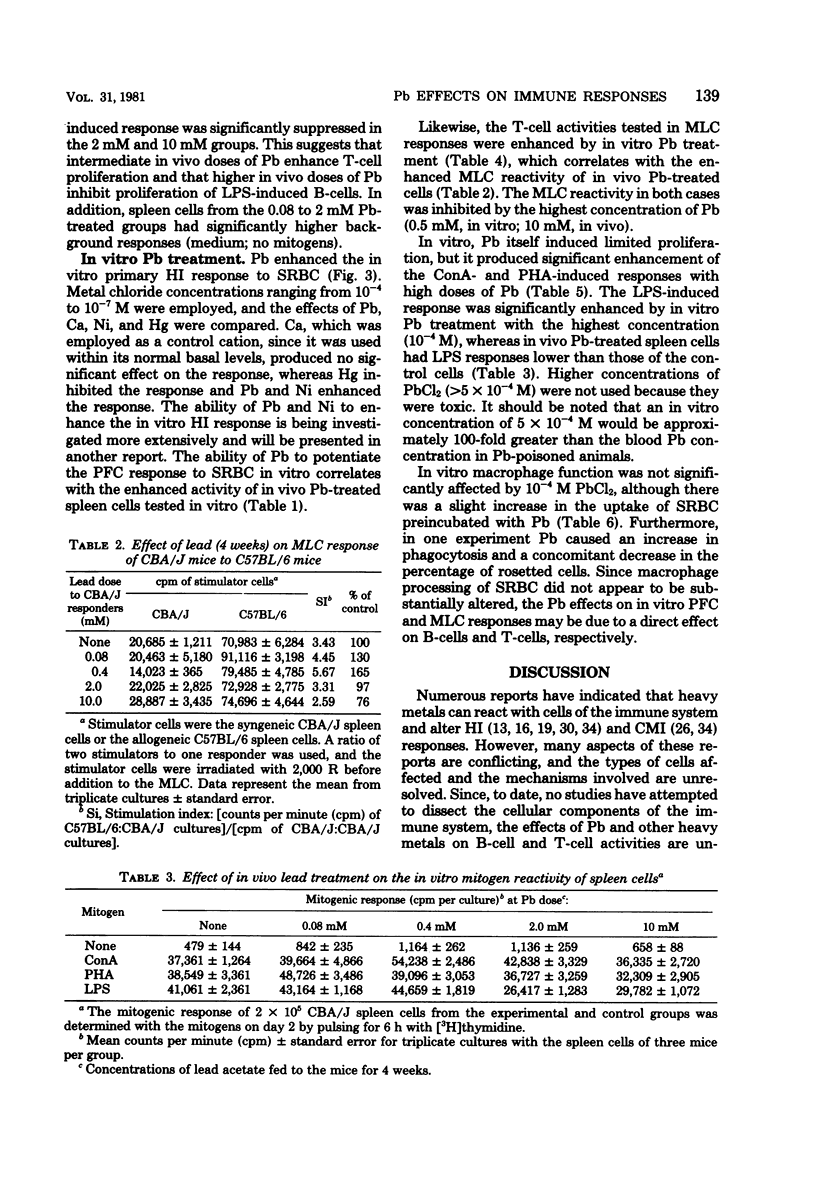
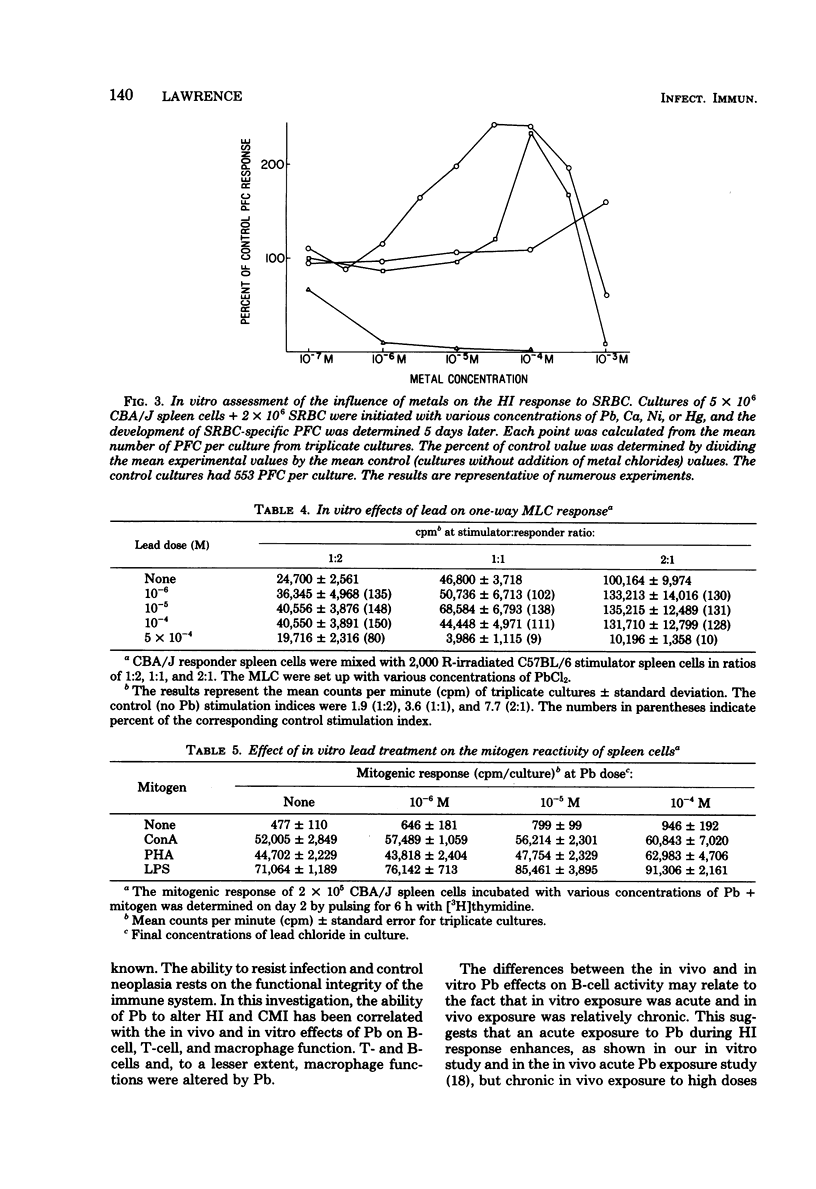
The humoral and cell-mediated immune responses of murine lymphocytes exposed to lead in vivo and in vitro were investigated. In vivo Pb was administered via the drinking water (0 to 10 mM) for 1 to 10 weeks. In vivo exposure of the mice to Pb did not alter significantly their plaque-forming cell response to sheep erythrocytes; however, their susceptibility to Listeria infection was reduced significantly with Pb dosages of greater than 0.4 mM. Although the in vivo plaque-forming cell responses did not appear to be altered, in vitro assessment of the reactivity of these in vivo Pb-exposed lymphocytes indicated that intermediate doses enhanced, but a high dose (10 mM) was suppressive. The 10 mM in vivo Pb dose suppressed the in vitro plaque-forming cell response, the mixed-lymphocyte culture response, and lipopolysaccharide-induced proliferation, but it did not affect concanavalin A- or phytohemagglutinin-induced proliferation. Interestingly, in vitro Pb exposure (10(-6) to 10(-4) M) of murine spleen cells caused an enhancement of most activities even though these in vitro concentrations of Pb were slightly above the in vivo concentrations. Direct in vitro Pb effects on the lymphocytes could be measured, and Pb consistently enhanced humoral and cell-mediated immunity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanden R. V., Lefford M. J., Mackaness G. B. The host response to Calmette-Guérin bacillus infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1079–1107. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T-lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. I. The generation of functionally distinct T-cell subclasses is a differentiative process independent of antigen. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1376–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. A., Hoffmann E. O., Luzio NR D. i. Influence of lead and cadmium on the susceptibility of rats to bacterial challenge. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Dec;150(3):741–747. doi: 10.3181/00379727-150-39117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. A., Marconi E. A., Di Luzio N. R. Lead, cadmium, endotoxin interaction: effect on mortality and hepatic function. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1974 May;28(2):292–302. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(74)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filkins J. P., Buchanan B. J. Effects of lead acetate on sensitivity to shock, intravascular carbon and endotoxin clearances, and hepatic endotoxin detoxification. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Feb;142(2):471–475. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowles R. E., Fajardo I. M., Leibowitch J. L., David J. R. The enhancement of macrophage bacteriostasis by products of activated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):952–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gainer J. H. Effects of heavy metals and of deficiency of zinc on mortality rates in mice infected with encephalomyocarditis virus. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jun;38(6):869–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gainer J. H. Lead aggravates viral disease and represses the antiviral activity of interferon inducers. Environ Health Perspect. 1974 May;7:113–119. doi: 10.1289/ehp.747113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub E. S., Mishell R. I., Weigle W. O., Dutton R. W. A modification of the hemolytic plaque assay for use with protein antigens. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):133–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyer R. A. Lead toxicity: a problem in environmental pathology. Am J Pathol. 1971 Jul;64(1):167–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Janossy G. Elicitation of selective T and B lymphocyte responses by cell surface binding ligands. Transplant Rev. 1972;11:87–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemphill F. E., Kaeberle M. L., Buck W. B. Lead suppression of mouse resistance to Salmonella typhimurium. Science. 1971 Jun 4;172(3987):1031–1032. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3987.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann E. O., Trejo R. A., Di Luzio N. R., Lamberty J. Ultrastructural alterations of liver and spleen following acute lead administration in rats. Exp Mol Pathol. 1972 Oct;17(2):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(72)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K., Nordin A. A. Plaque Formation in Agar by Single Antibody-Producing Cells. Science. 1963 Apr 26;140(3565):405–405. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3565.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller L. D., Brauner J. A. Decreased b-lymphocyte response after exposure to lead and cadmium. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;42(3):621–624. doi: 10.1016/s0041-008x(77)80050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller L. D., Exon J. H., Roan J. G. Humoral antibody response in mice after single dose exposure to lead or cadmium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Feb;151(2):339–342. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller L. D. Immunosuppression produced by lead, cadmium, and mercury. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Nov;34(11):1457–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller L. D., Kovacic S. Decreased antibody formation in mice exposed to lead. Nature. 1974 Jul 12;250(462):148–150. doi: 10.1038/250148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller L. D., Roan J. G. Effects of lead and cadmium on mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1977 Jan;21(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. A., Eastman A., Weigle W. O. Murine T-cell preparations: radiosensitivity of helper activity. Cell Immunol. 1978 Mar 1;36(1):97–114. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The monocyte in cellular immunity. Semin Hematol. 1970 Apr;7(2):172–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani B. Different roles of IgG and complement receptors in phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):15–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Mond J. J., Goldings E. A. The ontogeny of thymic independent antibody responses in vitro in normal mice and mice with an X-linked B cell defect. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):1874–1878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Karnovsky M. L., David J. R. Alterations of macrophage functions by mediators from lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1356–1376. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Importance of thymus-derived lymphocytes in cell-mediated immunity to infection. Cell Immunol. 1973 Apr;7(1):166–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell R. F., Lawrence D. A. Differential effects of concanavalin A and phytohemagglutinin on murine immunity. Suppression and enhancement of cell-mediated immunity. Cell Immunol. 1977 Jun 1;31(1):142–154. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selye H., Tuchweber B., Bertók L. Effect of lead acetate on the susceptibility of rats to bacterial endotoxins. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):884–890. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.884-890.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyberth H. W., Schmidt-Gayk H., Hackenthal E. Toxicity, clearance and distribution of endotoxin in mice as influenced by actinomycin D, cycloheximide, -amanitin and lead acetate. Toxicon. 1972 Aug;10(5):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(72)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. B., Sheagren J. N. Cellular immunity in vitro. I. Immunologically mediated enhancement of macrophage bactericidal capacity. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1377–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trejo R. A., Di Luzio N. R., Loose L. D., Hoffman E. Reticuloendothelial and hepatic functional alterations following lead acetate administration. Exp Mol Pathol. 1972 Oct;17(2):145–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(72)90064-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


