Abstract
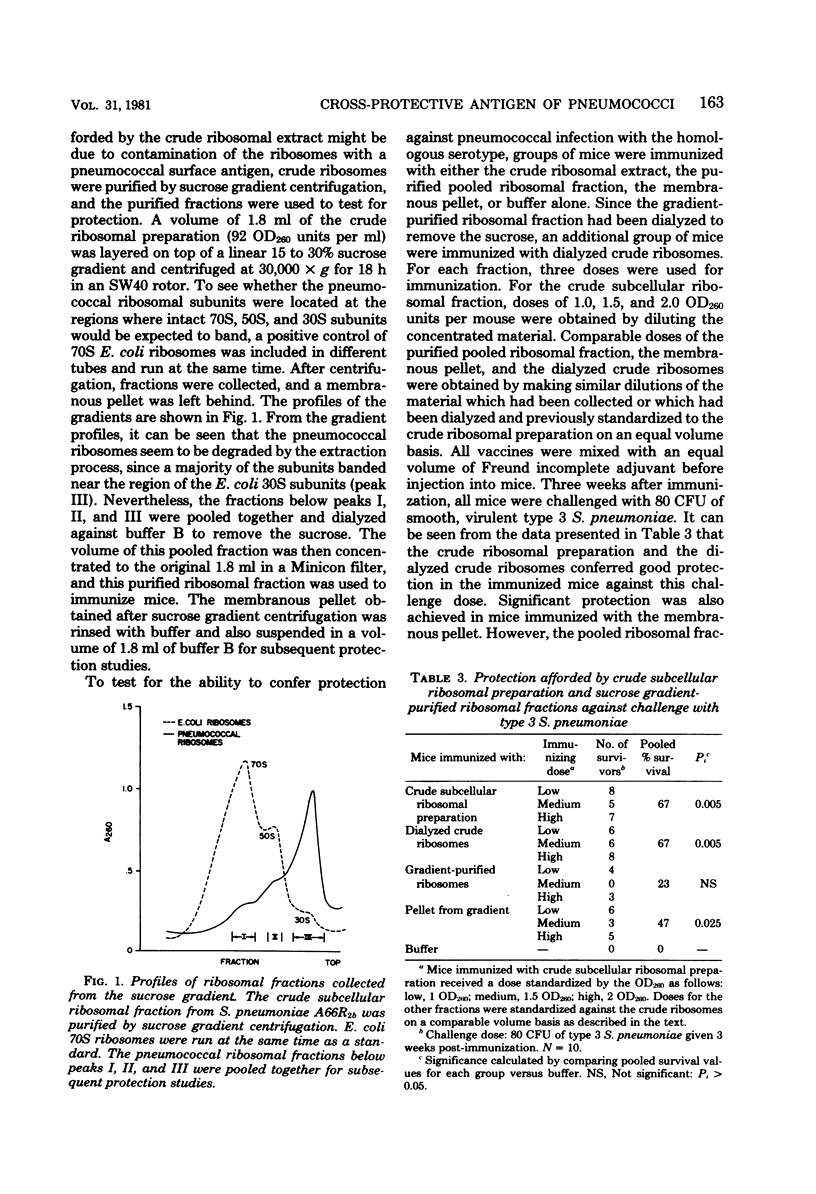
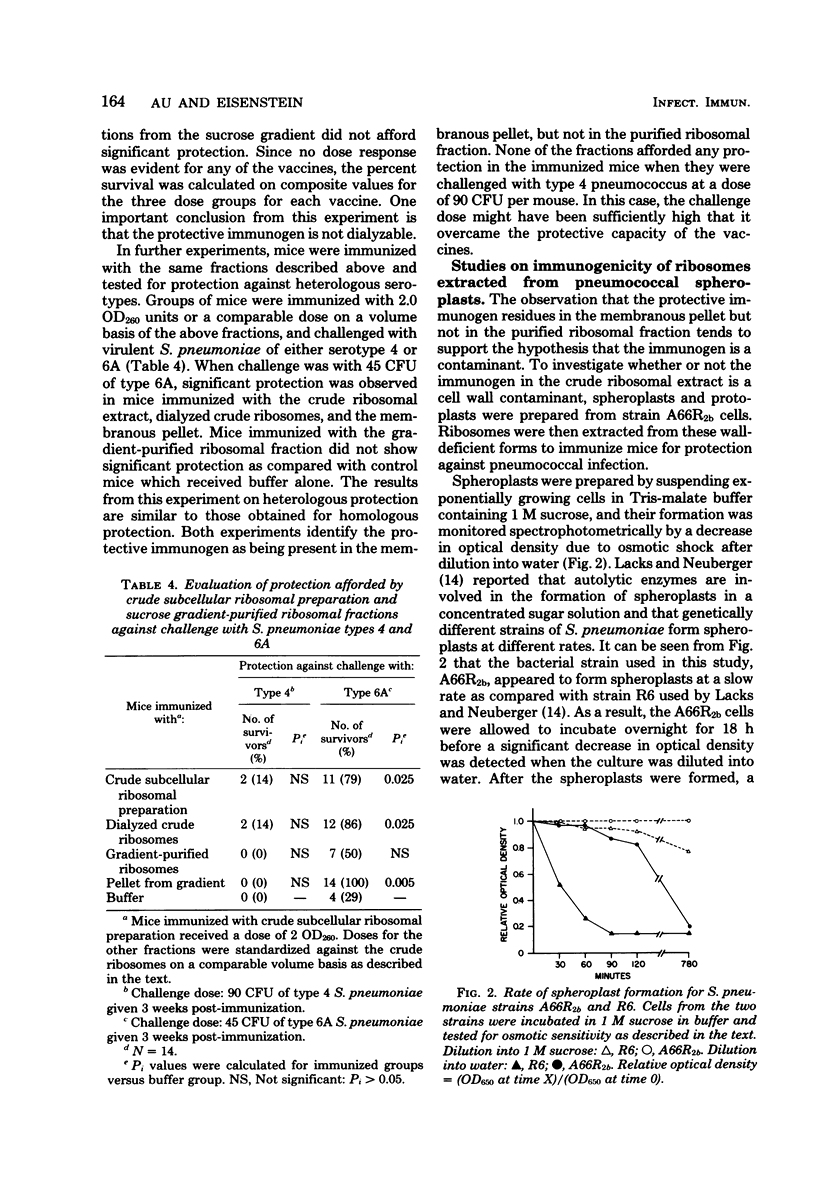
Studies have been carried out to investigate the nature of the antigen present in subcellular extracts of a rough strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae A662b which has been shown to confer protection in mice against challenge with smooth, virulent organisms of the homologous and heterologous serotypes. The finding that whole, heat-killed cells were also capable of immunizing mice against challenge with organisms of heterologous serotypes suggests that the immunogen is present on the surface of the rough pneumococcal cell. Ribosomes purified by sucrose gradient centrifugation were not protective, but material recovered in the pellet retained activity. Subcellular extracts prepared from spheroplasts with a partial absence of cell wall showed decreased protective capacity, and extracts prepared from wall-deficient protoplasts were not protective. Crude cell walls evidenced cross-serotype protection, but purified walls did not protect. These results are interpreted as suggesting that the active moiety in the subcellular vaccine is present on the surface of rough pneumococci and is either a wall antigen that must be part of a larger macromolecular complex to be immunogenic, or a substance associated with the cell wall that is present in crude, but not purified, cell wall fractions.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Au C. C., Einsenstein T. K. Evaluation of the role of the pneumococcal Forssman antigen (F-polysaccharide) in the cross-serotype protection induced by pneumococcal subcellular preparations. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):169–173. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.169-173.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun W., Nakano M. Antibody formation: stimulation by polyadenylic and polycytidylic acids. Science. 1967 Aug 18;157(3790):819–821. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3790.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles E. B., Tomasz A. Pneumococcal Forssman antigen. A choline-containing lipoteichoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6394–6397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundish D. E., Baddiley J. Pneumococcal C-substance, a ribitol teichoic acid containing choline phosphate. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):573–582. doi: 10.1042/bj1100573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara M. Immunological properties of anti-pneumococcus rabbit serum as heterophile antibodies. Jpn J Exp Med. 1968 Feb;38(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara M. The Forssman antigen of pneumococcus. Jpn J Exp Med. 1967 Dec;37(6):581–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. A., Johnson W. Immunogenicity of ribosomes from enzymatically lysed Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):424–430. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.424-430.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Integration efficiency and genetic recombination in pneumococcal transformation. Genetics. 1966 Jan;53(1):207–235. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Neuberger M. Membrane location of a deoxyribonuclease implicated in the genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1321–1329. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1321-1329.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser J. L., Tomasz A. Choline-containing teichoic acid as a structural component of pneumococcal cell wall and its role in sensitivity to lysis by an autolytic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 25;245(2):287–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., PARK J. T., THOMPSON R. E. Composition of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus: its relation to the mechanism of action of penicillin. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3263–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalla W. O., Johnson W. Immunogenicity of ribosomal vaccines isolated from group A, type 14 Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1195–1202. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1195-1202.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swendsen C. L., Johnson W. Humoral immunity to Streptococcus pneumoniae induced by a pneumococcal ribosomal protein fraction. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):345–354. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.345-354.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. C., Eisenstein T. K. Biological properties of an immunogenic pneumococcal subcellular preparation. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):750–757. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.750-757.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. C., Snyder I. S. Protection against pneumococcal infection by a ribosomal preparation. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):16–23. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.16-23.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



