Abstract
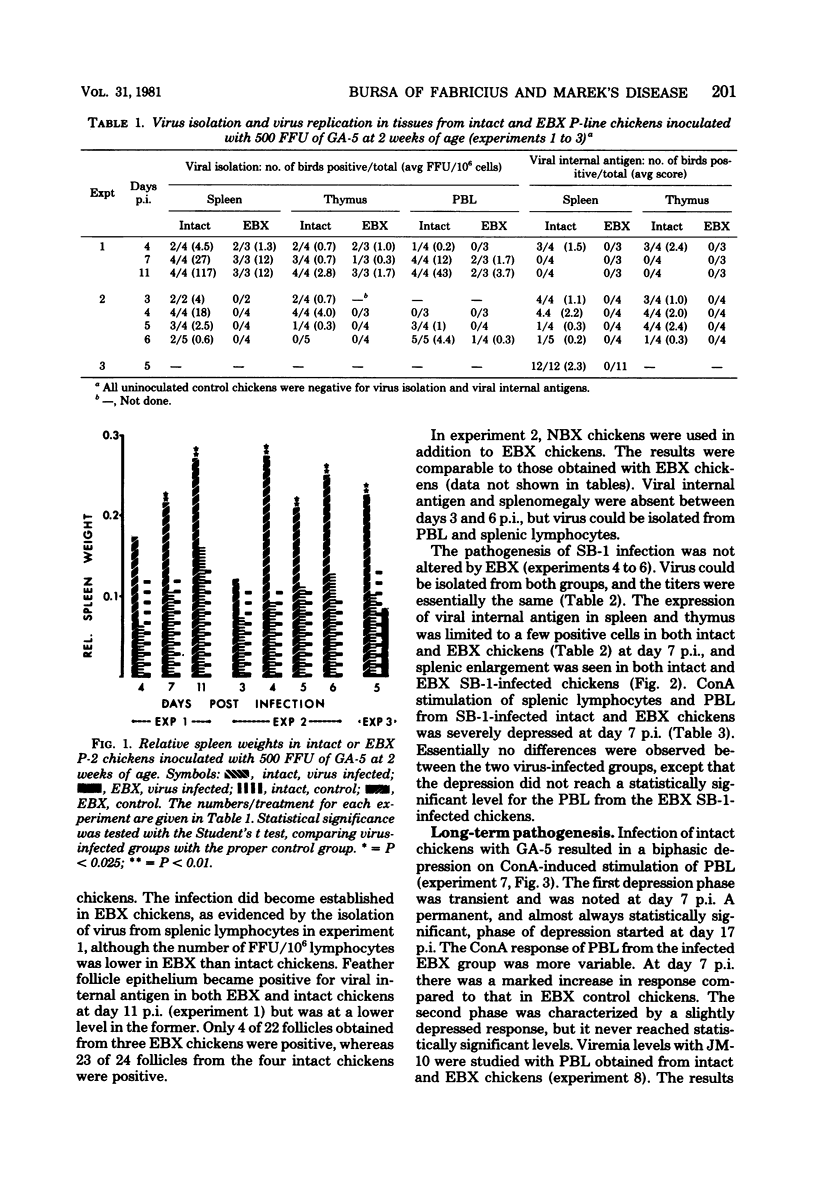
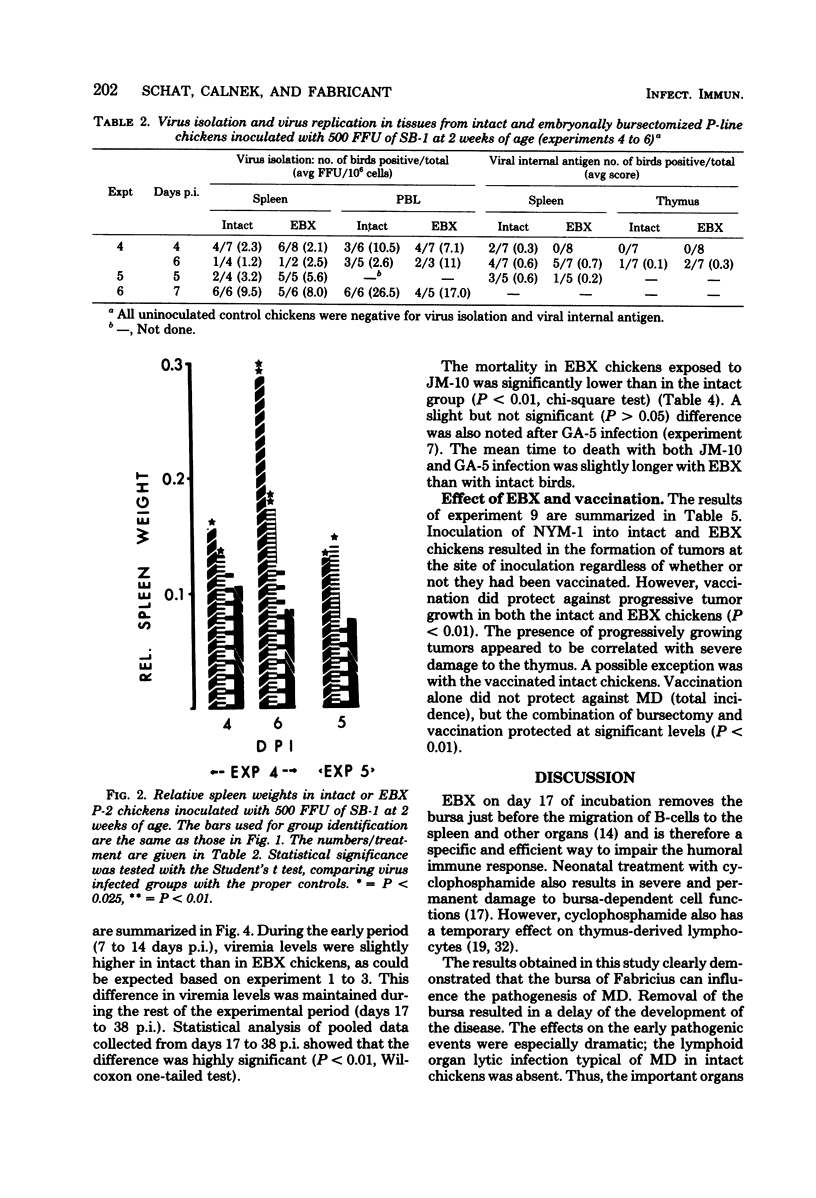
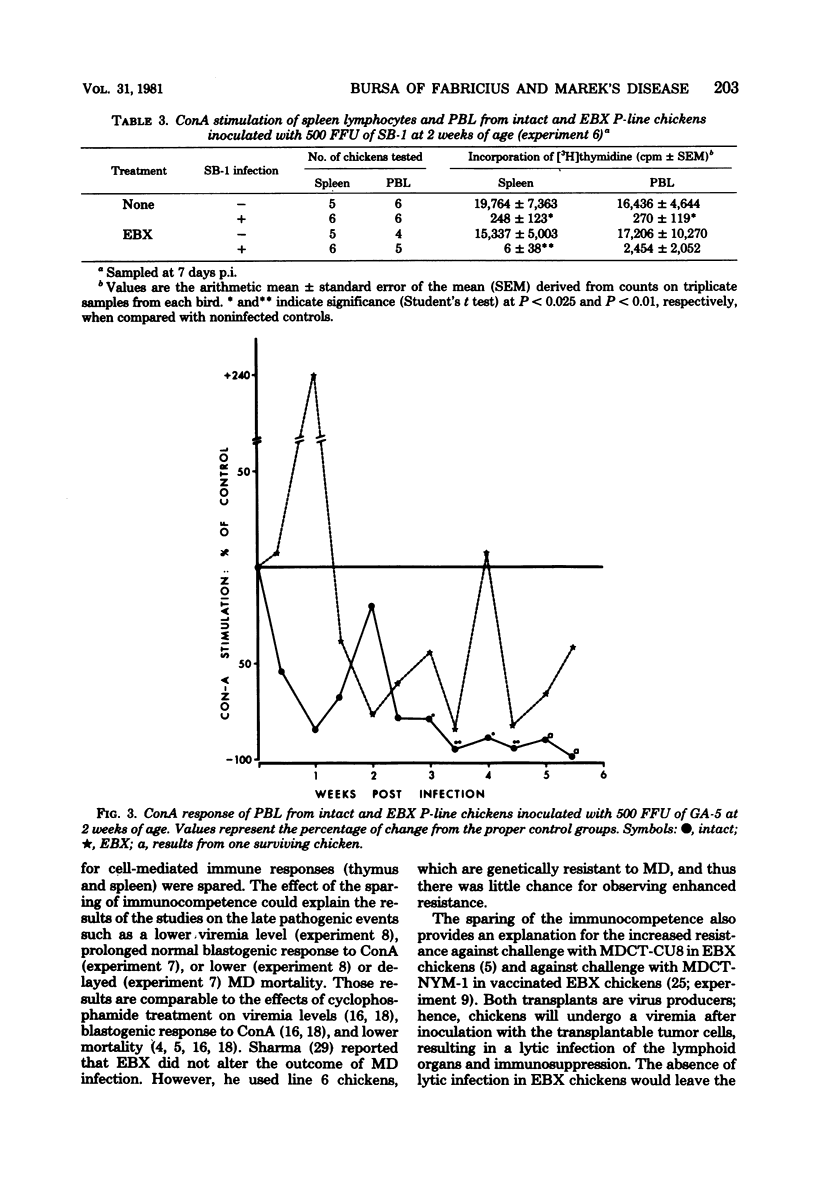
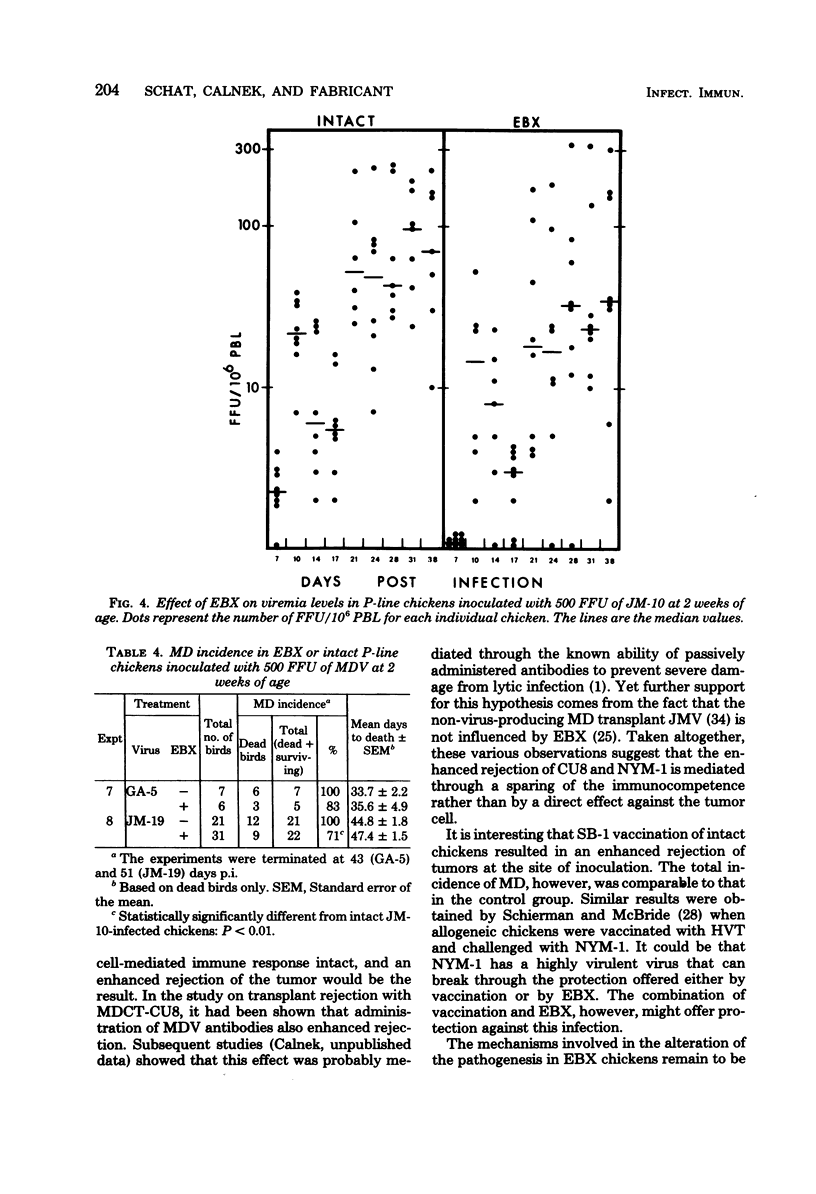
A series of experiments was conducted to study the influence of embryonal bursectomy (EBX) on the early and late pathogenesis of Marek's disease (MD). The early lytic infection in the lymphoid organs normally associated with oncogenic MD virus infection in intact chickens was not seen in EBX chickens. Therefore, the damage to the immune system was minimal. EBX chickens also had lower viremia levels, higher lymphocyte responses to mitogens, and a lower or delayed MD mortality when compared with intact chickens. Furthermore, it was shown that although vaccination with SB-1 by itself did not protect against a highly virulent MD transplantable tumor, the combination of EBX and vaccination gave significant protection. All these effects could be explained by an enhanced immune response in EBX birds. In contrast, the pathogenesis of nononcogenic MD virus was not influenced by EBX. The possible mechanism(s) involved in these observed effects of EBX on MD pathogenesis are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calnek B. W., Carlisle J. C., Fabricant J., Murthy K. K., Schat K. A. Comparative pathogenesis studies with oncogenic and nononcogenic Marek's disease viruses and turkey herpesvirus. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Apr;40(4):541–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W. Effects of passive antibody on early pathogenesis of Marek's disease. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):193–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.193-198.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Fabricant J., Schat K. A., Murthy K. K. Pathogenicity of low-virulence Marek's disease viruses in normal versus immunologically compromised chickens. Avian Dis. 1977 Jul-Sep;21(3):346–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Fabricant J., Schat K. A., Murthy K. K. Rejection of a transplantable Marek's disease lymphoma in normal versus immunologically deficient chickens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Mar;60(3):623–631. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.3.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W. Influence of age at exposure on the pathogenesis of Marek's disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Sep;51(3):929–939. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.3.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. K. Studies on genetic resistance to Marek's disease. Avian Dis. 1968 Feb;12(1):9–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droege W. Amplifying and suppressive effect of thymus cells. Nature. 1971 Dec 31;234(5331):549–551. doi: 10.1038/234549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droege W. Comparison of the suppressive effect of thymus cells and the suppression by neonatal application of antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Dec;3(12):804–811. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droege W. The antigen-inexperienced thymic suppressor cells: a class of lymphocytes in the young chicken thymus that inhibits antibody production and cell-mediated immune responses. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Apr;6(4):279–287. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant J., Ianconescu M., Calnek B. W. Comparative effects of host and viral factors on early pathogenesis of Marek's disease. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):136–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.136-144.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando W. W., Calnek B. W. Influence of bursa of Fabricius on infection and pathological response of chickens exposed to Marek's disease herpesvirus. Avian Dis. 1971 Jul-Sep;15(3):467–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. G., Moll T. Effect of immunosuppression on clinical and pathologic manifestations of Marek's disease in chickens. Am J Vet Res. 1968 Sep;29(9):1831–1835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi J. Immunodeficiency in the chicken. I. Disparity in suppression of antibody responses to various antigens following surgical bursectomy. Immunology. 1975 Jun;28(6):1007–1013. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermani-Arab V., Leslie G. A. Suppression of immunoglobulin synthesis by transplantation of T cells from anti-mu bursectomized chickens into normal recipients. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):530–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermani-Arab V., Moll T., Cho B. R., Davis W. C., Lu Y. S. Effect of cyclophosphamide on the response of chickens to a virulent strain of Marek's disease virus. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1058–1064. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1058-1064.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linna T. J., Frommel D., Good R. A. Effects of early cyclophosphamide treatment on the development of lymphoid organs and immunological functions in the chickens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;42(1):20–39. doi: 10.1159/000230590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y. S., Kermani-Arab V., Moll T. Cyclophosphamide-induced amelioration of Marek's disease in Marek's disease-susceptible chickens. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Jun;37(6):687–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride R. A., Watanabe D. H., Schierman L. W. Rous sarcomas in chickens: enhanced growth coexisting with concomitant immunity. Science. 1977 Sep 9;197(4308):1079–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.196336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. R., Jerome FNREINHART B. S. Surgical bursectomy and the incidence of Marek's disease (MD) in domestic chickens. Poult Sci. 1969 Jul;48(4):1513–1515. doi: 10.3382/ps.0481513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moticka E. J. The presence of immunoregulatory cells in chicken thymus: function in B and T cell responses. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):987–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne L. N., Rennie M. Lack of effect of bursectomy on Marek's disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Aug;45(2):387–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudczynski A. B., Mortensen R. F. Suppressor cells in mice with murine mammary tumor virus-induced mammary tumors. I. Inhibition of mitogen-induced lymphocyte stimulation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Jan;60(1):205–211. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.1.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schat K. A., Calnek B. W. Characterization of an apparently nononcogenic Marek's disease virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 May;60(5):1075–1082. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.5.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schat K. A., Calnek B. W. Protection against Marek's disease-derived tumor transplants by the nononcogenic SB-1 strain of Marek's disease virus. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):225–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.225-232.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schierman L. W., McBride R. A. Effects of vaccination for Marek's disease on growth of a Marek's-virus-induced transplantable lymphoma in syngeneic and allogeneic chickens. Avian Dis. 1979 Jan-Mar;23(1):47–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma J. M., Lee L. F. Suppressive effect of cyclophosphamide on the T-cell system in chickens. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):227–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.227-230.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma J. M. Resistance to Marek's disease in immunologically deficient chickens. Nature. 1974 Jan 11;247(5436):117–118. doi: 10.1038/247117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma J. M., Witter R. L. The effect of B-cell immunosuppression on age-related resistance of chickens to Marek's disease. Cancer Res. 1975 Mar;35(3):711–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens E. A., Witter R. L., Lee L. F., Sharma J. M., Nazerian K., Longenecker B. M. Characteristics of JMV Marek's disease tumor: a nonproductively infected transplantable cell lacking in rescuable Virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Oct;57(4):865–874. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.4.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theis G. A., Schierman L. W., McBride R. A. Transplantation of a Marek's disease lymphoma in syngeneic chickens. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1710–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


