Abstract
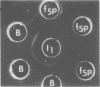
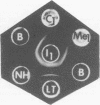
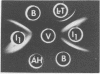
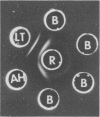
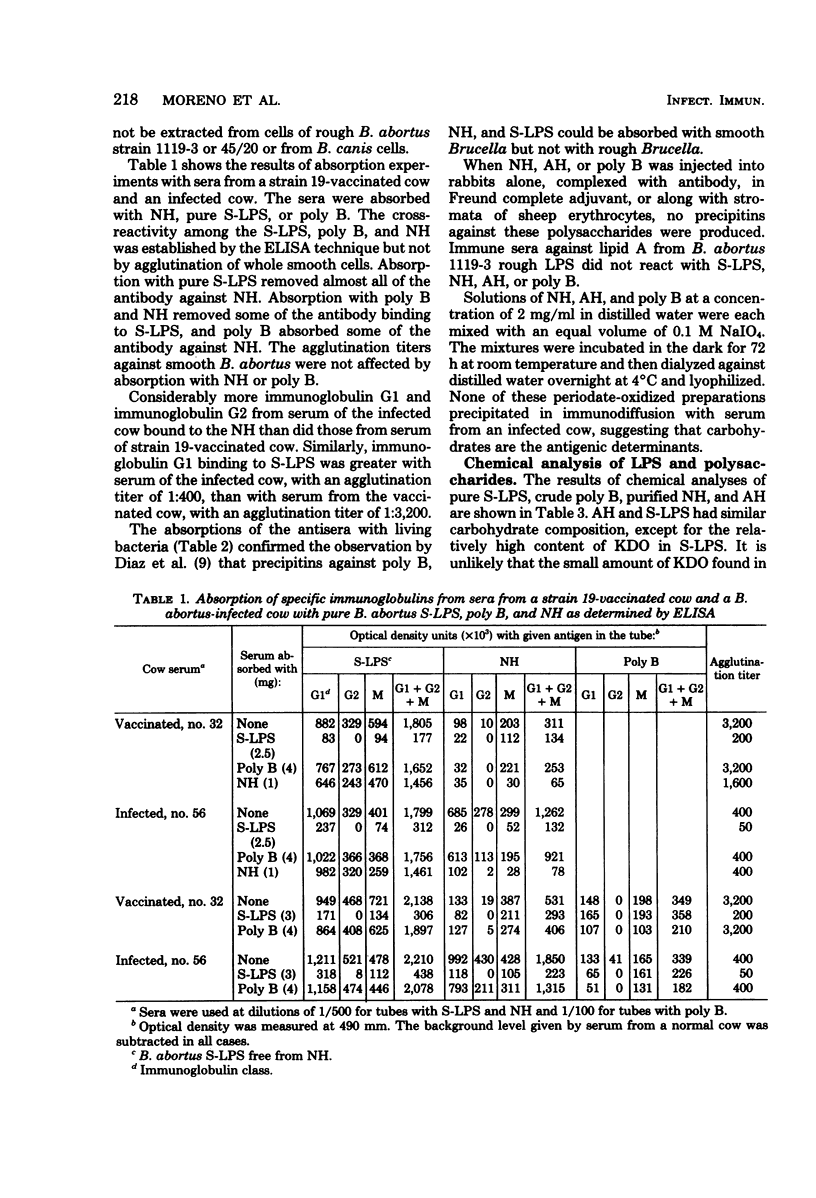
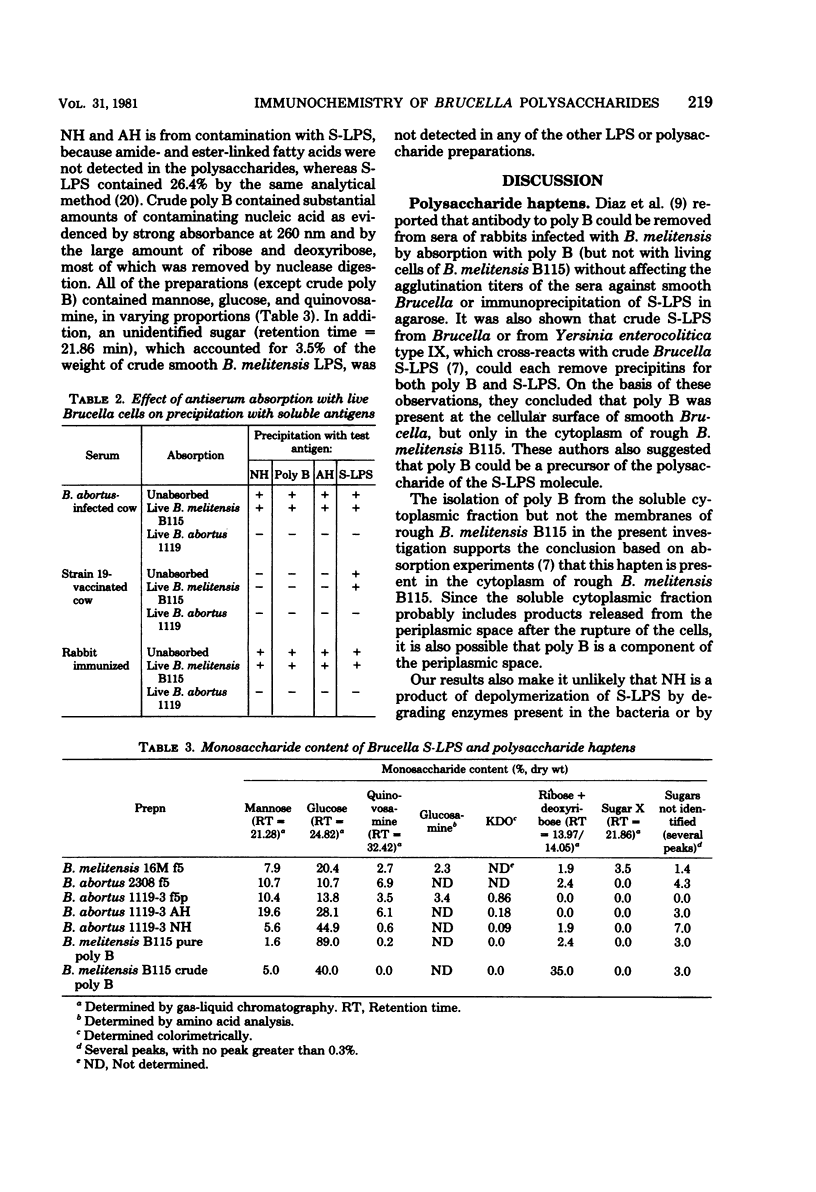
Purified lipopolysaccharide (LPS) extracted with phenol-water from smooth Brucella abortus was hydrolyzed with 1% acetic acid at 100 degrees C. The degraded polysaccharide (AH) released gave reactions of identity with the native polysaccharide hapten (NH) in phenol-water- or trichloroacetic acid-extracted endotoxin preparations of B. abortus and with the polysaccharide (poly B) extracted by trichloroacetic acid from rough B. melitensis strain B115. Poly B was present in the soluble cytoplasmic fraction but not in the membrane fraction, of disrupted B115 cells. It could not be extracted from three rough mutants of B. abortus or from B canis or B. ovis cells. Both AH and NH shared determinants present on smooth LPS and missing from poly B. Sugars found in purified LPS, NH, and AH included mannose, glucose, quinovosamine, glucosamine, and 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate. Poly B contained only a trace amount of quinovosamine and no 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate detectable by the thiobarbiturate assay. Sera from some rabbits immunized with pure smooth LPS and some, but not all, cows infected with field strains of B. abortus recognized the determinants missing from poly B. A subclass-specific enzyme-linked immunoassay showed that most of the antibody in sera from infected cows which binds to smooth LPS and to NH is of the immunoglobulin G1 subclass.
Full text
PDF

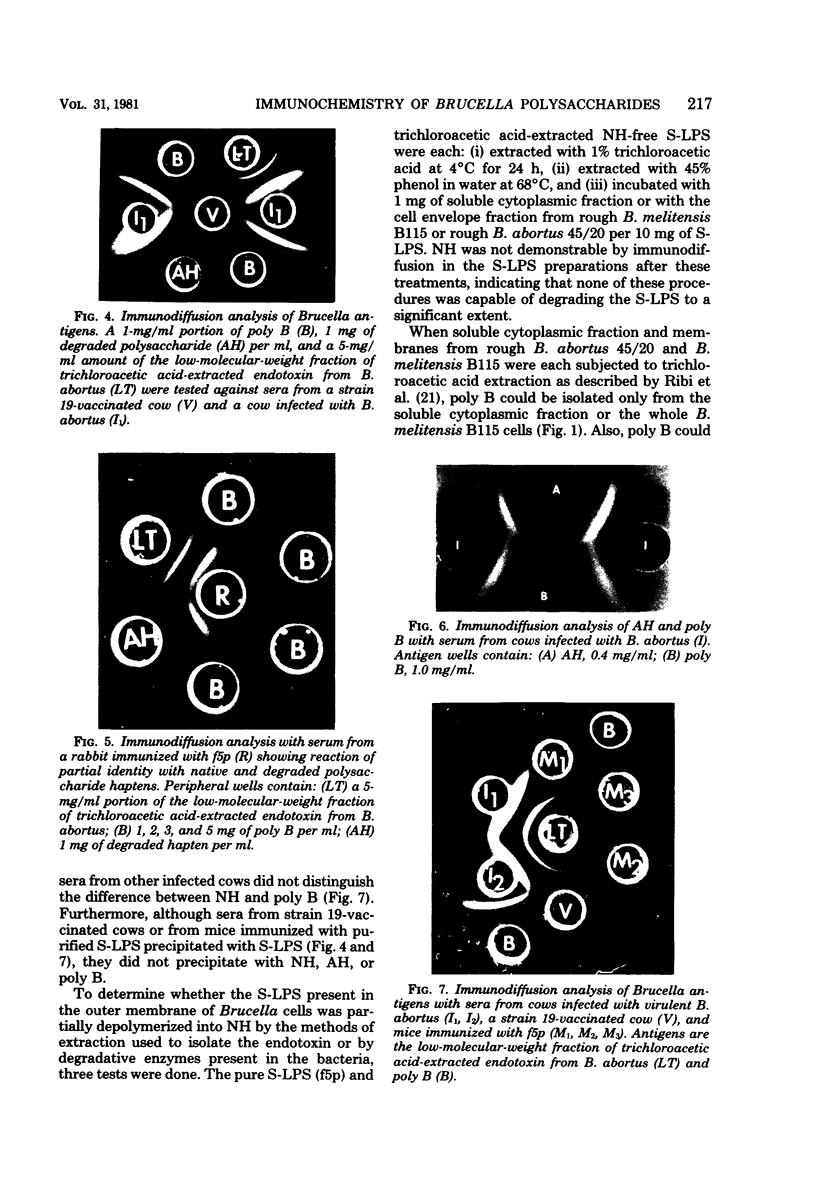



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANACKER R. L., FINKELSTEIN R. A., HASKINS W. T., LANDY M., MILNER K. C., RIBI E., STASHAK P. W. ORIGIN AND PROPERTIES OF NATURALLY OCCURRING HAPTEN FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1705–1720. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1705-1720.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman D. T., Wilson B. L., Moreno E., Angus R. D., Jones L. M. Characterization of Brucella abortus soluble antigen employed in immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):355–362. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.355-362.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Keegstra K. Carbohydrate structure of Sindbis virus glycoprotein E2 from virus grown in hamster and chicken cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):546–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.546-554.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Garatea P., Jones L. M., Moriyon I. Radial immunodiffusion test with a Brucella polysaccharide antigen for differentiating infected from vaccinated cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):37–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.37-41.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Jones L. M., Leong D., Wilson J. B. Surface antigens of smooth brucellae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):893–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.893-901.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz R., Bosseray N. Estudio de las relaciones antigénicas entre Yersinia enterocolitica serotipo 9 y otras especies bacterianas gram-negavtivas. Microbiol Esp. 1974 Jan-Mar;27(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz R., Dorronsoro I. Contribución al diagnóstico serológico de brucelosis y yersiniosis. I. Utilidad de la reacción de precipitación en gel. Rev Clin Esp. 1971 May;121(4):367–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSTER J. W., RIBI E. Immunological role of Brucella abortus cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:258–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.258-268.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Preparation and properties of antisera against the lipid-A component of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 22;24(1):116–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb19661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B., Lindberg A. A. Serological cross-reactions between different Brucella species and Yersinia enterocolitica. Immunochemical studies on phenol-water extracted lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica type IX. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Berman D. T., Moreno E., Deyoe B. L., Gilsdorf M. J., Huber J. D., Nicoletti P. Evaluation of a radial immunodiffusion test with polysaccharide B antigen for diagnosis of bovine brucellosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):753–760. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.753-760.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Diaz R., Berman D. T. Endotoxic activity of rough organisms of Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1638–1641. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1638-1641.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb V. L., Jones L. M., Schurig G. G., Berman D. T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for bovine immunoglobulin subclass-specific response to Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):240–247. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.240-247.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Berman D. T., Boettcher L. A. Biological activities of Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):362–370. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.362-370.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Berman D. T. Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharide is mitogenic for spleen cells of endotoxin-resistant C3H/HeJ mice. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2915–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Pitt M. W., Jones L. M., Schurig G. G., Berman D. T. Purification and characterization of smooth and rough lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):361–369. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.361-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIBI E., HASKINS W. T., MILNER K. C., ANACKER R. L., RITTER D. B., GOODE G., TRAPANI R. J., LANDY M. Physicochemical changes in endotoxin associated with loss of biological potency. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:803–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.803-814.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. G., Jones L. M., Speth S. L., Berman D. T. Antibody response to antigens distinct from smooth lipopolysaccharide complex in Brucella infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):994–1002. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.994-1002.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Eschen K. B., Rudbach J. A. Immunological responses of mice to native protoplasmic polysaccharide and lipopolysaccharide: functional separation of the two signals required to stimulate a secondary antibody response. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1604–1614. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]