Abstract
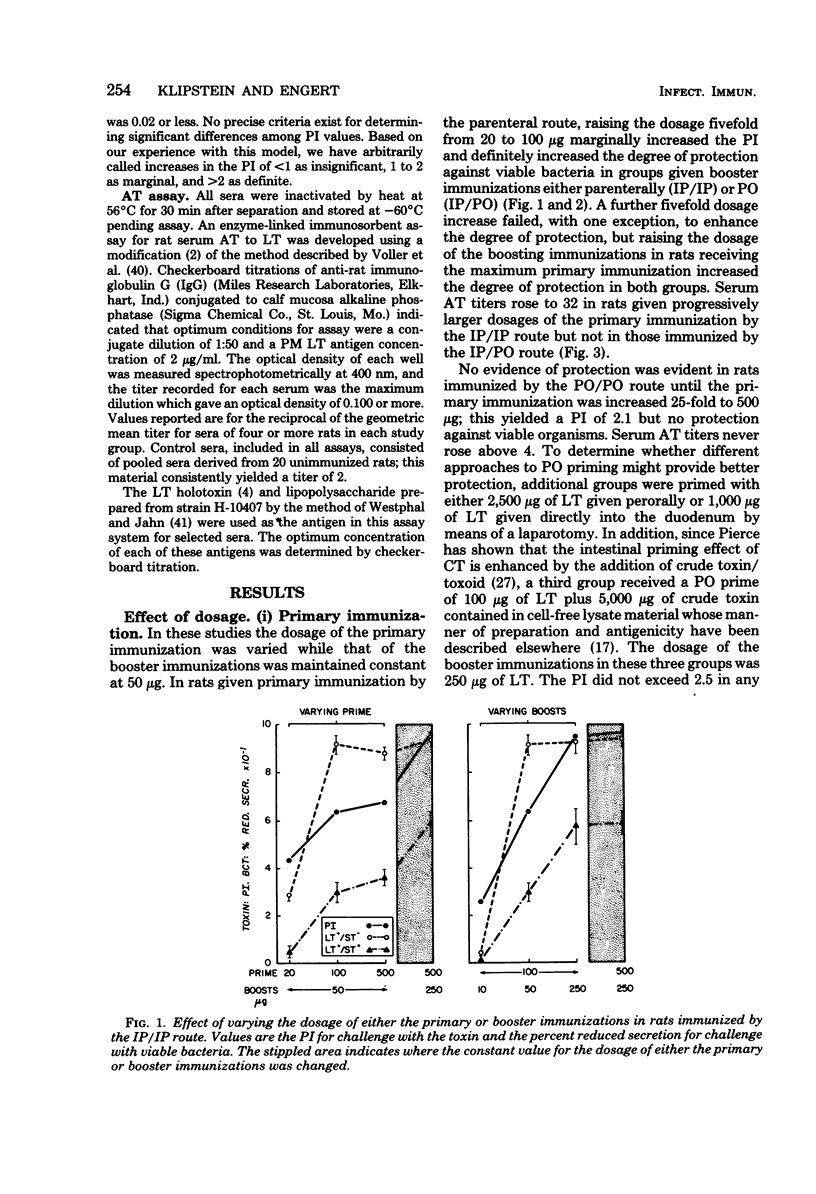
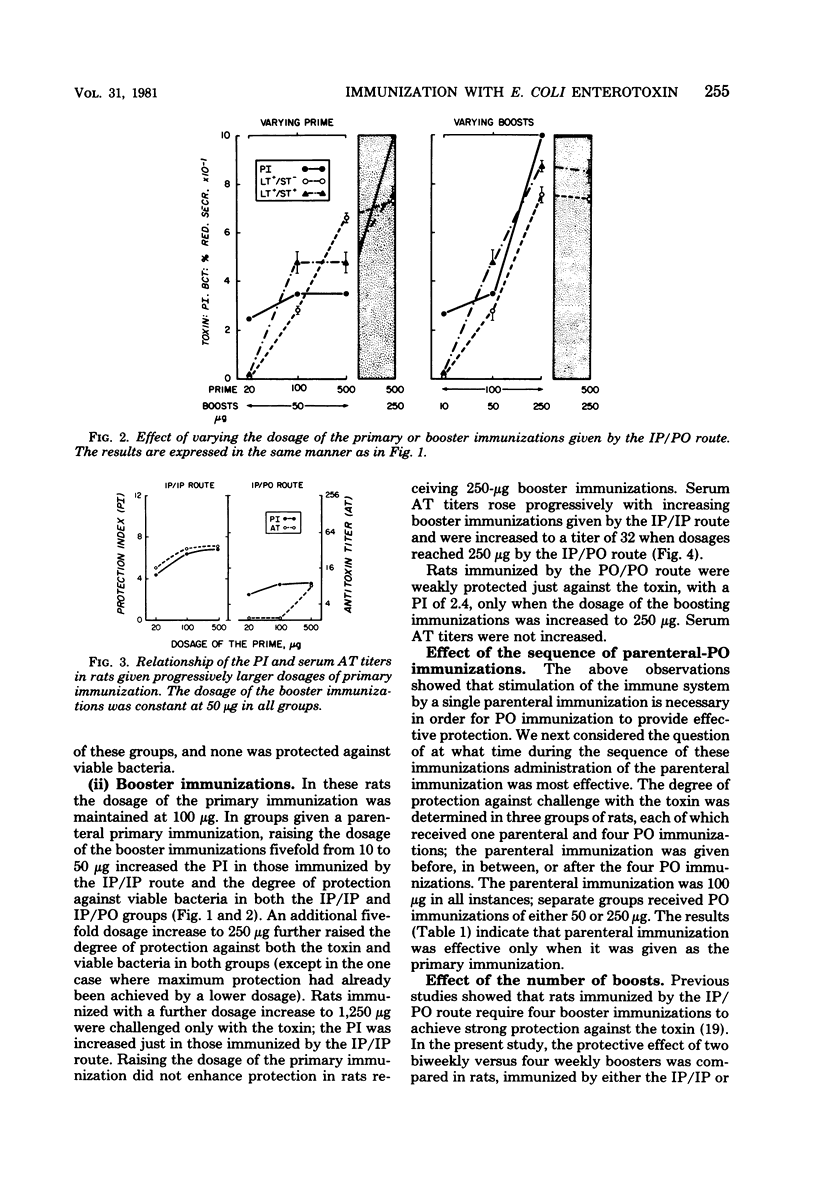
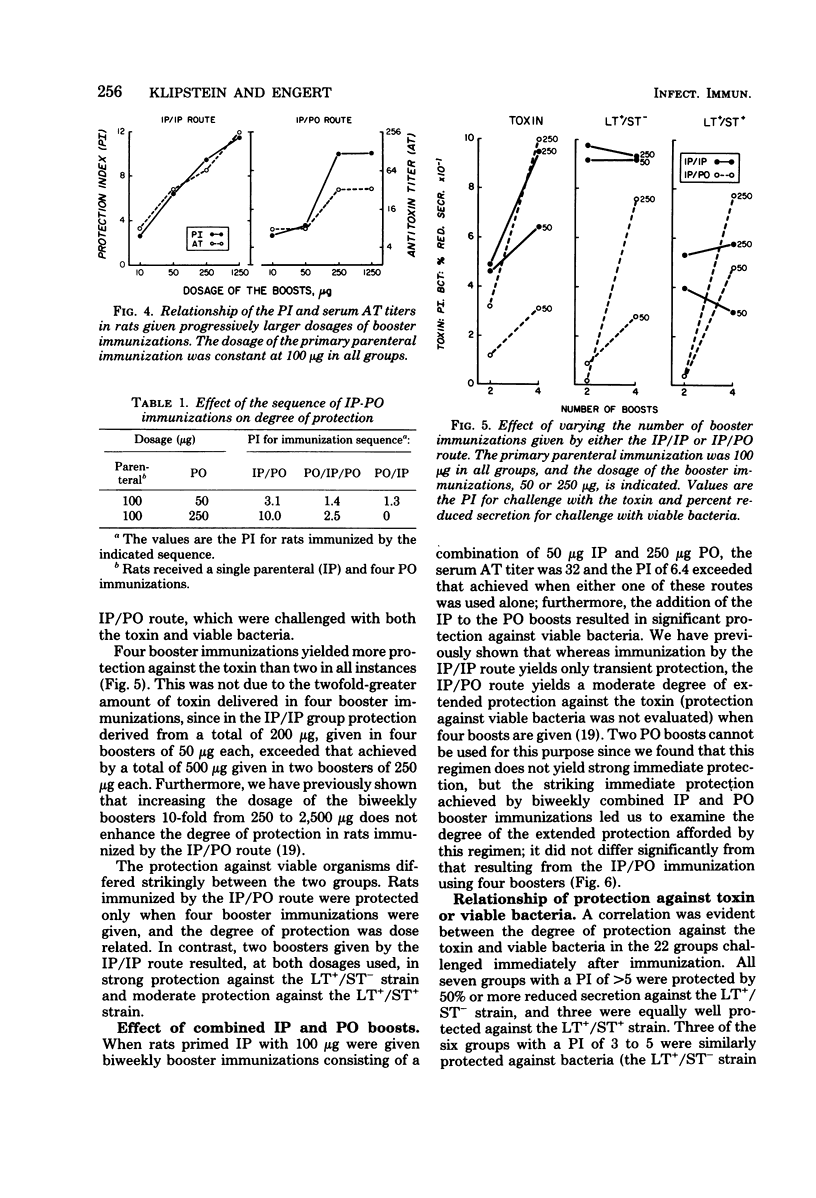
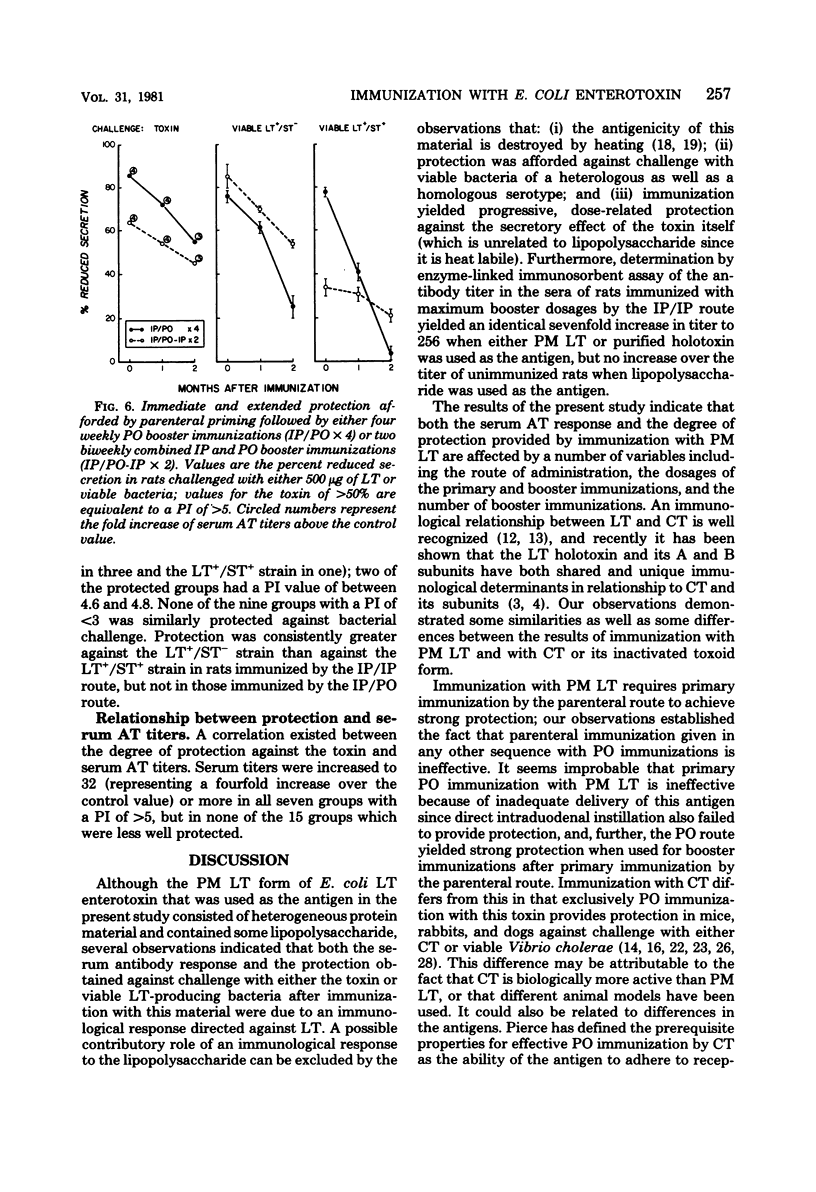
The respective contributions to protection of the route and dosage of primary and booster immunizations with Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin were evaluated in rats. The degree of protection was determined by challenge with toxin and viable bacteria in ligated ileal loops, and the serum antitoxin response was assayed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Primary immunization was effective only when given by the parenteral route. The degree of protection was enhanced a fivefold dosage increase in the primary parenteral immunization in rats given constant dosages of booster immunizations either parenterally or perorally, but not by further dosage increases. In contrast, the degree of protection rose when dosages of the booster immunizations were increased over a 25-fold range. Four weekly peroral, but only two biweekly parenteral, booster immunizations were necessary to achieve strong protection; biweekly combined parenteral and peroral booster immunizations yielded both strong, immediate and extended protection. The degree of protection against the toxin correlated with that against viable bacteria and with elevated serum antitoxin titers: all seven groups with a protection index of greater than 5 against the toxin had strong protection against heat-labile toxin-producing strains and fourfold or greater increases in the antitoxin titers, whereas none of the nine groups with a protection index of less than 3 was protected against bacteria or had an equivalent antitoxin response. These observations show that once an adequate parenteral primary immunization is given, the degree of protection is influenced primarily by the dosage of the booster immunizations, the necessary number of which is dependent on their route of administration.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brimblecombe R. W., Duncan W. A., Durant G. J., Emmett J. C., Ganellin C. R., Leslie G. B., Parsons M. E. Characterization and development of cimetidine as a histamine H2-receptor antagonist. Gastroenterology. 1978 Feb;74(2 Pt 2):339–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg S., Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitating the humoral immune response to the colonization factor antigen of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):525–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.525-531.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Demonstration of shared and unique immunological determinants in enterotoxins from Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):709–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.709-713.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Falkow S. The molecular nature of heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) of escherichia coli. Nature. 1979 Feb 1;277(5695):406–407. doi: 10.1038/277406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Polymyxin B-Induced Release of Low-Molecular-Weight, Heat-Labile Enterotoxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1010–1017. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1010-1017.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G. Inhibition of immune hemolysis: serological assay for the heat-labile enterotoxin of Excherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.100-105.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: observations with purified antigens and the ligated ileal loop model. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):464–467. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.464-467.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita K., Finkelstein R. A. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: comparison of immunity induced perorally and parenterally in mice. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):647–655. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Relationships among heat-labile enterotoxins of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):277–283. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. R., Yardley J. H., Brown G. D. Suppression of local intestinal immunoglobulin A immune response to cholera toxin by subcutaneous administration of cholera toxoids. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):422–426. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.422-426.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Andersson A., Wallerstrom G., Ouchterlony O. Experimental studies on cholera immunization. II. Evidence for protective antitoxic immunity mediated by serum antibodies as well as local antibodies. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):662–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.662-667.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M., Lönnroth I., Fall-Persson M., Markman B., Lundbeck H. Development of improved cholera vaccine based on subunit toxoid. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):602–604. doi: 10.1038/269602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M., Ouchterlony O., Anderson A., Walletström G., Westerberg-Berndtsson U. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: protection, and serum and local antibody responses in rabbits after enteral and parenteral immunization. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1331–1340. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1331-1340.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Immunological interrelationships between cholera toxin and the heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of coliform bacteria. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):110–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.110-117.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Influence of route of administration on immediate and extended protection in rats immunized with Escherichia coli heart-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):81–86. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.81-86.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Protective effect of active immunization with purified Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin in rats. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):592–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.592-599.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Short H. B. Protective effect of immunization with heat-labile enterotoxin in gnotobiotic rats monocontaminated with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):163–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.163-170.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-labile enterotoxin produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):586–596. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.586-596.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange S., Hansson H. A., Molin S. O., Nygren H. Local cholera immunity in mice: intestinal antitoxin-containing cells and their correlation with protective immunity. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):743–750. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.743-750.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange S., Holmgren J. Protective antitoxic cholera immunity in mice: influence of route and number of immunizations and mode of action of protective antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1978 Aug;86C(4):145–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb02572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W. Protection against experimental cholera by oral or parenteral immunization. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):594–598. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.594-598.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Cray W. C., Jr, Engel P. F. Antitoxic immunity to cholera in dogs immunized orally with cholera toxin. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):632–637. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.632-637.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Cray W. C., Jr, Sircar B. K. Induction of a mucosal antitoxin response and its role in immunity to experimental canine cholera. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):185–193. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.185-193.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Gowans J. L. Cellular kinetics of the intestinal immune response to cholera toxoid in rats. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1550–1563. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Kaniecki E. A., Northrup R. S. Protection against experimental cholera by antitoxin. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):606–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Koster F. T. Priming and suppression of the intestinal immune response to cholera toxoid/toxin by parenteral toxoid in rats. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):307–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Sack R. B., Sircar B. K. Immunity to experimental cholera. III. Enhanced duration of protection after sequential parenteral-oral administration of toxoid to dogs. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jun;135(6):888–896. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.6.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F. The role of antigen form and function in the primary and secondary intestinal immune responses to cholera toxin and toxoid in rats. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):195–206. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Sack R. B. Test for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli using Y-1 adrenal cells in miniculture. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.334-336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Immunization with Escherichia coli enterotoxin protects against homologous enterotoxin challenge. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):641–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.641-644.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. W., Sack R. B. Immunologic cross-reactions of enterotoxins from Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):164–170. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J. Synergistic protective effect in rabbits of immunization with Vibrio cholerae lipopolysaccharide and toxin/toxoid. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):735–740. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.735-740.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yardley J. H., Keren D. F., Hamilton S. R., Brown G. D. Local (immunoglobulin A) immune response by the intestine to cholera toxin and its partial suppression with combined systemic and intra-intestinal immunization. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):589–597. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.589-597.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



