Abstract
This work was designed to study MCT effect in histopathological analysis of hippocampus (HC) and parahippocampal cortex (PHC) and in oxidative stress (OS) parameters in brain areas such as hippocampus (HC), prefrontal cortex (PFC), and striatum (ST). Swiss mice (25–30 g) were administered a single i.p. dose of MCT (5, 50, or 100 mg/kg) or 4% Tween 80 in saline (control group). After 30 minutes, the animals were sacrificed by decapitation and the brain areas (HC, PHC, PFC, or ST) were removed for histopathological analysis or dissected and homogenized for measurement of OS parameters (lipid peroxidation, nitrite, and catalase) by spectrophotometry. Histological evaluation of brain structures of rats treated with MCT (50 and 100 mg/kg) revealed lesions in the hippocampus and parahippocampal cortex compared to control. Lipid peroxidation was evident in all brain areas after administration of MCT. Nitrite/nitrate content decreased in all doses administered in HC, PFC, and ST. Catalase activity was increased in the MCT group only in HC. In conclusion, monocrotaline caused cell lesions in the hippocampus and parahippocampal cortex regions and produced oxidative stress in the HC, PFC, and ST in mice. These findings may contribute to the neurological effects associated with this compound.
1. Introduction
Monocrotaline (MCT) is a pyrrolizidine alkaloid produced by Crotalaria genus, which causes hepatotoxic effects in animals and man [1, 2]. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are activated in vivo by liver cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidases, producing generation of electrophilic pyrrolic intermediates [3]. Dehydromonocrotaline appears to be detoxified by conjugation with glutathione (GSH) [4]. Dehydromonocrotaline inhibits the activity of the respiratory chain complex I NADH oxidase. The probable mechanism is a change in the conformation of complex I resulting from modification of cysteine thiol groups by the metabolite [5].
Humans are exposed to MCT following consumption of herbal teas or contaminated food grains [1, 6]. Lethal toxicity has been reported in sheep 38–120 h after administration of Crotalaria retusa 5–40 g/kg [7, 8]. Horses are particularly sensitive to intoxication by MCT and show classic picture of liver fibrosis and neurological symptoms (Kimberley horse disease) with chronic exposure to the alkaloid [9, 10]. Preliminary studies show that MCT causes lesions in some organs, such as liver [11] and lungs [12]. There are also reports of histological changes in these organs and MCT neurotoxicity is associated with its lipophilicity [9, 13], but there is a little information about the associated histological changes in the central nervous system (CNS).
Oxidative stress (OS) is classically defined as a redox imbalance caused by an excess of oxidants or a lack of natural antioxidants in the system [14, 15]. The normal brain consumes higher rate of oxygen per unit mass of tissue and contains low levels of antioxidants. There are excitatory amino acids in normal brain, and these amino acids are important to normal function. Also, neurotransmitters are molecules involved with oxidation process. For example, dopamine and noradrenaline react with molecular oxygen to form quinines and semiquinone, which can deplete glutathione [16, 17]. Likewise, in brain, the oxidation of dopamine by monoamine oxidase releases hydrogen peroxide as a metabolic product that can cause tissue injury, including lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, and enzyme inactivation [18]. Brain lipids are highly enriched with polyunsaturated fatty acids [16, 19]. In addition, certain regions of the central nervous system, such as striatum and hippocampus, may be particularly sensitive to OS because of their low endogenous level of vitamin E, an important biochemical antioxidant, relative to other brain regions [20]. Some studies with MCT observed that the levels of glutathione (GSH) are more than 50% increase in rat liver after MCT (65 mg/kg, i.p.) administration [4]. On the other hand, MCT increases the intensity of cellular OS in pulmonary artery endothelial cells [1, 12]. Based on the facts cited above and that MCT administration to mice caused CNS alterations [21], we decided to assess the effect of MCT administration in histopathological analysis as well as in tests of oxidative stress through thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), as an indicator of lipid peroxidation, as well as catalase activity and nitrite/nitrate content in the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and striatum. The idea is to study the relation of ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) with MCT neurotoxic effects.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
Crotalaria retusa leaves were collected in the district of Patos-Paraiba (Brazil), in November 2009, and identified by the botanist Maria de Fatima Agra. A voucher specimen Agra e Gois 3607 is kept at the Professor Lauro Pires Xavier herbarium (Joao Pessoa, PB, Brazil).
2.2. Extraction and Isolation of Monocrotaline
The ground seeds (640 g) of C. retusa were extracted three times with 95% ethanol for 72 h. The ethanolic extracts were evaporated under reduced pressure to yield a brown viscous residue (53.4 g), which was extracted with 3% hydrochloric acid until the washing was negative to Dragendorff's reagent. The acidic aqueous solution was made alkaline (pH 9) with ammonia (25%) and repeatedly extracted with chloroform. The chloroformic solution was dried with Na2SO4 anhydrous, filtered, and evaporated until dryness to obtain the total alkaloid fraction (10.48 g). Analytical thin layer chromatography showed the presence of a single alkaloid. The dried residue was recrystallized from ethanol to give colorless prismatic crystals (yield ca. 1.4% based on the dry weight of the seeds material), which melted at 197-198°C. It was identified as monocrotaline based on 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HMQC, and HMBC spectroscopic data and comparison with those reported by Barreiro et al. (1980) and Cheng et al. (1986) [22, 23].
2.3. Animals
Male Swiss mice, 25–35 g, from the Animal House of the Federal University of Ceará were used. Experiments were carried out according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the US Department of Health and Human Services, Washington, DC, USA, (1985) and were performed under the consent and surveillance of the Department of Physiology and Pharmacology of Federal University of Ceará Ethics Committee for the use of animals in research (CEPA N°10/08).
2.4. Drugs and Animal Treatment
Purified MCT was provided by Dr. José Maria Barbosa Filho from Pharmaceutical Technology Laboratory, Federal University of Paraíba (Brazil). MCT was emulsified with 4% Tween 80 (SIGMA, USA) in saline 0.9% [24].
Animals were treated once with MTC at the doses of 5, 50, or 100 mg/kg i.p. and divided into 3 groups of 10 animals each. Control groups (vehicle) received 4% Tween 80 dissolved in saline 0.9% at the same volume as treated animals (10 mL/kg). Twenty-four hours after the drug administration the animals were sacrificed and their brain areas (hippocampus-HC, parahippocampal cortex-PHC, prefrontal cortex-PFC, or striatum-ST) were removed for histological analysis or dissected and homogenized with 10% phosphate buffer 0.05 M pH 7.4 for OS (HC, PFC, or ST) parameters determinations.
2.5. Histopathological Analysis
The brains were rapidly dissected, fixed in 4% neutral-buffered paraformaldehyde, and processed routinely for paraffin embedding. Sagittal sections, 5 μm thick, were cut serially at the level of the hippocampus, parahippocampal cortex, and selected sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H/E) for light microscopy examination. The histological observations (evaluated by a pathologist using a double-blind method) were scored using a pathological scoring scale modified in work of Gilat et al. (2005) [25]. The histological scoring scale is presented below.
-
(0)
Normal morphology.
-
(1)
Minor damage (edema, few pyknotic cells).
-
(2)
Moderate damage (structural disorganization, edema, moderate pyknotic cells, vacuolization, inflammatory cell infiltration).
-
(3)
Intense damage (structural disorganization, edema, intense pyknotic cells, vacuolization, inflammatory cell infiltration).
We included immunohistochemistry analysis in our results. Immunohistochemistry for caspase-3 was performed using the streptavidin-biotin-peroxidase method [26] in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections (4 μm thick), mounted on poly-L-lysine-coated microscope slides. The sections were deparaffinized and rehydrated through xylene and graded alcohols. After antigen retrieval, endogenous peroxidase was blocked (15 min) with 3% (v/v) hydrogen peroxide and washed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Sections were incubated overnight (4°C) with primary anti-caspase-3 antibody (polyclonal goat anti-mouse) diluted 1 : 200 in PBS plus bovine serum albumin (PBS-BSA). The slides were then incubated with biotinylated goat anti-IgG, diluted 1 : 200 in PBS-BSA. After washing, the slides were incubated with avidin-biotin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate (Strep ABC complex by Vectastain ABC reagent and peroxidase substrate solution) for 30 min, according to the Vectastain protocol. Caspase-3 was visualized with the chromogen 3,3′ diaminobenzidine (DAB). Negative control sections were processed simultaneously as described above but with the first antibody being replaced by PBS-BSA 5%. None of the negative controls showed caspase-3 immunoreactivity. Slides were counterstained with Harry's hematoxylin, dehydrated in a graded alcohol series, cleared in xylene, and coverslipped.
2.6. Measurement of Lipid Peroxidation
Lipid peroxides formation was analyzed by measuring the thiobarbituric-acid reacting substances (TBARS) in the homogenates [27]. The samples were added to a catalytic system of formation of free radicals (FeSO4 0.01 mM and ascorbic acid 0.1 mM) and then incubated at 37°C for 30 min. The reaction was stopped with 0.5 mL of 10% trichloroacetic acid, then the samples were centrifuged (3000 rpm/15 min), and the supernatants were retrieved and mixed with 0.5 mL of 0.8% thiobarbituric acid then heated in a boiling water bath for 15 min and after this period, they were immediately kept cold in a bath of ice. Lipid peroxidation was determined by the absorbance at 532 nm and was expressed as μmol of malondialdehyde (MDA)/g tissue.
2.7. Nitrite-Nitrate Determination
For the assessment of nitrite, derived from nitric oxide (NO), 100 μL of Griess reagent (1% sulfanilamide in 1% H3PO4/0.1% N-(1-naphthyl)-ethylenediamine dihydrochloride/1% H3PO4/distilled water, 1 : 1 : 1 : 1) were added to 100 μL of brain homogenates or to 100 μL of NaNO2 at concentrations ranging from 0.75 to 100 μL (standard curve). The absorbance was measured with a reader plate at 560 nm. The standard curve was used for the determination of nitrite concentrations in samples [28]. Results were expressed as μM.
2.8. Evaluation of Catalase Activity
The catalase activity was measured by the method that employs hydrogen peroxide to generate H2O and O2 [27]. The activity was measured by the degree of this reaction. The assay mixture contained 0.3 mL of hydrogen peroxide in 50 mL of 0.05 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.0. The sample aliquot (20 μL) was added to 980 μL of the substrate mixture. Initial and final absorbances were recorded at 230 nm after 1 and 6 min, respectively. A standard curve was established using purified catalase (Sigma, MO, USA) under identical conditions. All samples were diluted with 0.1 mmol/L phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) to provoke a 50% inhibition of the diluent rate (i.e., the uninhibited reaction). Protein was determined using bovine serum albumin as standard [29]. Results were expressed as mM/min/mg protein.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
The results were analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Student-Newman-Keuls test (post hoc) by GraphPad Prism 5.0 version for Windows, GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA USA. Differences were considered statistically significant at P < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Histopathological Analysis
Histological evaluation of brain structures of the rat treated with MCT (50 or 100 mg/kg) revealed lesions in the hippocampus and parahippocampal cortex compared to control (score: 0 (0-1)). The scores show severe structural disorganization, edema, moderate pyknotic cells, vacuolization, and inflammatory cell infiltration in both concentration 50 mg/kg (score: 2 (2-3)) and 100 mg/kg (score: 2 (1-3)) (Figure 1). Immunohistochemistry analysis in our results showed an increase of caspase 3, indicating apoptosis caused by MCT in relation to control animals (Figure 2).
Figure 1.
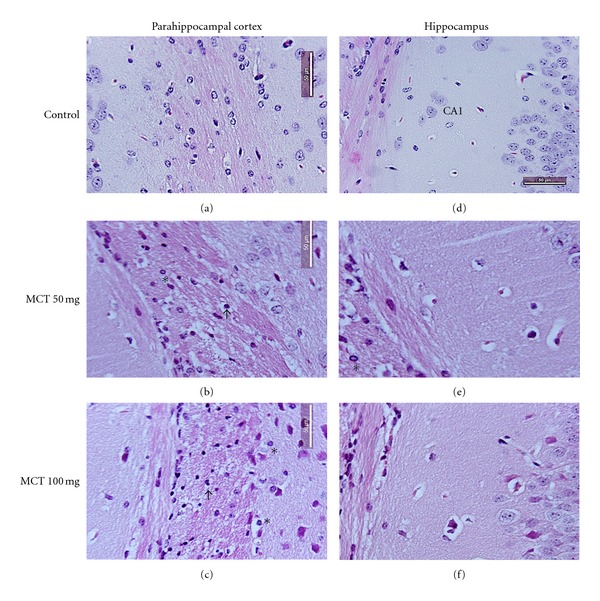
Histologic analysis of representative parahippocampal cortex and hippocampus sections. Control mice showing normal brain tissue ((a) and (d)). MCT-induced severe structural disorganization, edema, moderate pyknotic cells (arrow), vacuolization (arrowhead), inflammatory cell infiltration (*) in parahippocampal ((b) and (c)), and hippocampus ((e) and (f)) regions in 50 and 100 mg/kg concentrations, respectively. H&E staining ((a), (b), (c), (d), (e), and (f) 400x).
Figure 2.
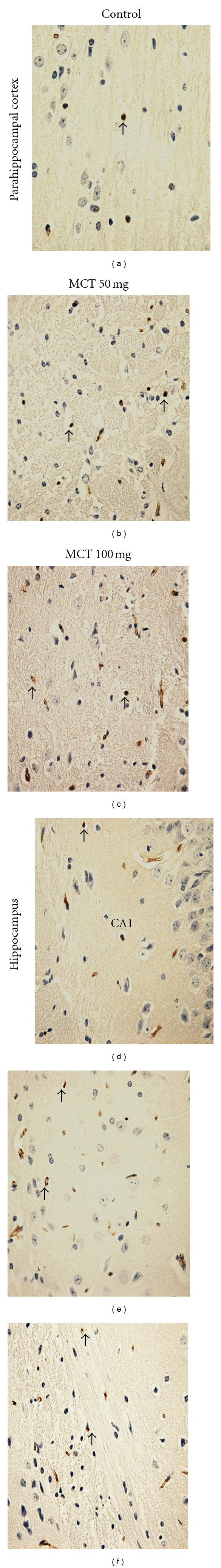
Representative examples of caspase-3 immunohistochemistry in the parahippocampal cortex and hippocampus of mice (400x). (a) and (d) Control groups. (b) and (e) Presented is an increase of the immunostaining for caspase-3 (arrow) in parahippocampal cortex and hippocampus of mice treated MCT (50 mg/kg). (c) and (f) Presented is an increase of the immunostaining for caspase-3 (arrow) in parahippocampal cortex and hippocampus of mice treated MCT (100 mg/kg).
3.2. Oxidative Stress Parameters
3.2.1. Lipid Peroxidation
The effect of MCT in lipid peroxidation is presented in Figure 3. MCT administration, in both doses (50 or 100 mg/kg), increased MDA levels (a lipid peroxidation marker) in the HC (F(3,27) = 6.353; P = 0.0025), PFC (F(3,26) = 4.441; P = 0.0133), and ST (F(3,27) = 8.143; P = 0.0007) as compared to control (HC: 2.26 ± 0.32; PFC: 1.39 ± 0.30; ST: 1.26 ± 0.23) and MCT 5 mg/kg (HC: 1.57 ± 0.25; PFC: 1.46 ± 0.43; ST: 1.13 ± 0.16) groups.
Figure 3.
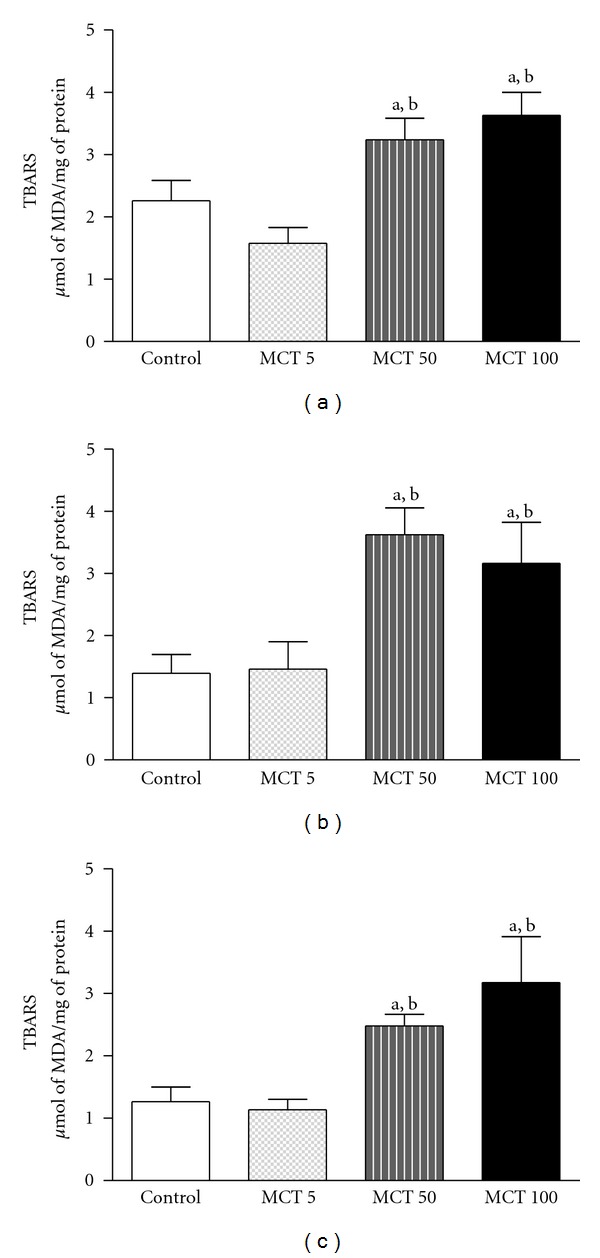
Levels of TBARS (lipid peroxidation level) in HC (a), PFC (b), or ST (c) of adult mice treated with vehicle or MCT (5, 50 or 1000 mg/kg). The results are presented as mean ± S.E.M. In parentheses, there is the number of animals per group. ((a) and (b)) P < 0.05 when compared to controls or MCT 5 mg/kg, respectively (ANOVA and Student-Newman-Keuls test as a post hoc).
3.2.2. Nitrite Content
MCT in all doses (5, 50 or 100 mg/kg) resulted in low levels of nitrite in HC (F(3,35) = 5.447; P = 0.0039) and PFC (F(3,28) = 5.528; P = 0.0047) as compared to the control group (HC: 9.17 ± 0.66; PFC: 7.25 ± 0.41) (Figures 4(a) and 4(b)). Similar effect was observed in ST (Figure 4(c)) in the levels of nitrite only with high doses of MCT (50 or 100 mg/kg) as compared to control (F(3,36) = 4.160; P = 0.0132).
Figure 4.
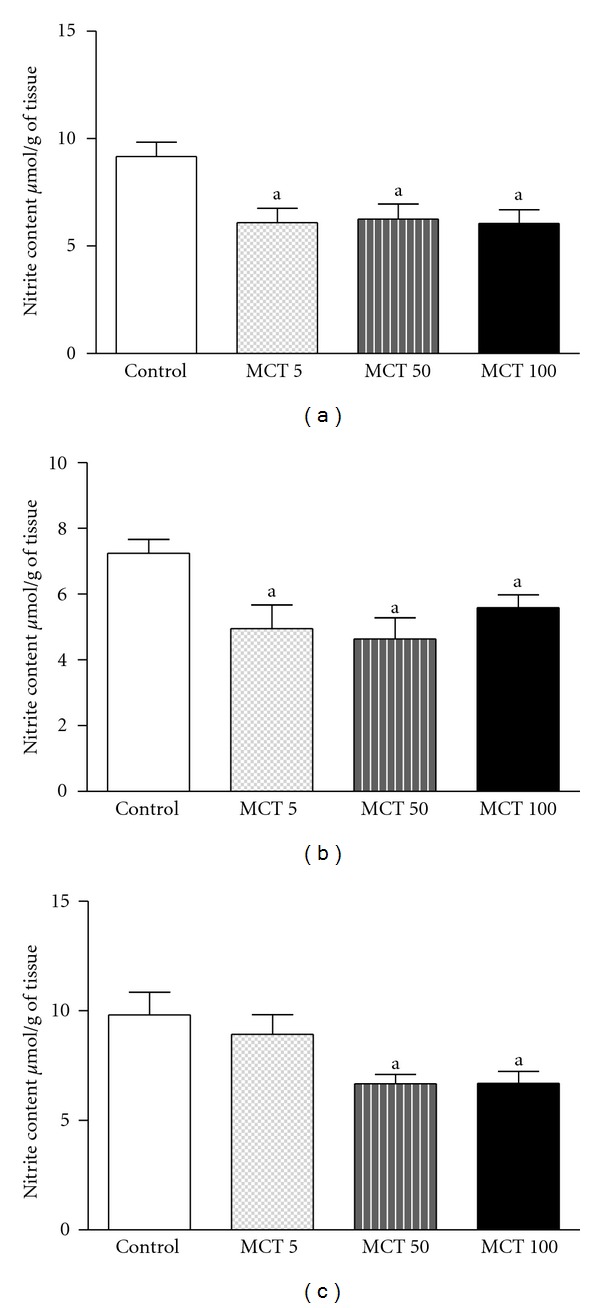
Content of nitrite HC (a), PFC (b), or ST (c) of adult mice treated with vehicle or MCT (5, 50 or 1000 mg/kg). The results are presented as mean ± S.E.M. In parentheses, there is the number of animals per group. (a) P < 0.05 when compared to controls (ANOVA and Student-Newman-Keuls test as a post hoc).
3.2.3. Catalase Activity
An increase in catalase activity was seen in the MCT group, in all doses, in HC (F(3,21) = 7.976; P = 0.0014) as compared to the control group (control: 14.12 ± 1.53) (Figure 5(a)). No alteration was observed in catalase activity in PFC (F(3,27) = 4.243; P = 0.0154) or ST (F(3,35) = 0.4684; P = 0.7064) after administration of MCT (5, 50 or 100 mg/kg) as compared to control group (PFC: 37.38 + 5.41; ST: 23.99 + 5.52) (Figures 5(b) and 5(c)).
Figure 5.
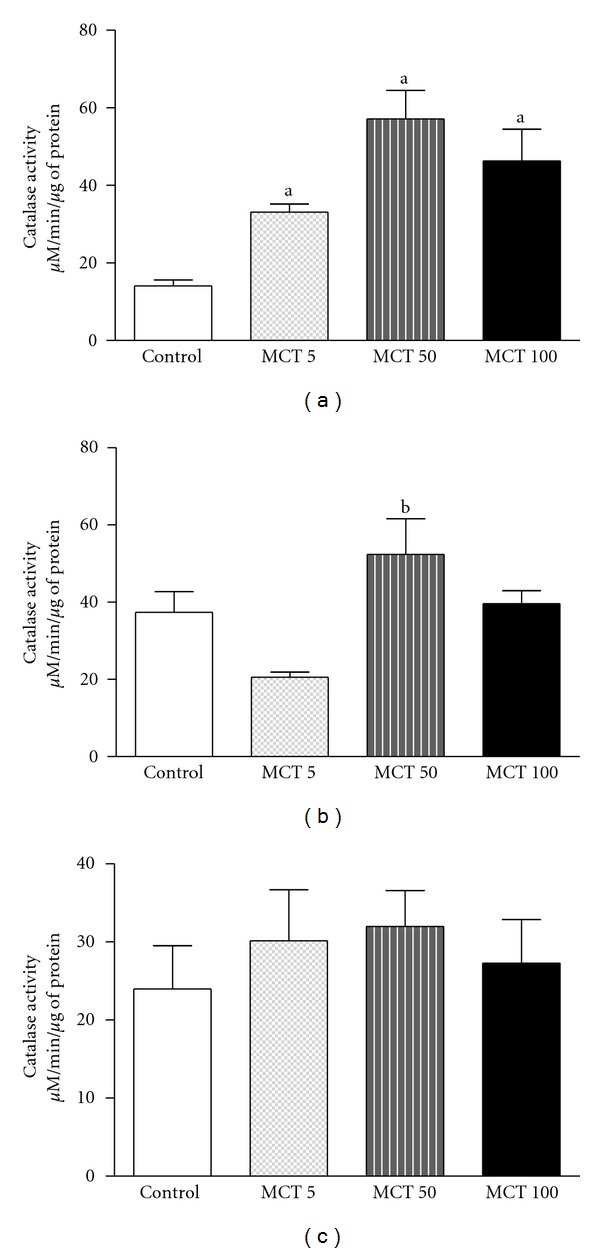
Catalase activity in HC (a), PFC (b), or ST (c) of adult mice treated with vehicle or MCT (5, 50 or 1000 mg/kg). The results are presented as mean ± S.E.M. In parentheses, there is the number of animals per group. ((a) and (b)) P < 0.05 when compared to controls or MCT 5 mg/kg, respectively, (ANOVA and Student-Newman-Keuls test as a post hoc).
4. Discussion
The alkaloids are molecules that may cause hepatotoxic, pneumotoxic, mutagenic, and neurotoxic effects [4]. Kimberley horse disease is observed in horses intoxicated with monocrotaline (pyrrolizidine alkaloid) and it presents neurological symptoms which have been associated with neural alteration [30]. On this way, Nobre et al. observed that animals intoxicated with MCT showed clinical symptoms related to CNS such as depression, decreased locomotor activity, and motor incoordination [9, 24].
Our histopathological results showed that 50 or 100 mg/kg of monocrotaline caused lesions in the hippocampus and parahippocampal cortex regions. Lesions observed in our work were severe structural disorganization, edema, moderate pyknotic cells, vacuolization, and inflammatory cell infiltration. These results are according to previous studies that showed vacuolization and increase in cell body in cortical astrocyte/neuron primary co-ultures, referring to neuronal damage induced by MCT [31]. Similarly, another study showed that pyrrolizidine alkaloid monocrotaline induced cytotoxicity, morphological changes, and oxidative and genotoxic damages to glial cells, using the human glioblastoma cell line GL-15 as a model [32]. The results of monocrotaline immunochemistry in two doses showed an increase of caspase 3 in brain areas compared to control, indicating apoptosis, so these results are according to histological data. Apoptosis is characterized by DNA fragmentation, membrane blebbing, cell shrinkage, and disassembly into membrane-enclosed vesicles, which prevents a host inflammatory response to intracellular components [33]. At molecular level, classical apoptosis is caused by the activation of a family of cysteine protease known as caspases that cleave their target protein at specific aspartic acids. Two major apoptotic pathways culminate in the activation of downstream executioner caspases 3 and 6 [34, 35]. So caspase 3 is an immunohistochemistry marker to apoptosis.
Based on these histological alterations in hippocampus and parahippocampal cortex regions and behavioral studies that demonstrated that MCT is able to cause serious alterations in CNS [9, 13, 24], we decided to investigate oxidative stress in HC, PFC, and ST of mice treated with MCT. These brain areas were selected due to susceptibility to oxidative stress and they are involved with motor behavior.
Several studies have shown that ROS have an important role in the pathogenesis of many diseases, especially neurological and psychiatric diseases [36–38]. Oxidative stress may be a common pathogenic mechanism underlying many disorders in CNS, since the brain has comparatively greater vulnerability to oxidative damage [39]. The data presented in this study demonstrated that MCT (50 or 100 mg/kg) in the three brain areas increased TBARS, indicating an increase in lipid peroxidation. Membrane lipid derangements, including lipid peroxidation, have been reported to contribute significantly to paroxysmal membrane dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases [40]. McEwen indicates that stressors were having neurotoxic effects on the hippocampus which predisposes to the development of depression [41]. Our results showed that the dose of MCT 50 or 100 mg/kg could contribute to alteration in CNS due to increased lipid peroxidation in the HP, PFC, and ST. In fact, besides the brain is more vulnerable to injury by lipid peroxidation products than other tissues, animals with high OS have an increase in prostaglandin levels and the overproduction of the compounds could release O2 − and OH• [42].
Many studies have focused on the biochemical and molecular actions of nitric oxide (NO) in normal conditions, as well as its potential alteration in CNS [37, 43, 44]. We investigated MCT effects on nitrite levels and observed low levels of nitrite in all studied brain areas after MCT administration. The low response in the levels of nitrite/nitrate and in the values of HC, PFC, and ST may has occurred because the nitric oxide is an unstable molecule [45, 46]. In the CNS, the major reactive nitrogen species (RNS) mediator of oxidative stress is peroxynitrite ONOO− [47]. The participation of peroxynitrite in oxidative stress is difficult to determine due to their reduced life span and interaction with other molecules [48]. However, it has been demonstrated that stressful conditions produce changes in NO metabolism and glutamatergic receptors to produce part of its stimulatory action on the CNS [49]. NO, in physiological levels, participates in a variety of physiological processes consisting of neurotransmission and regulation of blood vessel wall [50].
An elevation in free radical formation can be accompanied by an immediate compensatory increase in the activities of the free radical scavenging enzymes [51]. In our experimental situation, the catalase activity followed the increased levels of lipid peroxidation only in the HC. HC is extremely sensitive to the OS effects as compared to other brain areas [52]. The greater susceptibility of the HC to stress in comparison to the other tissues can be explained on the basis of the differential blood supply to these regions and it is more deeply situated in the diffusion of respiratory gases [53]. These results may represent a neuroprotective mechanism of catalase against the oxidative effects caused by MCT administration related to TBARS increase in the brain regions studied.
Oxidative stress has been related to many neurodegenerative diseases, such as ischemia and Parkinson disease [16]. Rotenone, a chemical that belongs to the family of isoflavones naturally found in the roots and stems of several plants, is used as a broad-spectrum pesticide [54]. It has characteristics alike MCT, such as potent inhibitor of mitochondrial complex-I and crosses the blood-brain barrier as well as the cell membrane easily because of its lipophilic structure [55]. The present results showed that MCT increases lipidic peroxidation and catalase activity, only in HC, while it decreases nitrite/nitrate contente. Hippocampus was probably more affected because it is a rich area in mitochondria. These are related to a production of antioxidant defense when the brain is attacked by a harmful agent as monocrotaline [56, 57]. Rotenone, a neurotoxin used as a Parkinson model, also augments lipidic peroxidation and nitric oxide content in chronically treated rats [54]. This substance also increases catalase activity after chronic administration to rats [55].
5. Conclusion
Our findings showed that monocrotaline caused cell lesions in the HC and PFC regions. Also, it produced oxidative stress in the HC, PFC, and ST in mice. These alterations may contribute to the neurological effects related to this compound.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge support from the Brazilian National Research Council (CNPq).
References
- 1.Huxtable RJ. Activation and pulmonary toxicity of pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 1990;47(3):371–389. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vasconcelos SMM, Honório-Júnior JER, Abreu RNDC, Silva MCC, Barbosa-Filho JM, Lobato RFG. Pharmacologic study of some plant species from the Brazilian Northeast: Calotropis procera Agava sisalana, Solanum paludosum, Dioscorea cayenensis and Crotalaria retusa In: Varela A, Jasiah Ibanez J, editors. , Medicinal Plants: Classification, Biosynthesis and Pharmacology. Vol. 4. Hauppauge, NY, USA: Nova Science; 2009. pp. 189–202. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kosogof C, Tepe JJ, Williams RM. DNA cross-linking by a phototriggered pyrrolic progenitor developed from monocrotaline. Tetrahedron Letters. 2001;42(38):6641–6643. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yan CC, Huxtable RJ. Effects of taurine and guanidinoethane sulfonate on toxicity of the pyrrolizidine alkaloid monocrotaline. Biochemical Pharmacology. 1996;51(3):321–329. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(95)02185-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mingatto FE, Dorta DJ, dos Santos AB, et al. Dehydromonocrotaline inhibits mitochondrial complex I. A potential mechanism accounting for hepatotoxicity of monocrotaline. Toxicon. 2007;50(5):724–730. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2007.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.de Souza AC, Hatayde MR, Bechara GH. Pathological aspects of poisoning by Crotalaria spectabilis (Fabaceae) seeds in swine. Pesquisa Veterinaria Brasileira. 1997;17(1):12–18. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Petry TW, Bowden GT, Huxtable RJ, Sipes IG. Characterization of hepatic DNA damage induced in rats by the pyrrolizidine alkaloid monocrotaline. Cancer Research. 1984;44(4):1505–1509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rose AL, Garden CA, McConnell JD, Bull LB. Field and experimental investigations of, “walk-about” disease of horses (Kimberly horse disease) in Northern Australia. Crotalaria poisoning in horses. Australian Veterinary Journal. 1957;33:25–33. [Google Scholar]
- 9.da Trindade Nobre VM, Riet-Correa F, Dantas AF, Barbosa Filho JM, Tabosa IM, Vasconcelos JS. Poisoning by Crotalaria retusa (Fabaceae) in Equidae in the semiarid region of Paraíba. Pesquisa Veterinaria Brasileira. 2004;24(3):132–143. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sies H, Cadenas E. Oxidative stress: damage to intact cells and organs. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society. 1985;311(1152):617–631. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1985.0168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Joseph B, Kumaran V, Berishvili E, Bhargava KK, Palestro CJ, Gupta S. Monocrotaline promotes transplanted cell engraftment and advances liver repopulation in rats via liver conditioning. Hepatology. 2006;44(6):1411–1420. doi: 10.1002/hep.21416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Morimatsu Y, Sakashita N, Komohara Y, et al. Development and characterization of an animal model of severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Journal of Vascular Research. 2011;49(1):33–42. doi: 10.1159/000329594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Huxtable RJ, Yan CC, Wild S, Maxwell S, Cooper R. Physicochemical and metabolic basis for the differing neurotoxicity of the pyrrolizidine alkaloids, trichodesmine and monocrotaline. Neurochemical Research. 1996;21(2):141–146. doi: 10.1007/BF02529131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Graham DG. Oxidative pathways for catecholamines in the genesis of neuromelanin and cytotoxic quinones. Molecular Pharmacology. 1978;14(4):633–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Poljsak B, Milisav I. The neglected significance of, ‘antioxidative stress’. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2012;2012:12 pages. doi: 10.1155/2012/480895.480895 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine. 1999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dugan LL, Choi DW. Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury and oxidative stress. In: Siegel GJ, Agranoff BW, Alberts EW, Fisher SK, Uhler MD, editors. Basic Neurochemistry: Molecular, Cellular and Medical Aspects. 6th edition. Baltimore, Md, USA: Williams & Wilkins; 1999. pp. 722–723. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bergamini CM, Gambetti S, Dondi A, Cervellati C. Oxygen, reactive oxygen species and tissue damage. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2004;10(14):1611–1626. doi: 10.2174/1381612043384664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gottlieb M, Leal-Campanario R, Campos-Esparza MR, et al. Neuroprotection by two polyphenols following excitotoxicity and experimental ischemia. Neurobiology of Disease. 2006;23(2):374–386. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2006.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Aziz SM, Toborek M, Hennig B, Endean E, Lipke DW. Polyamine regulatory processes and oxidative stress in monocrotaline-treated pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Cell Biology International. 1997;21(12):801–812. doi: 10.1006/cbir.1997.0200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Huong NTT, Matsumoto K, Kasai R, Yamasaki K, Watanabe H. In vitro antioxidant activity of Vietnamese ginseng saponin and its components. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 1998;21(9):978–981. doi: 10.1248/bpb.21.978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Barreiro EJ, Pereira AL, Gomes LNLF, Silva JR. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance of pyrrolizidine alkaloids: a reassignment. Journal of Chemical Research. 1980:330–331. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cheng DL, Tu SB, Enti AA, Roder E. Occurrence of the pyrrolizidine alkaloid monocrotaline in Crotalaria assamica Benth. and Crotalaria calycina Schrank. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 1986;54(4):351–355. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nobre VMT, Dantas AFM, Riet-Correa F, Barbosa Filho JM, Tabosa IM, Vasconcelos JS. Acute intoxication by Crotalaria retusa in sheep. Toxicon. 2005;45(3):347–352. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2004.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gilat E, Kadar T, Levy A, et al. Anticonvulsant treatment of sarin-induced seizures with nasal midazolam: an electrographic, behavioral, and histological study in freely moving rats. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 2005;209(1):74–85. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2005.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hsu SM, Raine L. Protein A, avidin, and biotin in immunohistochemistry. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 1981;29(11):1349–1353. doi: 10.1177/29.11.6172466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Maehly AC, Chance B. The assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods of Biochemical Analysis. 1954;1:357–424. doi: 10.1002/9780470110171.ch14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Green LC, Tannenbaum SR, Goldman P. Nitrate synthesis in the germfree and conventional rat. Science. 1981;212(4490):56–58. doi: 10.1126/science.6451927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1951;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gardiner MR, Royce R, Bokora A. Studies on crotalaria crispata, a newly recognised cause of kimberley horse disease. Journal of Pathology & Bacteriology. 1965;89(1):43–55. doi: 10.1002/path.1700890106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pitanga BPS, Silva VDA, Souza CS, et al. Assessment of neurotoxicity of monocrotaline, an alkaloid extracted from Crotalaria retusa in astrocyte/neuron co-culture system. NeuroToxicology. 2011;32(6):776–784. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2011.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Silva-Neto JP, Barreto RA, Pitanga BPS, et al. Genotoxicity and morphological changes induced by the alkaloid monocrotaline, extracted from Crotalaria retusa, in a model of glial cells. Toxicon. 2010;55(1):105–117. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Crysns V, Yuan J. The cutting edge: caspases in apoptosis and disease. In: Lockshin R, zakeri Z, Tilly J, editors. When Cells Die. New York, NY, USA: Wiley-Liss; 1998. pp. 177–210. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kang JJ, Schaber MD, Srinivasula SM, et al. Cascades of mammalian caspase activation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1999;274(5):3189–3198. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.5.3189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Brito GAC, Fujji J, Carneiro-Filho BA, Lima AAM, Obrig T, Guerrant RL. Mechanism of Clostridium difficile toxin A-induced apoptosis in T84 cells. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2002;186(10):1438–1447. doi: 10.1086/344729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Essick EE, Sam F. Oxidative stress and autophagy in cardiac disease, neurological disorders, aging and cancer. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2010;3(3):168–177. doi: 10.4161/oxim.3.3.2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Aguiar CC, Almeida AB, Araujo PV, et al. Oxidative stress and epilepsy: literature review. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2012;2012:12 pages. doi: 10.1155/2012/795259.795259 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Takuma K, Baba A, Matsuda T. Astrocyte apoptosis: implications for neuroprotection. Progress in Neurobiology. 2004;72(2):111–127. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2004.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ng F, Berk M, Dean O, Bush AI. Oxidative stress in psychiatric disorders: evidence base and therapeutic implications. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;11(6):851–876. doi: 10.1017/S1461145707008401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Naffah-Mazzacoratti MG. Profile of prostaglandin levels in the rat hippocampus in pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Neurochemistry International. 1995;27(6):461–466. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(95)00053-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.McEwen BS, Sapolsky RM. Stress and cognitive function. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 1995;5(2):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bellissimo MI, Amado D, Abdalla DSP, Ferreira EC, Cavalheiro EA, Naffah-Mazzacoratti MG. Superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase activities and the hydroperoxide concentration are modified in the hippocampus of epileptic rats. Epilepsy Research. 2001;46(2):121–128. doi: 10.1016/s0920-1211(01)00269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zoroğlu SS, Herken H, Yürekli M, et al. The possible pathophysiological role of plasma nitric oxide and adrenomedullin in schizophrenia. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 2002;36(5):309–315. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3956(02)00014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Garg R, Kumar A. Possible role of citalopram and desipramine against sleep deprivation-induced anxiety like-behavior alterations and oxidative damage in mice. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology. 2008;46(11):770–776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bonner FT, Stedman G. Methods in Nitric Oxide Research. New York, NY, USA: John Wiley & Sons; 1996. The chemistry of nitric oxide and redox-related species; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bonner FT. Nitric oxide gas. Methods in Enzymology. 1996;268:50–57. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(96)68008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Beckman JS. The double-edged role of nitric oxide in brain function and superoxide-mediated injury. Journal of Developmental Physiology. 1991;15(1):53–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Fukuto J, Ignarro LJ. In vivo aspects of nitric oxide (NO) chemistry: does peroxynitrite (-OONO) play a major role in cytotoxicity? Accounts of Chemical Research. 1997;30(4):149–152. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ignarro LJ, Buga GM, Wood KS, Byrns RE, Chaudhuri G. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1987;84(24):9265–9269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Barros DO, Xavier SML, Barbosa CO, et al. Effects of the vitamin E in catalase activities in hippocampus after status epilepticus induced by pilocarpine in Wistar rats. Neuroscience Letters. 2007;416(3):227–230. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Watson BD. Evaluation of the concomitance of lipid peroxidation in experimental models of cerebral ischemia and stroke. Progress in Brain Research. 1993;96:69–95. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Erecinska M, Silver IA. Calcium handling by hippocampal neurons under physiologic and pathologic conditions. Advances in Neurology. 1996;71:119–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Dymond AM, Crandall PH. Oxygen availability and blood flow in the temporal lobes during spontaneous epileptic seizures in man. Brain Research. 1976;102(1):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90587-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Verma R, Nehru B. Effect of centrophenoxine against rotenone-induced oxidative stress in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochemistry International. 2009;55(6):369–375. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2009.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bashkatova V, Alam M, Vanin A, Schmidt WJ. Chronic administration of rotenone increases levels of nitric oxide and lipid peroxidation products in rat brain. Experimental Neurology. 2004;186(2):235–241. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2003.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lauritzen KH, Cheng C, Wiksen H, Bergersen LH, Klungland A. Mitochondrial DNA toxicity compromises mitochondrial dynamics and induces hippocampal antioxidant defenses. DNA Repair. 2011;10(6):639–653. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Dugan LL, Kim-Han JS. Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury and oxidative stress. In: Siegel GJ, editor. Basic Neurochemistry Molecular, Cellular, and Medical Aspects. Burlington, Mass, USA: Elsevier/Academic Press; 2006. [Google Scholar]


