Abstract
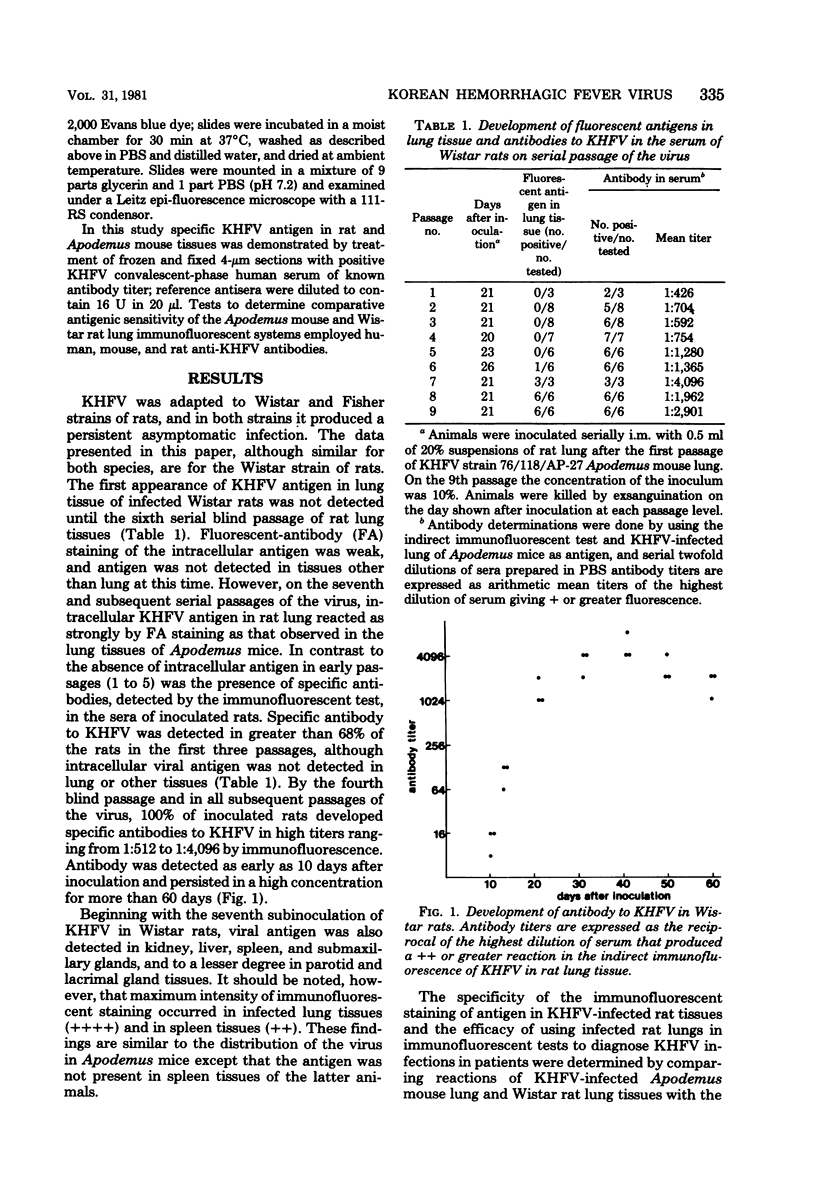
Korean hemorrhagic fever virus (KHFV) has been adapted to the Wistar and Fisher strains of rats. Infection was detected by the appearance of specific antigen in the lung tissue of the infected rats at 14 to 64 days after inoculation and by the appearance of circulating antibodies in ther serum which reacted specifically with KHFV antigen in the lungs of infected Apodemus agrarius subsp. coreae 3 weeks after inoculation. Distribution of antigen in rat tissues as determined by immunofluorescent staining was the same as that in Apodemus mice except that antigen was present in the spleens of rats. Adaptation of KHFV to the laboratory rat provides an animal model that is free of wild rodent viruses and is readily available for use in studies on the characterization of KHFV.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brummer-Korvenkontio M., Vaheri A., Hovi T., von Bonsdorff C. H., Vuorimies J., Manni T., Penttinen K., Oker-Blom N., Lähdevirta J. Nephropathia epidemica: detection of antigen in bank voles and serologic diagnosis of human infection. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):131–134. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CH'IU F. H., HOU T. C., HUANG P. S., LIU W. C., SUNG H. Y., LI Y. Epidemic hemorrhagic fever; investigations in T'uliho area, Inner Mongolia, and clinical study of 104 cases. Chin Med J. 1959 Jun;78:515–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAJDUSEK D. C. Virus hemorrhagic fevers. Special reference to hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (epidemic hemorrhagic fever). J Pediatr. 1962 Jun;60:841–857. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(62)80170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. W., Lee P. W., Johnson K. M. Isolation of the etiologic agent of Korean Hemorrhagic fever. J Infect Dis. 1978 Mar;137(3):298–308. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.3.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. W., Lee P. W., Lähdevirta J., Brummer-Korventkontio M. Aetiological relation between Korean haemorrhagic fever and nephropathia epidemica. Lancet. 1979 Jan 27;1(8109):186–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Xu Z. Y. Aetiological relation between Korean haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in People's Republic of China. Lancet. 1980 Apr 12;1(8172):819–820. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91311-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C., Hsiang C. M., Hsiung G. D. Identification of epidemic haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in China with Korean haemorrhagic fever. Lancet. 1980 May 10;1(8176):1025–1026. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91458-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manasia M., Olinic N., Zăgreanu I., Serban A. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: report of 11 observations. Int Urol Nephrol. 1977;9(2):177–184. doi: 10.1007/BF02082021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLANK J., REZUCHA M., ROJKOVIC D. Prvé dva diagnostikované prípady hemoragickej nefrózo nefritídy na území nasej republiky; vírová nefrózo-nefritída Dalekeho východu. Cas Lek Cesk. 1955 Sep 30;94(40):1078–1084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEEDY J. A., FROEB H. F., BATSON H. A., CONLEY C. C., MURPHY J. P., HUNTER R. B., CUGELL D. W., GILES R. B., BERSHADSKY S. C., VESTER J. W. The clinical course of epidemic hemorrhagic fever. Am J Med. 1954 May;16(5):619–628. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(54)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMADEL J. E. Epidemic hemorrhagic fever. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1953 Oct;43(10):1327–1330. doi: 10.2105/ajph.43.10.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr A., Lee H. W., Berglund A., Hoorn B., Nyström K., Gajdusek D. C. Epidemic nephropathy in Scandinavia is related to Korean haemorrhagic fever. Lancet. 1979 Jan;1(8107):100–100. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr A., Lee P. W., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Nyström K. Antigenic differentiation of the viruses causing Korean haemorrhagic fever and epidemic (endemic) nephropathy of Scandinavia. Lancet. 1980 Aug 9;2(8189):315–316. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90260-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMURA M. OCCURRENCE OF EPIDEMIC HEMORRHAGIC FEVER IN OSAKA CITY: FIRST CASES FOUND IN JAPAN WITH CHARACTERISTIC FEATURE OF MARKED PROTEINURIA. Biken J. 1964 Oct;7:79–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umenai T., Lee H. W., Lee P. W., Saito T., Toyoda T., Hongo M., Yoshinaga K., Nobunaga T., Horiuchi T., Ishida N. Korean haemorrhagic fever in staff in an animal laboratory. Lancet. 1979 Jun 23;1(8130):1314–1316. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91948-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesenjak-Hirjan J., Hrabar A., Vince-Ribarić V., Borcić B., Brudnjak Z. An outbreak of hemorrhagic fever with a renal syndrome in the Plitvice Lakes area (preliminary report). Folia Parasitol (Praha) 1971;18(3):275–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



