Abstract
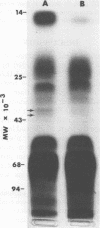
Immunochemical analyses of soluble antigens derived from microaerophilous stationary phase cultures of Babesia bovis demonstrated that at least three parasite antigens were released in vitro. These antigens have molecular weights within the range of 37,000 to 40,000, fast electrophoretic mobility in the albumin and alpha 1 regions, and are proteinaceous in nature as determined by the sensitivity to proteolytic enzymes trypsin and papain. Purification of these antigens should allow complete characterization of their respective physiochemical and immunogenic properties.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa M., Miller L. H., Johnson J., Rabbege J. Erythrocyte entry by malarial parasites. A moving junction between erythrocyte and parasite. J Cell Biol. 1978 Apr;77(1):72–82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C., Kreier J. P. Role of the surface coat in in vitro attachment and phagocytosis of Plasmodium berghei by peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):827–835. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.827-835.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke H. G., Freeman T. Quantitative immunoelectrophoresis of human serum proteins. Clin Sci. 1968 Oct;35(2):403–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Cline L. J. An improved stain for immunodiffusion tests. J Immunol Methods. 1977;17(3-4):379–381. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggitt M. J., Tappenden L., Brown K. N. Synthesis of Plasmodium knowlesi polypeptides in a cell-free system. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57 (Suppl 1):109–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erp E. E., Gravely S. M., Smith R. D., Ristic M., Osorno B. M., Carson C. A. Growth of Babesia bovis in bovine erythrocyte cultures. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Sep;27(5):1061–1064. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erp E. E., Smith R. D., Ristic M., Osorno B. M. Continuous in vitro cultivation of Babesia bovis. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Jul;41(7):1141–1142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodger B. V. Babesia argentina: intraerythrocytic location of babesial antigen extracted from parasite suspensions. Int J Parasitol. 1973 May;3(3):387–391. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(73)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodger B. V. Babesia argentina: observations on the immunogenicity of the cryofibrinogen complex. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Aug 25;53(1):47–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00383114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodger B. V. Babesia argentina: studies on the nature of an antigen associated with infection. Int J Parasitol. 1976 Jun;6(3):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(76)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodger B. V. Babesia bovis (= argentina): changes in erythrophylic and associated proteins during acute infection of splenectomized and intact calves. Z Parasitenkd. 1978 Mar 16;55(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00383470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodger B. V., Wright I. G., Mahoney D. F., McKenna R. V. Babesia bovis (Argentina): studies on the composition and location of antigen associated with infected erythrocytes. Int J Parasitol. 1980 Feb;10(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(80)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravely S. M., Smith R. D., Erp E. E., Cantó G. J., Aikawa M., Osorno B. M., Ristic M. Bovine babesiosis: partial purification and characterization of blood culture-derived Babesia bovis. Int J Parasitol. 1979 Dec;9(6):591–598. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(79)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G., Holasek A. Influence of dextran and polyethylene glycol on sensitivity of two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis and electroimmunodiffusion. Anal Biochem. 1972 Apr;46(2):680–683. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M. G., Ristic M. Babesia bovis: continuous cultivation in a microaerophilous stationary phase culture. Science. 1980 Mar 14;207(4436):1218–1220. doi: 10.1126/science.7355284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColm A. A., Shakespeare P. G., Trigg P. I. Release of protein by erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium knowlesi during cultivation in vitro. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):277–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Aikawa M., Dvorak J. A. Malaria (Plasmodium knowlesi) merozoites: immunity and the surface coat. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1237–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudzinska M. A., Trager W., Lewengrub S. J., Gubert E. An electron microscopic study of Babesia microti invading erythrocytes. Cell Tissue Res. 1976 Jun 28;169(3):323–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00219605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul K. W., Kreier J. P. Plasmodium berghei: immunization of rats with antigens from a population of free parasites rich in merozoites. Tropenmed Parasitol. 1977 Sep;28(3):302–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. D., Carpenter J., Cabrera A., Gravely S. M., Erp E. E., Osorno M., Ristic M. Bovine babesiosis: vaccination against tick-borne challenge exposure with culture-derived Babesia bovis immunogens. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Dec;40(12):1678–1682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida N., Nussenzweig R. S., Potocnjak P., Nussenzweig V., Aikawa M. Hybridoma produces protective antibodies directed against the sporozoite stage of malaria parasite. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):71–73. doi: 10.1126/science.6985745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]