Abstract
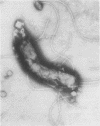
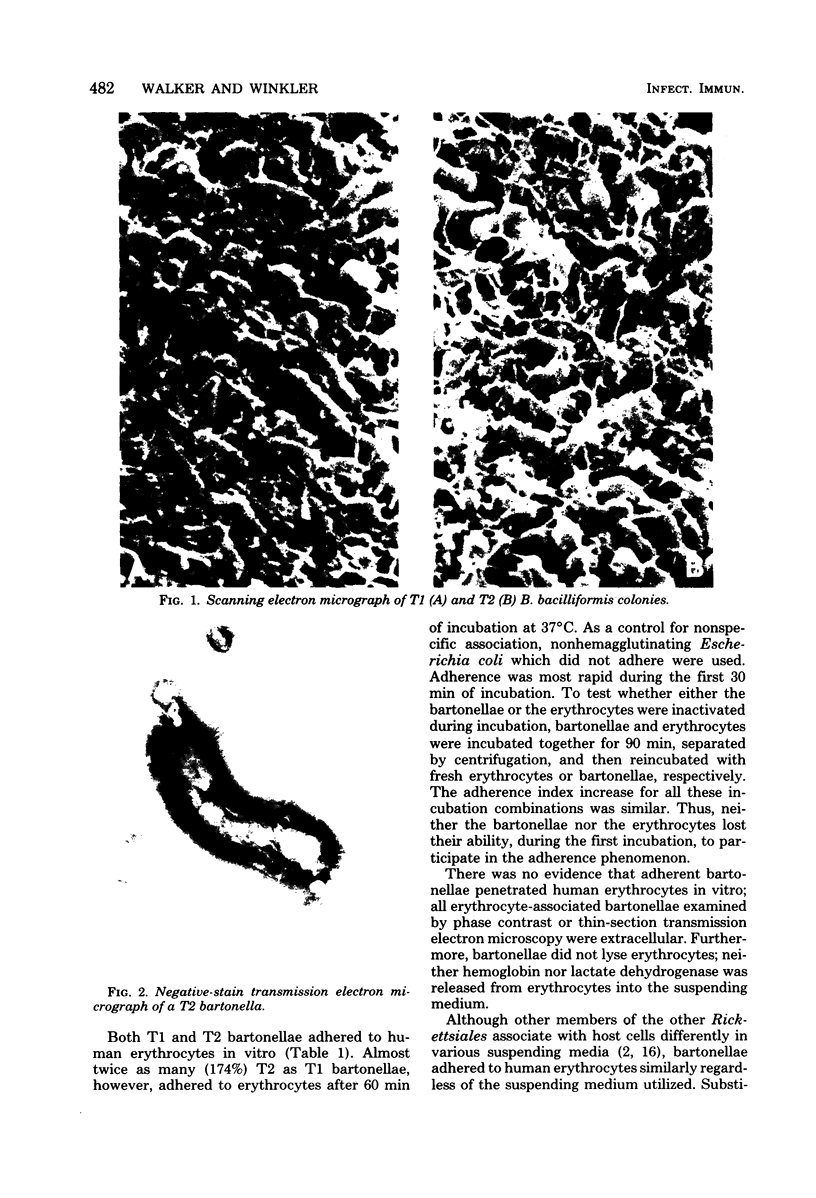
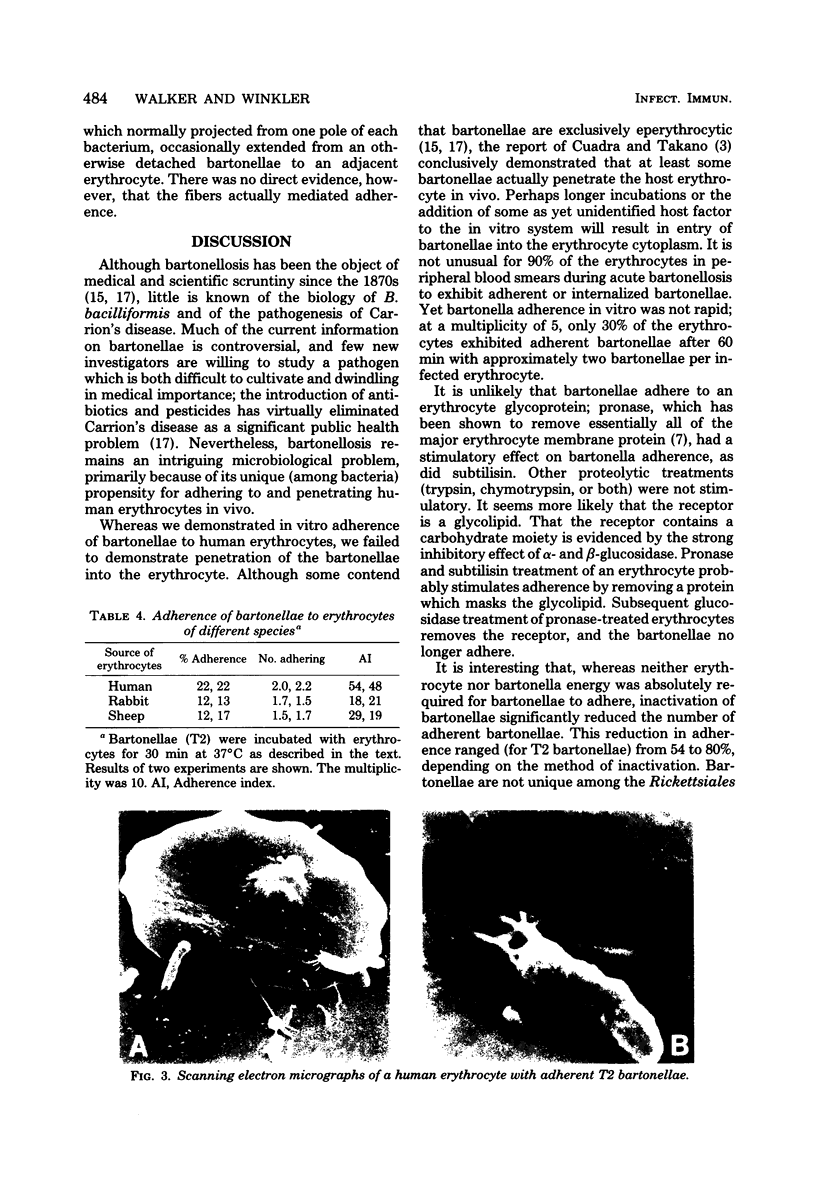
Bartonella bacilliformis was cultivated on a solid medium, and two bartonella colonial morphologies were differentiated and designated colony types T1 and T2. Although both T1 and T2 bartonellae adhered to human erythrocytes in vitro, approximately twice as many T2 bartonellae adhered as did T1. Maximum adherence required bartonella energy, most likely proton motive force-dependent motility. Bartonellae did not penetrate or lyse erythrocytes in vitro. Bartonellae adhered poorly to alpha- or beta-glucosidase-treated erythrocytes, but pronase or subtilisin treatment of erythrocytes stimulated adherence. This indicates that bartonellae probably adhere to an erythrocyte glycolipid moiety.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHN Z. A., BOZEMAN F. M., CAMPBELL J. M., HUMPHRIES J. W., SAWYER T. K. Study on growth of Rickettsia. V. Penetration of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi into mammalian cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1959 Mar 1;109(3):271–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuadra M., Takano J. The relationship of Bartonella bacilliformis to the red blood cell as revealed by electron microscopy. Blood. 1969 May;33(5):708–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden C. S., Eriksson B., Hanson L. A. Adhesion of Escherichia coli to human uroepithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):767–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.767-774.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Abrams G. D., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: adhesion to isolated rabbit brush border membranes and hemagglutinating activity. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):232–239. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.232-239.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: nature of the interaction with isolated rabbit brush border membranes and human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):240–245. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.240-245.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judson P. A., Anstee D. J. Comparative effect of trypsin and chymotrypsin on blood group antigens. Med Lab Sci. 1977 Jan;34(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERS D., WIGAND R. Neue Untersuchungen über Bartonella bacilliformis. I. Morphologie der Kulturform. Z Tropenmed Parasitol. 1952 Feb;3(3):313–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNAFARJE C., RAMOS J. The hemolytic anemia of human bartonellosis. Blood. 1961 May;17:562–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Winkler H. H. Rickettsial hemolysis: effect of metabolic inhibitors upon hemolysis and adsorption. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):550–555. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.550-555.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz M. G. A history of bartonellosis (Carrión's disease). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968 Jul;17(4):503–515. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1968.17.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIGAND R., PETERS D., URTEAGA O. Neue Untersuchungen über Bartonella bacilliformis. 4. Elektronenoptische Darstellung aus dem Blut. Z Tropenmed Parasitol. 1953 Oct;4(4):539–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIGAND R., WEYER F. Neue Untersuchungen über Bartonella bacilliformis. III. Ubertragungsversuche auf Rhesusaffen und auf Kleiderläuse. Z Tropenmed Parasitol. 1953 Mar;4(2):243–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Penetration of cultured mouse fibroblasts (L cells) by Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):200–208. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.200-208.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]