Abstract
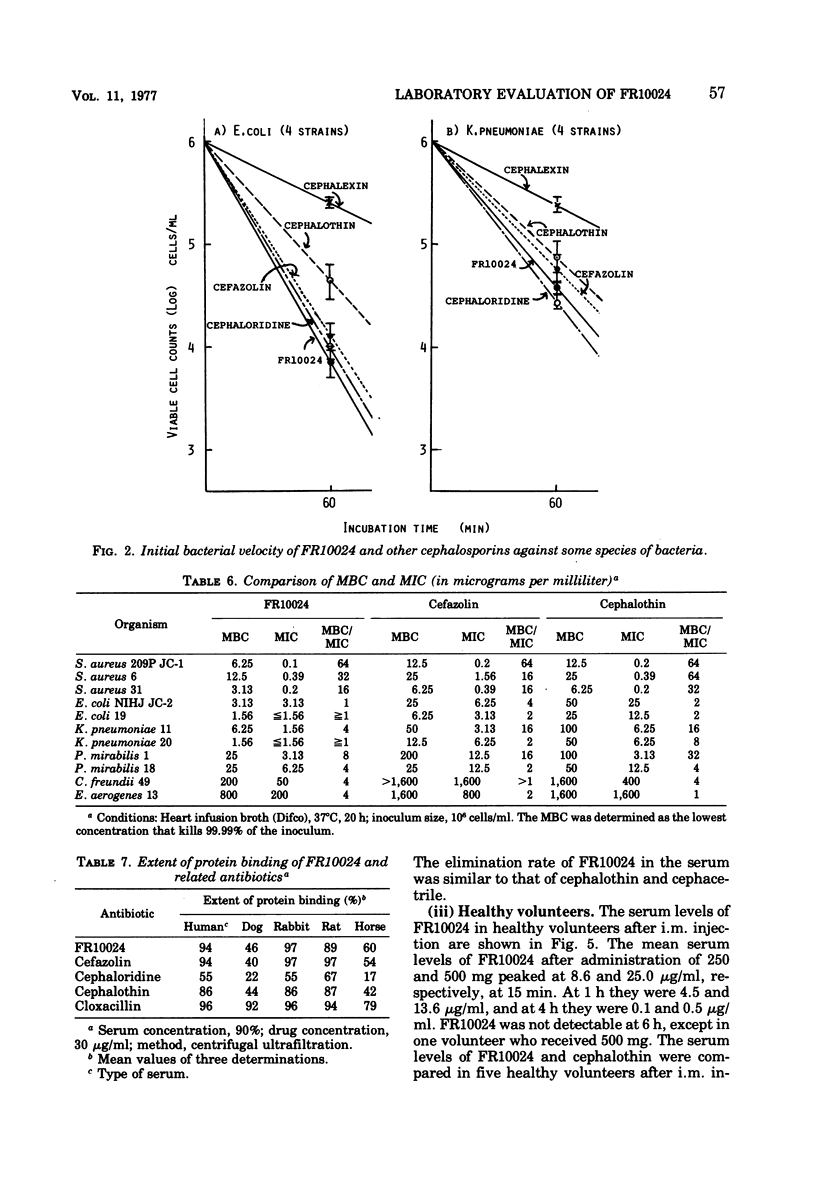
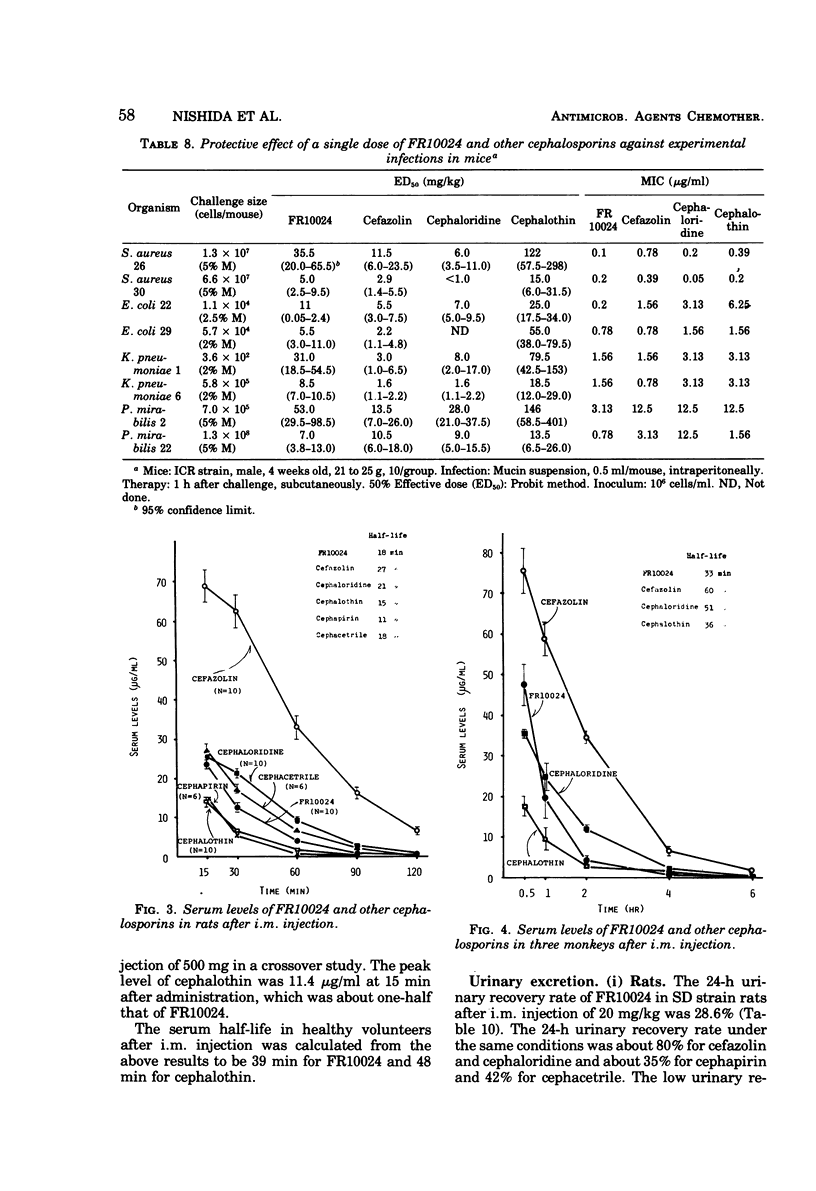
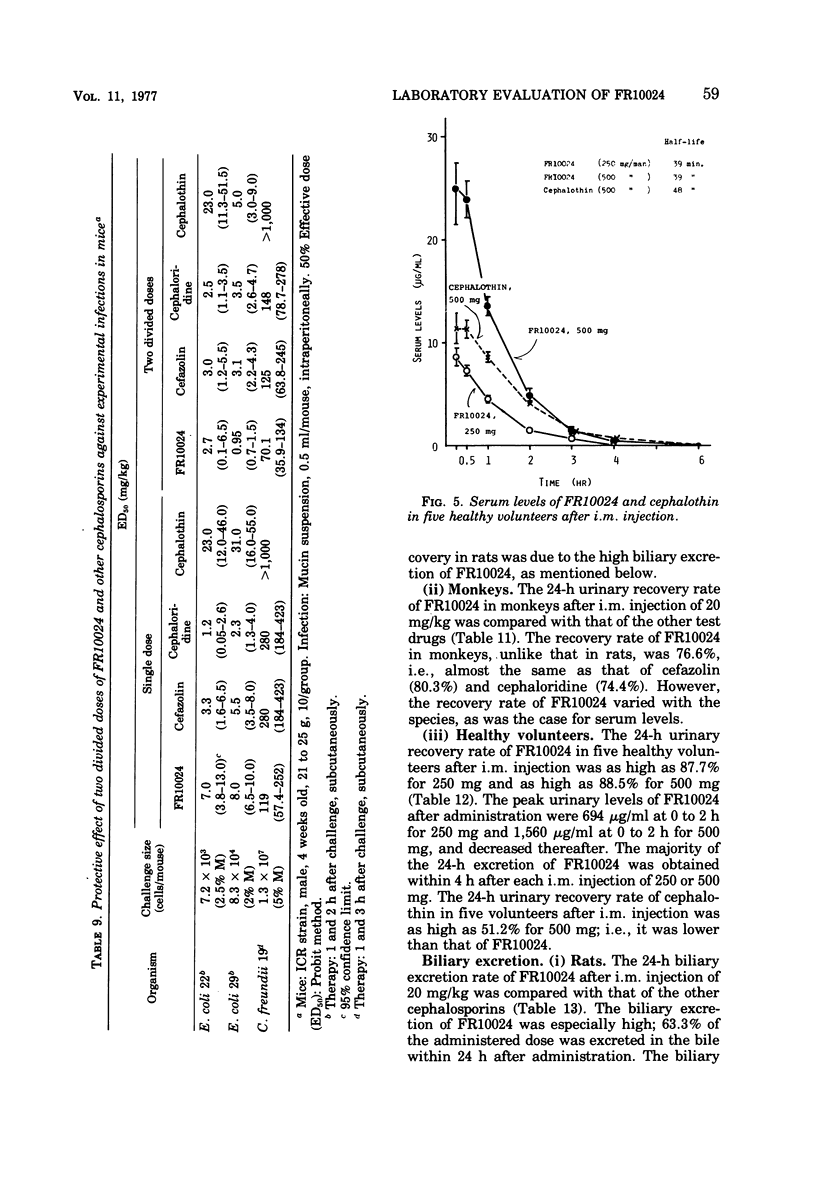
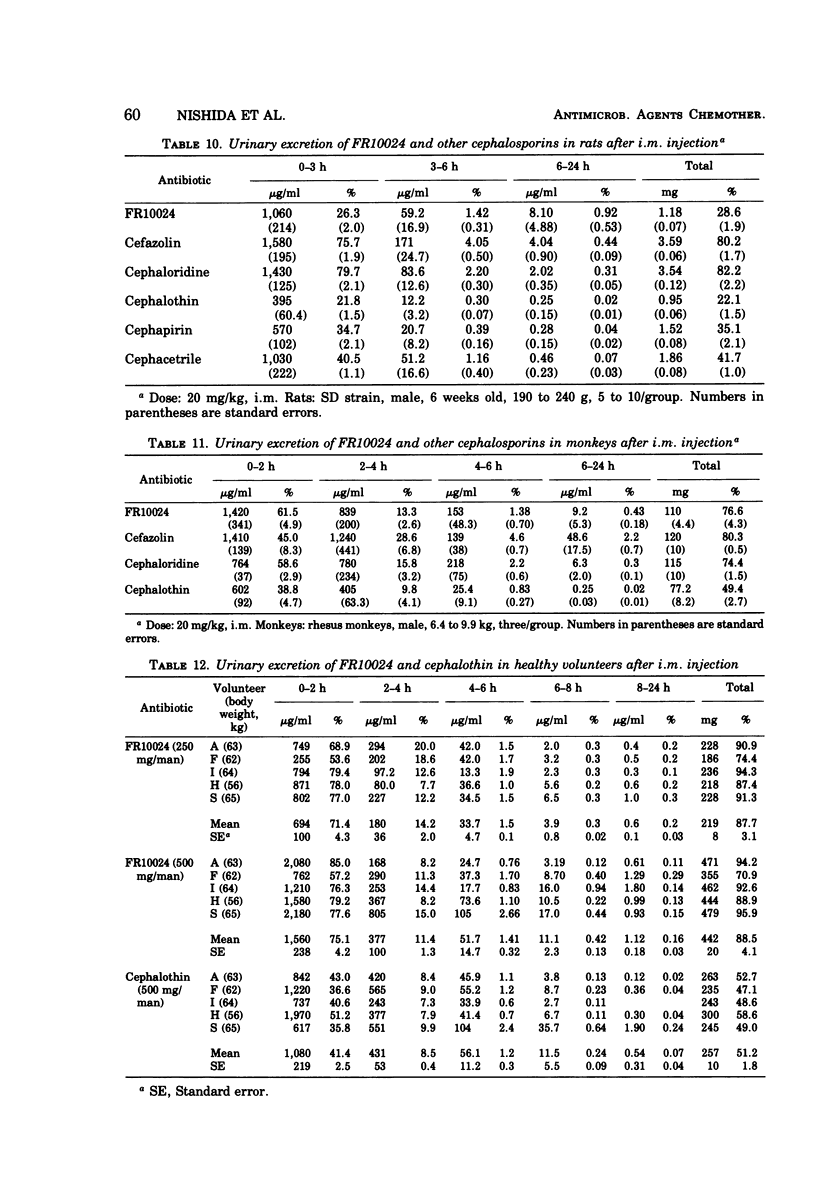
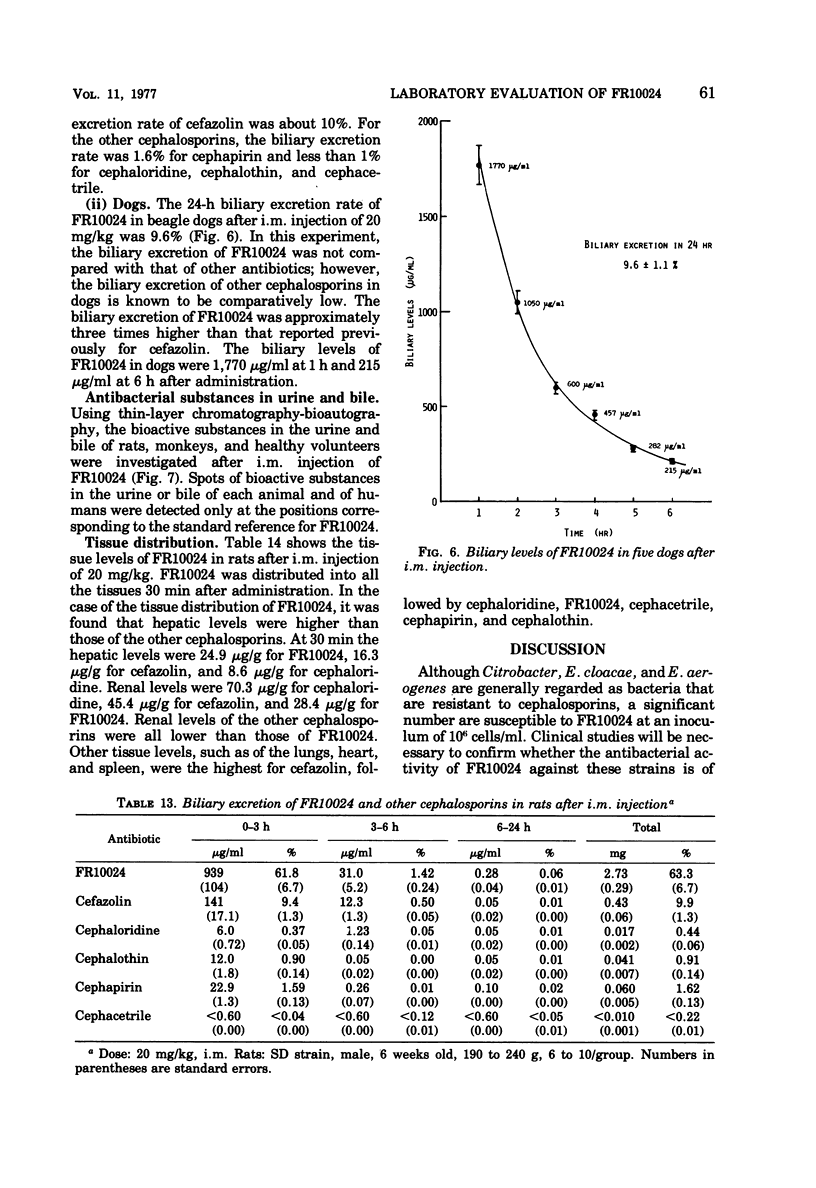
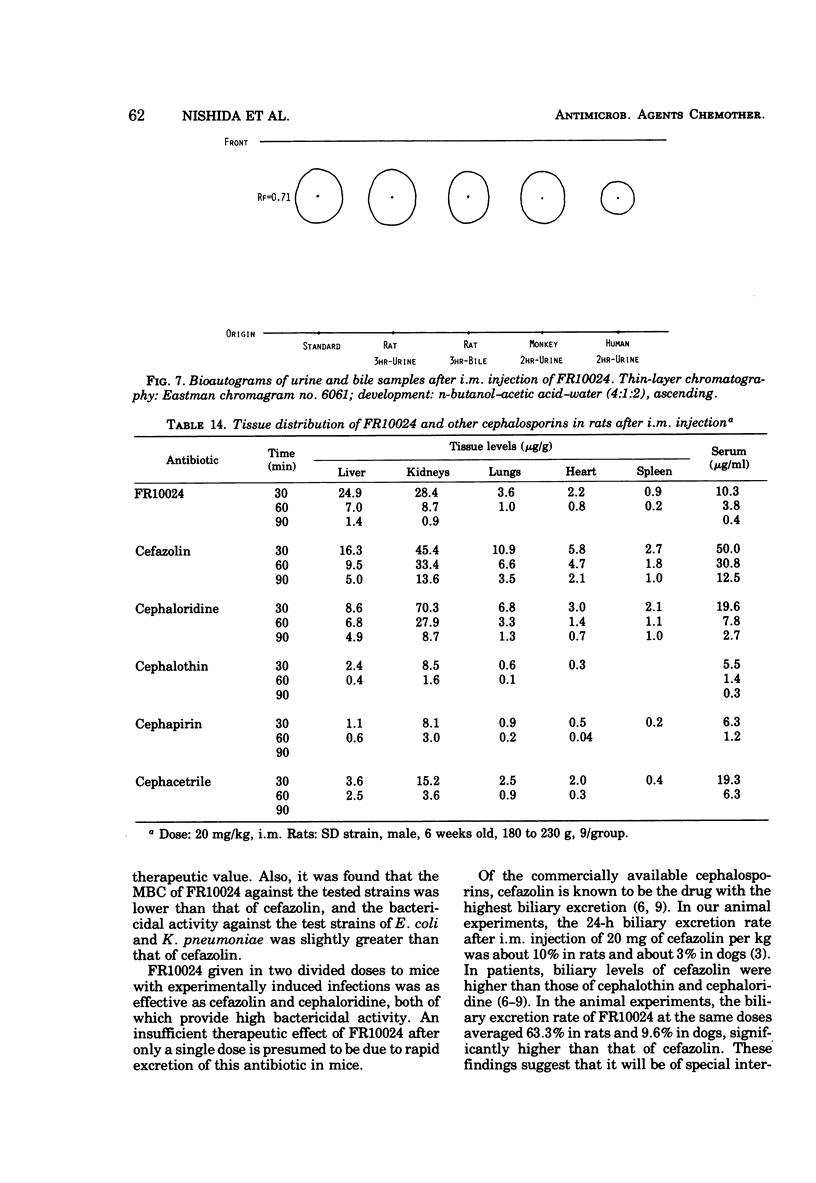
FR10024 is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. The in vitro antibacterial activity of FR10024 against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus mirabilis is greater than that of any of the cephalosporins developed to date. Indole-positive Proteus, Enterobacter, and Citrobacter are resistant to FR10024, as is true for the other cephalosporins. However, more than half of the strains of Enterobacter and Citrobacter tested were susceptible to FR10024 at an inoculum of 106 cells/ml. A single subcutaneous injection of FR10024 to mice with peritoneal infections due to S. aureus and several species of gram-negative bacilli gave a protective effect inferior to that of cefazolin but appeared to be superior to that of cephalothin. When given in two divided doses, however, the protective effect of FR10024 was enhanced and almost equaled that of cefazolin. The serum levels and rates of urinary recovery of FR10024 varied in different animal species. The mean peak serum level of FR10024 in humans after a single intramuscular injection of 500 mg was two times higher than that of cephalothin. The serum half-life after intramuscular injections of 250 and 500 mg was slightly shorter than that of cephalothin. After receiving 250 mg of FR10024 intramuscularly the urinary recovery rate was 87.7% in healthy volunteers. The biliary excretion rate of FR10024 was particularly high. The 24-h excretion of FR10024 in rats was 63.3%, this being six to seven times higher than that for cefazolin, which has the highest biliary excretion of the other known cephalosporins. When FR10024 was injected intramuscularly (20 mg/kg), it was found that the hepatic levels of FR10024 in rats were the highest of all the cephalosporins, including cefazolin, but the levels of FR10024 in other tissues were not as high as those of cefazolin.
Full text
PDF
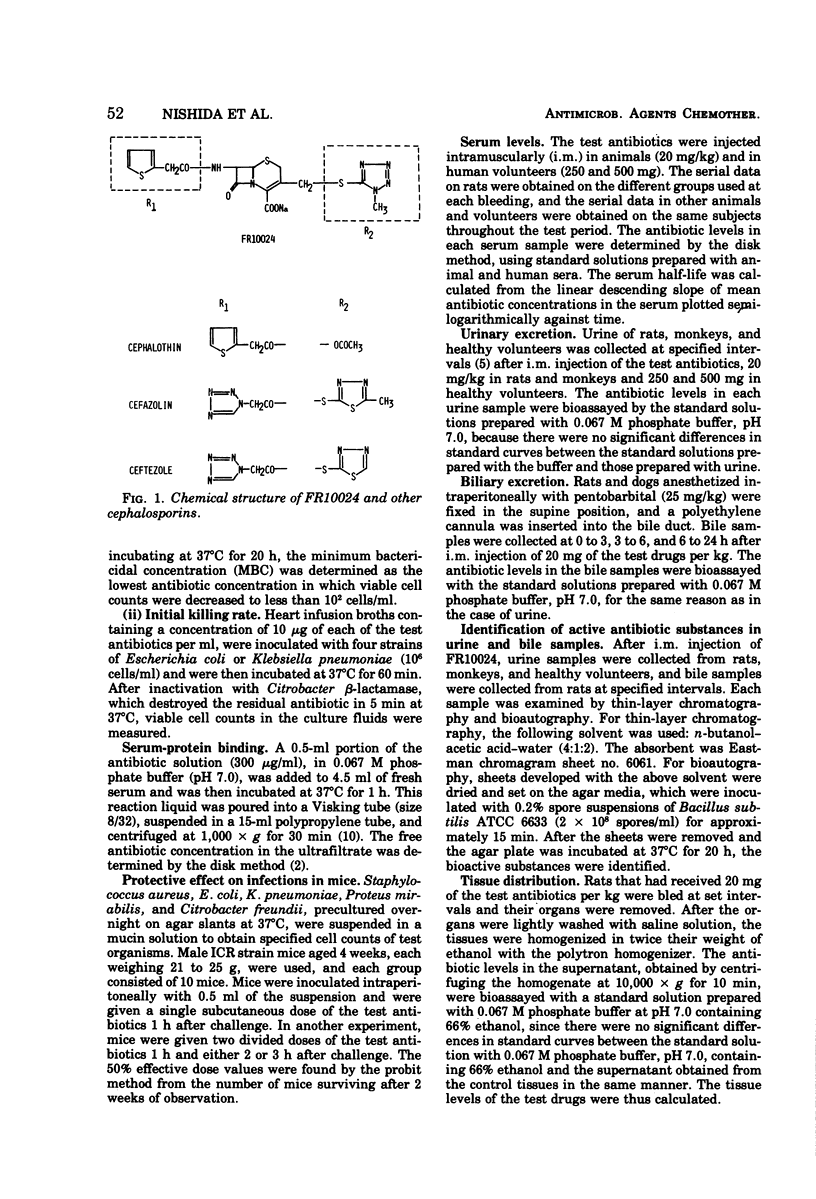
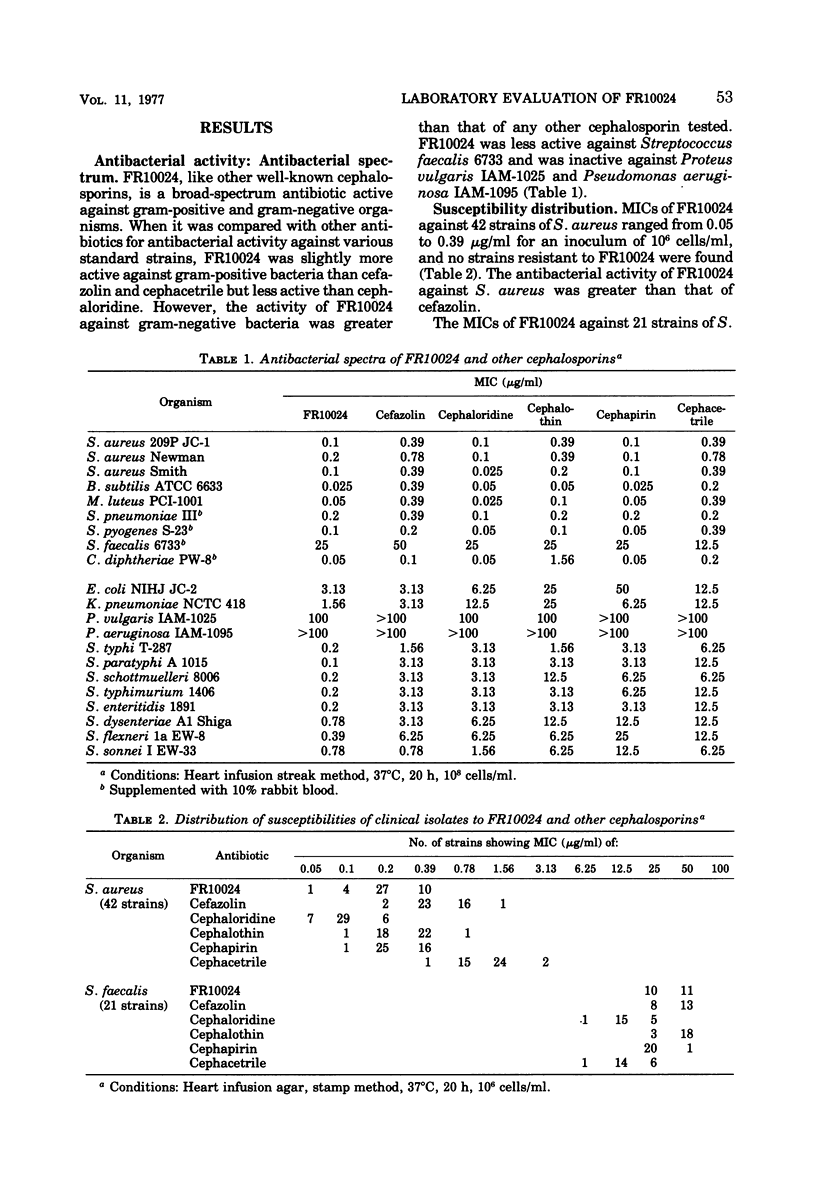
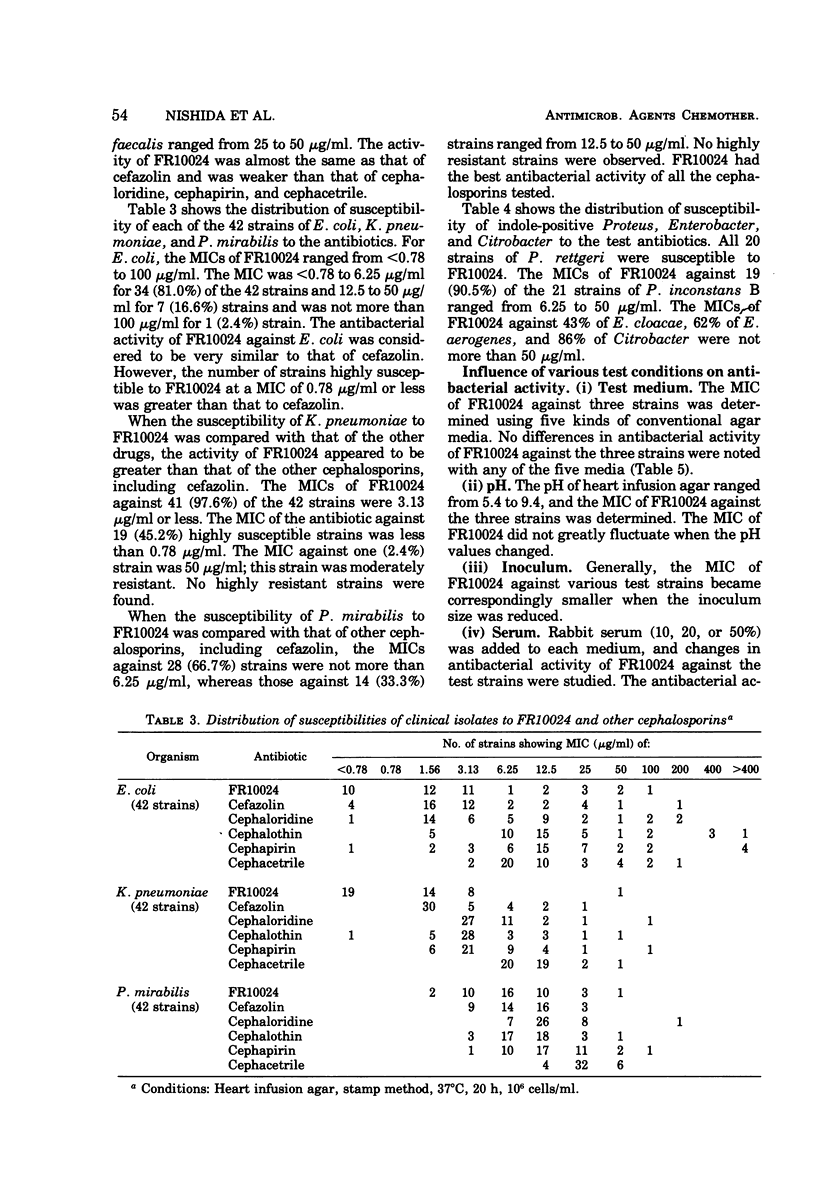

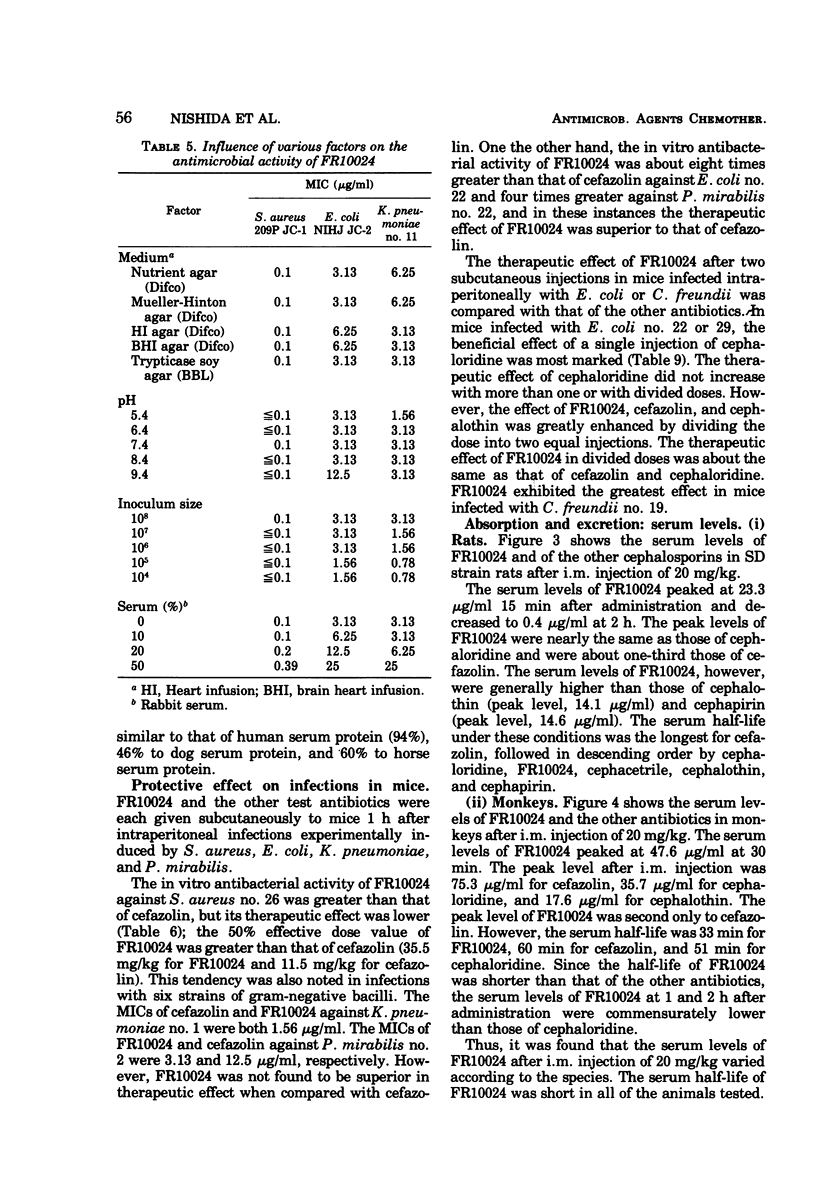

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brogard J. M., Haegele P., Dorner M., Lavillaureix J. Biliary excretion of a new semisynthetic cephalosporin, cephacetrile. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jan;3(1):19–23. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida M., Matsubara T., Murakawa T., Mine Y., Yokota Y. Cefazolin, a new semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic. II. In vitro and in vivo antimicrobial activity. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Mar;23(3):137–148. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida M., Matsubara T., Murakawa T., Mine Y., Yokota Y., Goto S., Kuwahara S. Cefazolin, a new semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic. 3. Absorption, excretion and tissue distribution in parenteral administration. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Apr;23(4):184–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida M., Murakawa T., Kamimura T., Okada N., Sakamoto H., Fukada S., Nakamoto S., Yokota Y., Miki K. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ceftezole, a new cephalosporin derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida M., Murakawa T., Matsubara T., Kohno Y., Yokota Y. Characteristics of biliary excretion of cefazolin and other cephalosporins with reference to the relationship between serum levels and administration conditions. Chemotherapy. 1976;22(1):30–36. doi: 10.1159/000221907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ram M. D., Watanatittan S. Levels of cefazolin in human bile. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(Suppl):S361–S363. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_2.s361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratzan K. R., Ruiz C., Irvin G. L., 3rd Biliary tract excretion of cefazolin, cephalothin, and cephaloridine in the presence of biliary tract disease. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Oct;6(4):426–431. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.4.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T. Studies on protein binding of cefazolin and other antibiotics. Jpn J Antibiot. 1974 Jun;27(3):296–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



