Abstract
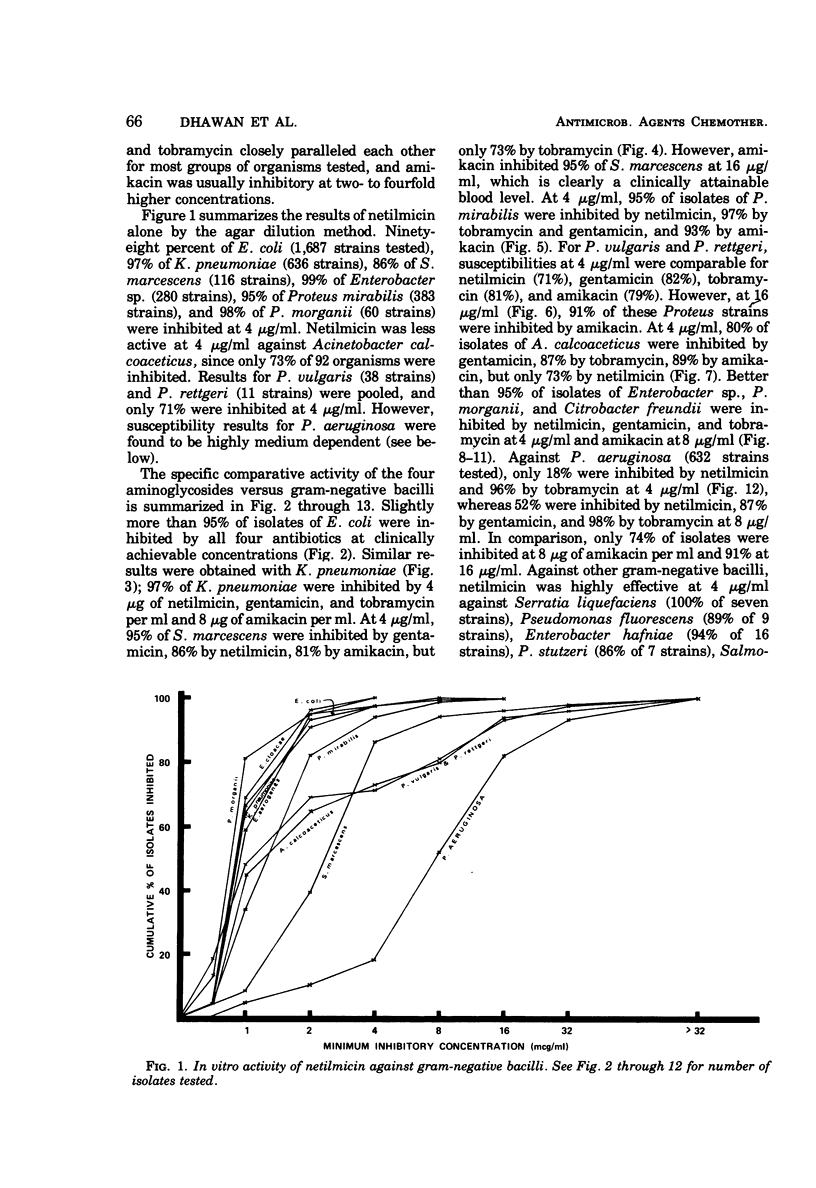
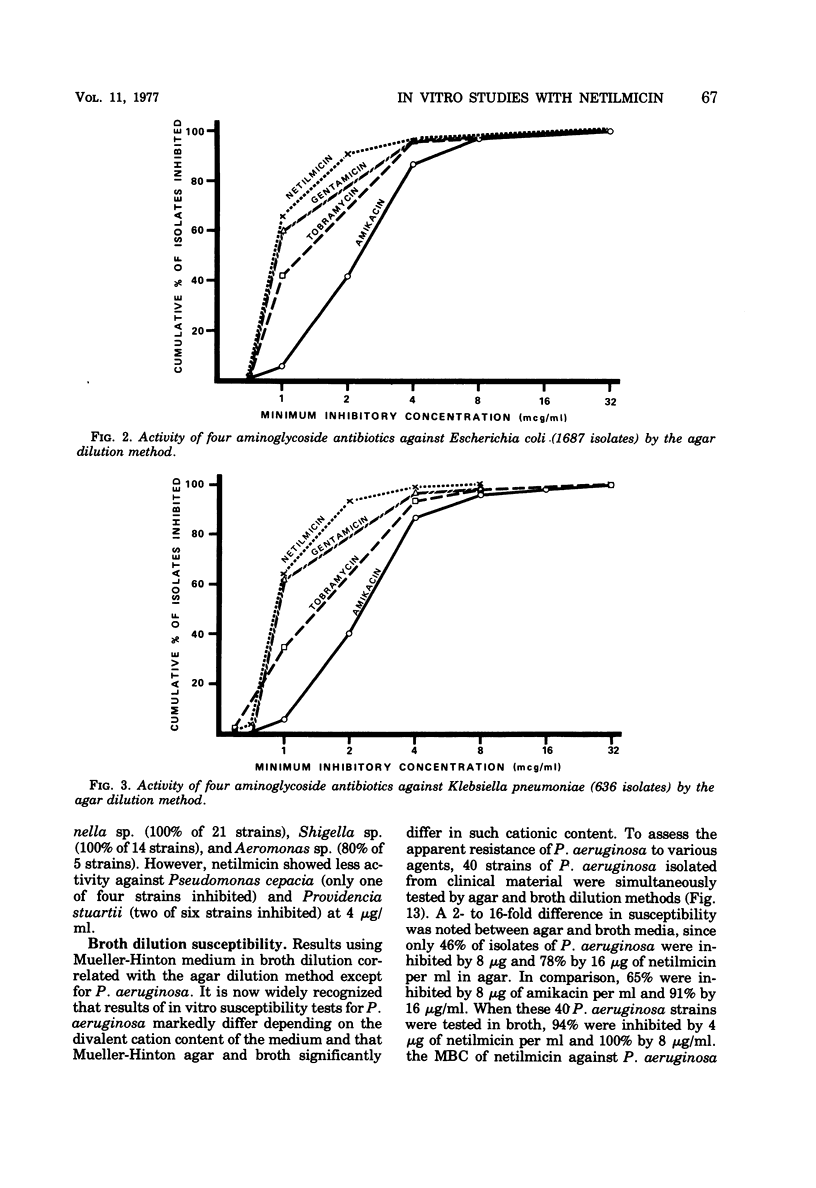
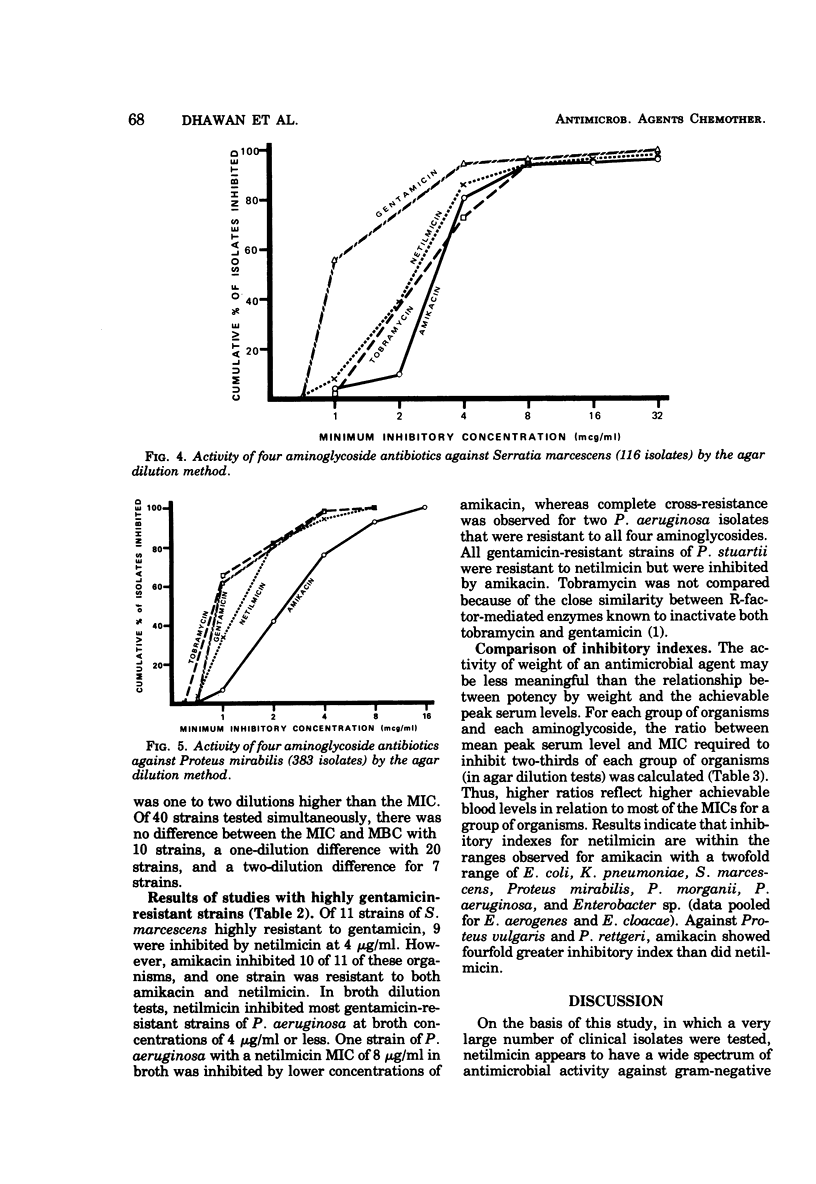
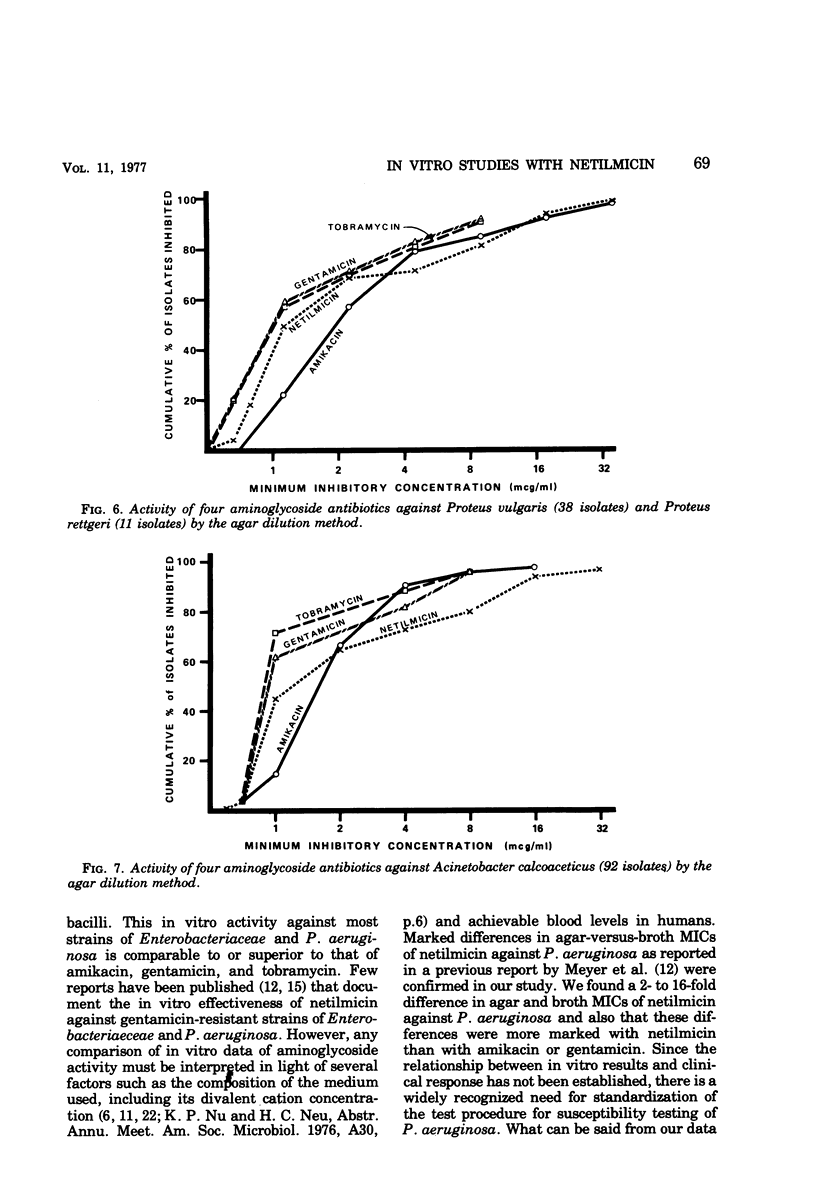
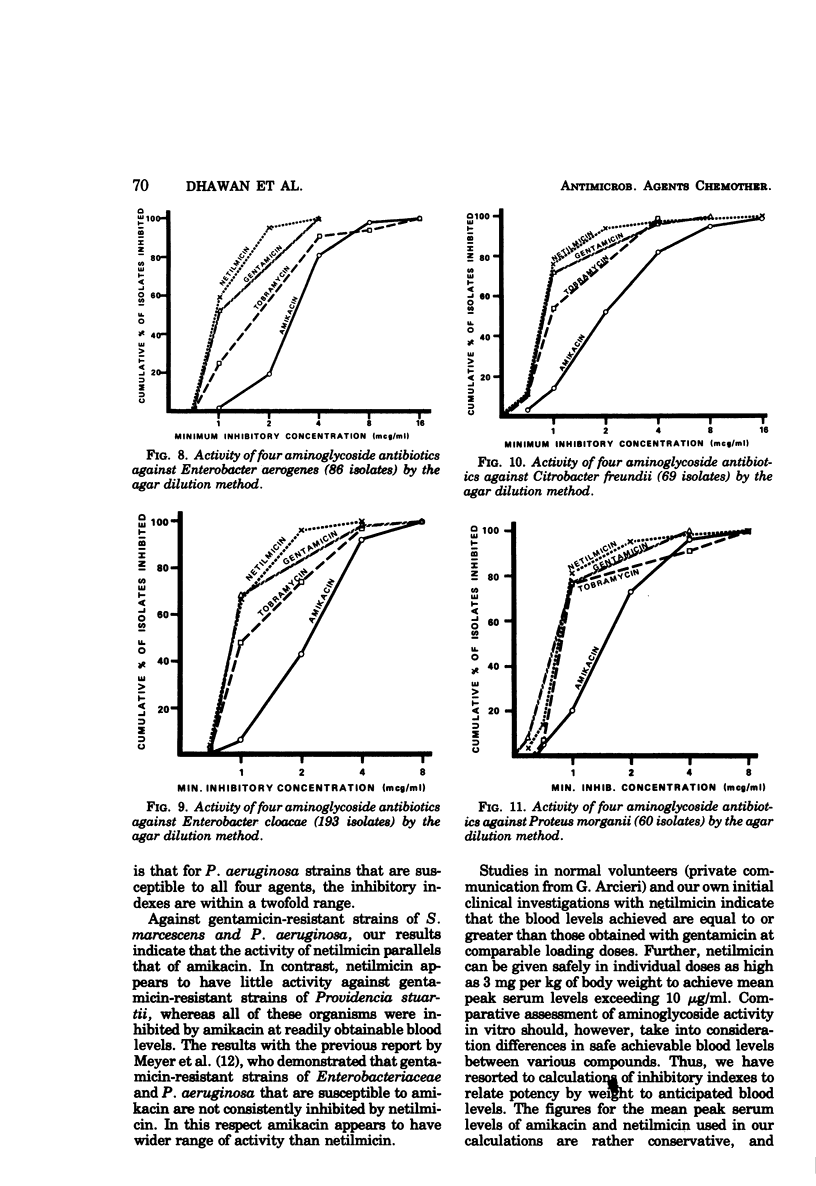
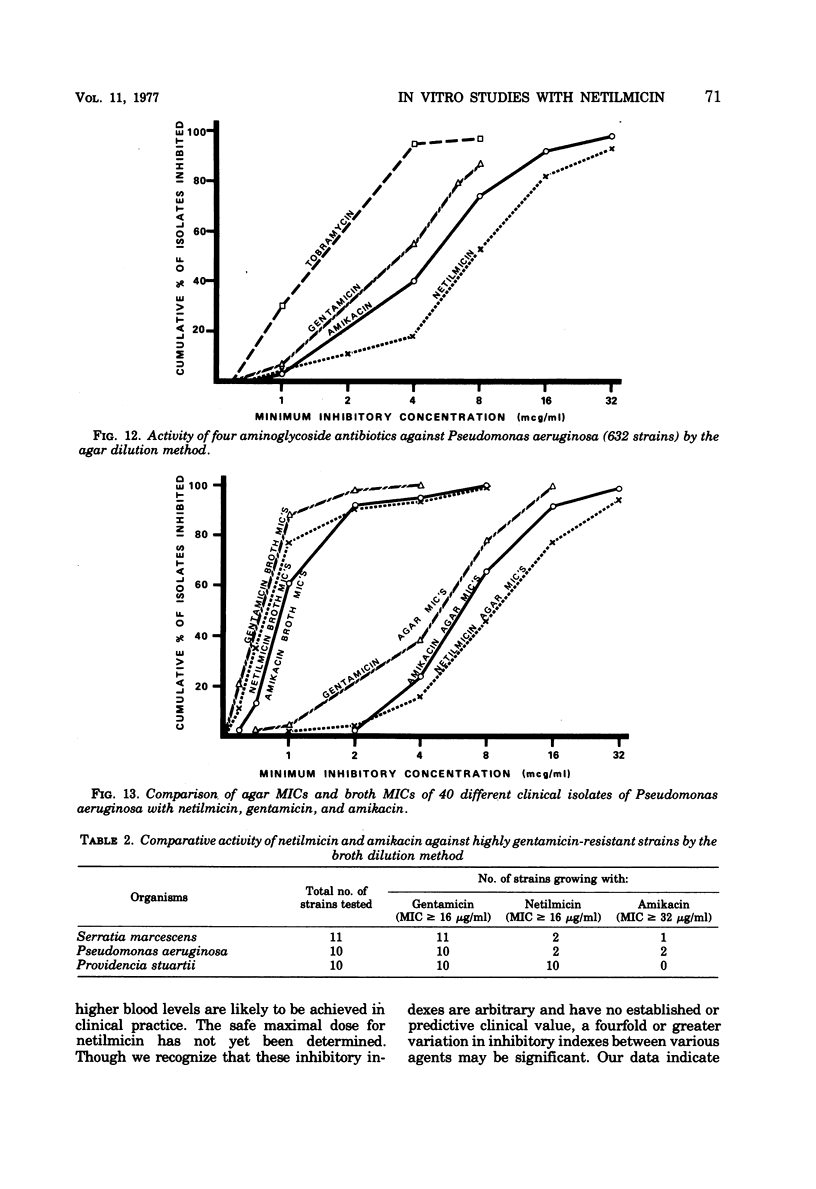
Netilmicin, a new semisynthetic aminoglycoside derived by ethylation of the 1-N position of the deoxystreptamine ring of sisomicin, was tested in vitro with 4,070 strains of gram-negative bacilli isolated at the UCLA Medical Center during 1975 to 1976, using the agar dilution technique and an inoculum of approximately 104 organisms. Results were compared with those simultaneously obtained for amikacin, gentamicin, and tobramycin. Using Mueller-Hinton medium, inhibitory concentrations in broth correlated with those obtained by the agar dilution method except for Pseudomonas aeruginosa, where a 2- to 16-fold difference in susceptibility was noted. For most clinically significant Enterobacteriaceae and P. aeruginosa, the activity of netilmicin in vitro was comparable or superior to that of gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin with respect to potency by weight and achievable blood levels. Against gentamicin-resistant strains (MIC > 16 μg/ml), the activity of netilmicin paralleled that of amikacin with the exception of Providencia stuartii, which was inhibited by amikacin but not by netilmicin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:471–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Shahrabadi M. S., van den Elzen H. M. Gentamicin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: R-factor-mediated resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):191–199. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Spink W. W. Infections due to gram-negative organisms: an analysis of 860 patients with bacteremia at the University of Minnesota Medical Center, 1958-1966. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 Jul;48(4):307–332. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196907000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson H. M., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;217(Suppl):1+–1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finland M. Changing patterns of susceptibility of common bacterial pathogens to antimicrobial agents. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Jun;76(6):1009–1036. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-6-1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod L. P., Waterworth P. M. Effect of medium composition on the apparent sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to gentamicin. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Sep;22(5):534–538. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.5.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Minshew B. H., Gould I. K., Sanford J. P. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to gentamicin and related aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):253–262. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C. M., Ikari N. S., Zimmerman J., Waitz J. A. A virulent nosocomial Klebsiella with a transferable R factor for gentamicin: emergence and suppression. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S24–S29. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., O'Brien T. F., Wacker W. E., Yulug N. F. Effect of salt concentration on the apparent in-vitro susceptibility of Pseudomonas and other gram-negative bacilli to gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S59–S64. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Draus L. L., Pasieczinik K. A. In vitro susceptibility of gentamicin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa to netilmicin and selected aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):677–681. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Lewis R. P., Halter J., White M. Gentamicin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens in a general hospital. Lancet. 1976 Mar 13;1(7959):580–583. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price K. E., Pursiano T. A., DeFuria M. D. Activity of BB-K8 (amikacin) against clinical isolates resistant to one or more aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):143–152. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahal J. J., Jr, Simberkoff M. S., Kagan K., Moldover N. H. Bactericidal efficacy of Sch 20569 and amikacin against gentamicin-sensitive and -resistant organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):595–599. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman J. A., Terry P. M., Hough C. E. Colonization with gentamicin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, pyocine type 5, in a burn unit. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S18–S23. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. B., Tomfohrde K. M., Rhoden D. L., Balows A. API system: a multitube micromethod for identification of Enterobacteriaceae. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Sep;24(3):449–452. doi: 10.1128/am.24.3.449-452.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein R. J., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Activity of three aminoglycosides and two penicillins against four species of gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):172–178. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Activity of five aminoglycoside antibiotics in vitro against gram-negative bacilli and Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Dec;4(6):617–625. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.6.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimelis V. M., Jackson G. G. Activity of aminoglycoside antibiotics aganst Pseudomonas aeruginosa: specificity and site of calcium and magnesium antagonism. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jun;127(6):663–669. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.6.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



