Abstract
Serum interferon activity was determined in 12 cynomolgus and 12 rhesus monkeys injected intravenously once daily for 10 days with from 0.1 to 6.0 mg of a stabilized polyriboinosinic acid · polyribocytidylic acid complex per kg, composed of polyriboinosinic acid · polyribocytidylic acid, poly-1-lysine, and carboxymethylcellulose [poly(ICLC)]. Interferon activity was detected 2 h after the first injection, with maximum activity occurring 8 h after the second injection. A period of hyporesponsiveness occurred after the third injection of poly(ICLC) in all monkeys and lasted until the sixth injection in the rhesus monkeys, when interferon activity again became more elevated. The delayed rebound was not as apparent in cynomolgus monkeys. Rhesus monkeys injected with 6 mg/kg did not exhibit serious side effects.
Full text
PDF
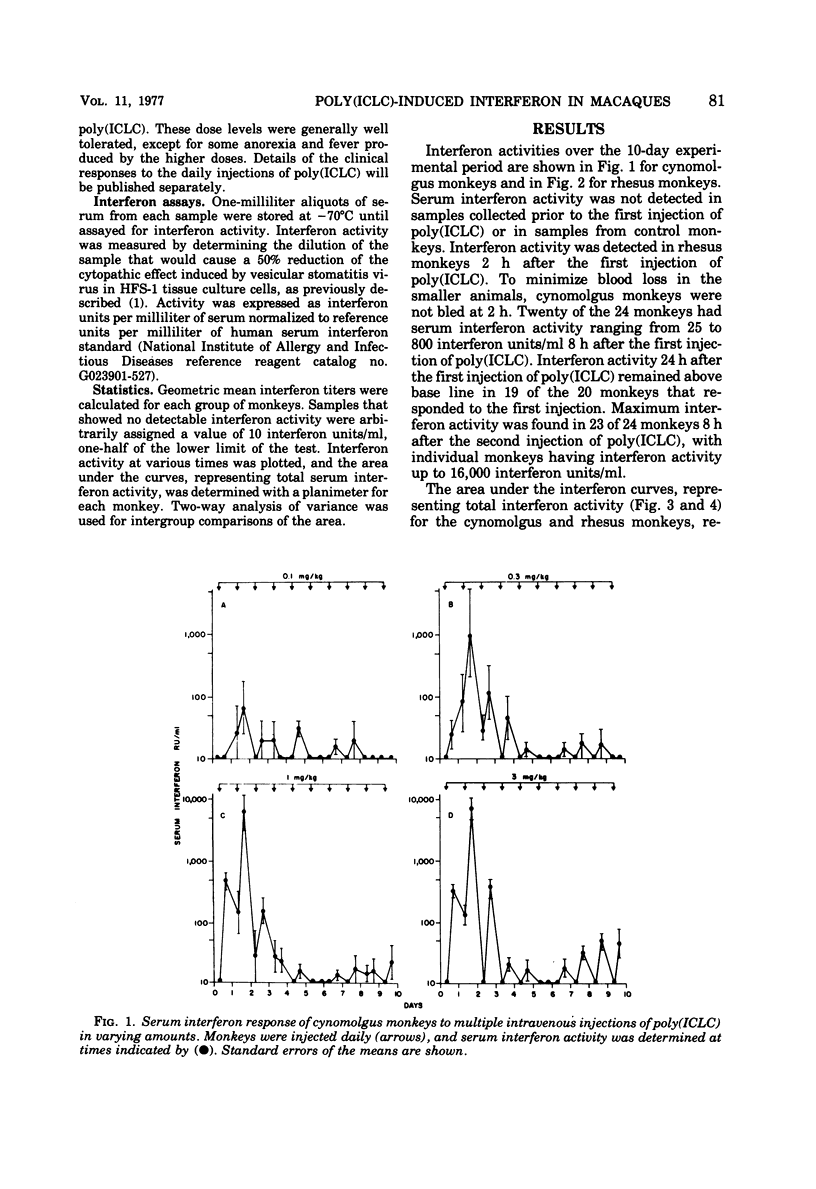
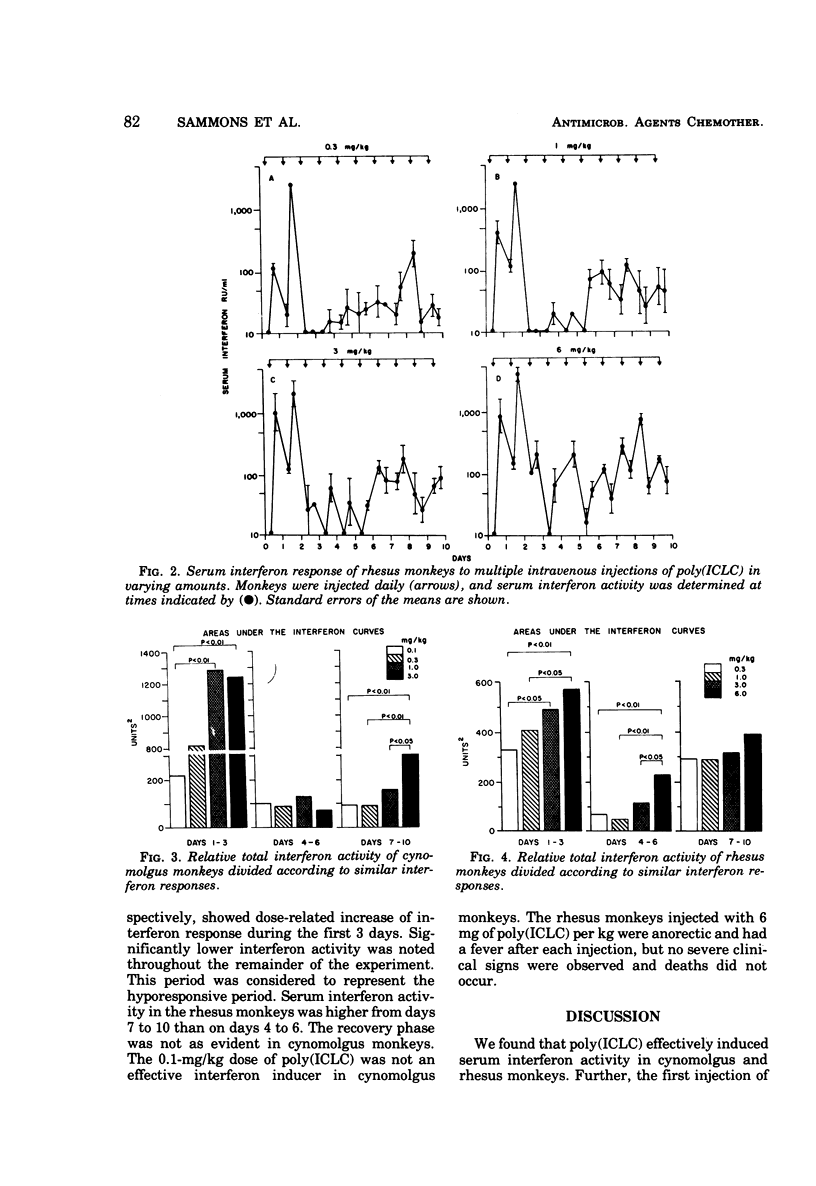

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A. Semi-micro, dye-binding assay for rabbit interferon. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):723–725. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.723-725.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borden E. C., Murphy F. A. The interferon refractory state: in vivo and in vitro studies of its mechanism. J Immunol. 1971 Jan;106(1):134–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borden E. C., Prochownik E. V., Carter W. A. The interferon refractory state. II. Biological characterization of a refractoriness-inducing protein. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):752–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler C. E., DuBuy H. G., Johnson M. L., Baron S. Kinetics of serum interferon response in mice after single and multiple injections of polyI-poly C. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Feb;136(2):394–398. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBuy H. G., Johnson M. L., Buckler C. E., Baron S. Relationship between dose size and dose interval of polyinosinic polycytidylic acid and interferon hyporesponsiveness in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):340–344. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. II. Multistranded synthetic polynucleotide complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. A., Baron S., Perkins J. C., Worthington M., Van Kirk J. E., Mills J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Evaluation of an interferon inducer in viral respiratory disease. JAMA. 1972 Feb 28;219(9):1179–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M., Kono Y., Breinig M. K. Tolerance to the induction of interferons by endotoxin and virus: role of a humoral factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Aug-Sep;119(4):1227–1232. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homan E. R., Zendzian R. P., Schott L. D., Levy H. B., Adamson R. H. Studies on poly I:C toxicity in experimental animals. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1972 Dec;23(4):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(72)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., Baer G., Baron S., Buckler C. E., Gibbs C. J., Iadarola M. J., London W. T., Rice J. A modified polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid complex that induces interferon in primates. J Infect Dis. 1975 Oct;132(4):434–439. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.4.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis S. A., Oie H., Levy H. B. The effect of interferon, interferon inducers or interferon induced virus resistance on subsequent interferon production. J Gen Virol. 1972 May;15(2):119–128. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-15-2-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund J. J., Wolff S. M., Levy H. B. Inhibition of biologic activity of poly I: poly C by human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):439–444. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenquist B. D. Polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid-induced interferons in calves. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Jan;32(1):35–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow D. A., Glasgow L. A. Hyporeactivity of infection: potential limitation to therapeutic use of interferon-inducing agents. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):743–747. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.743-747.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


