Abstract
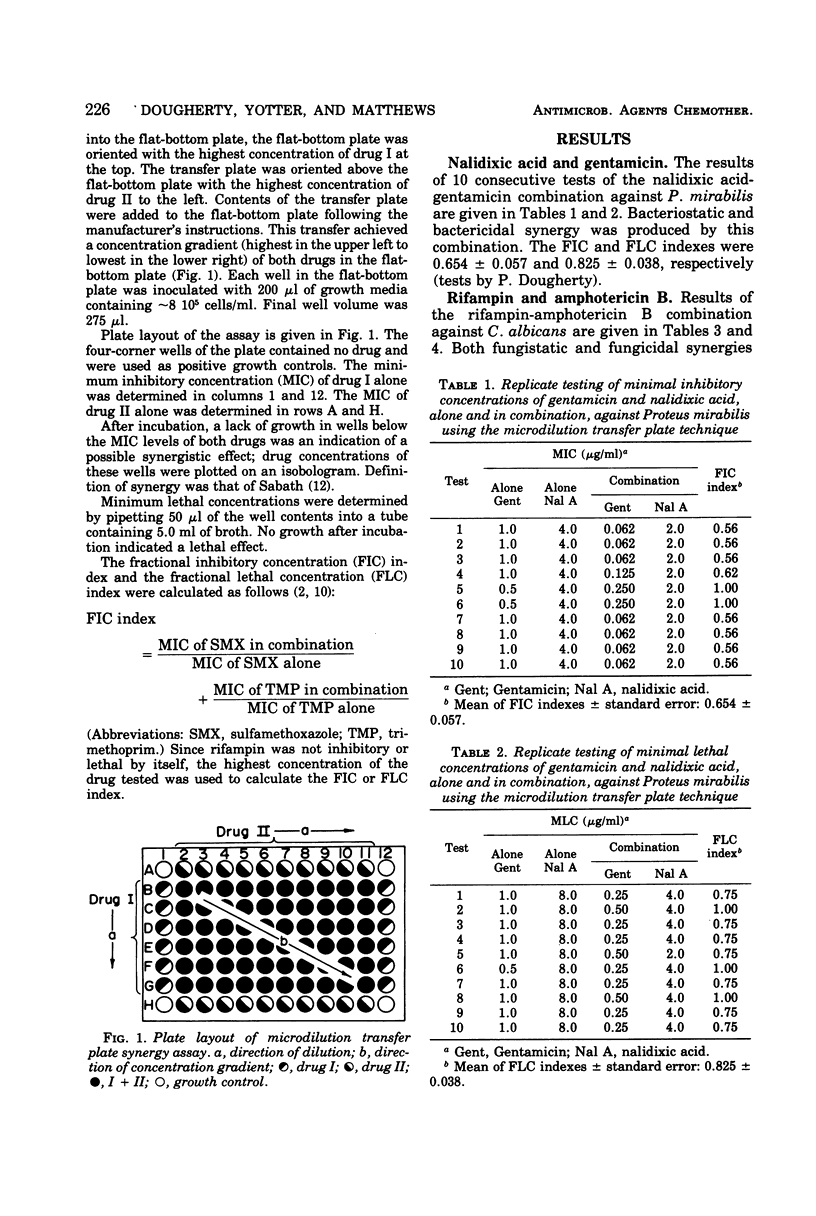
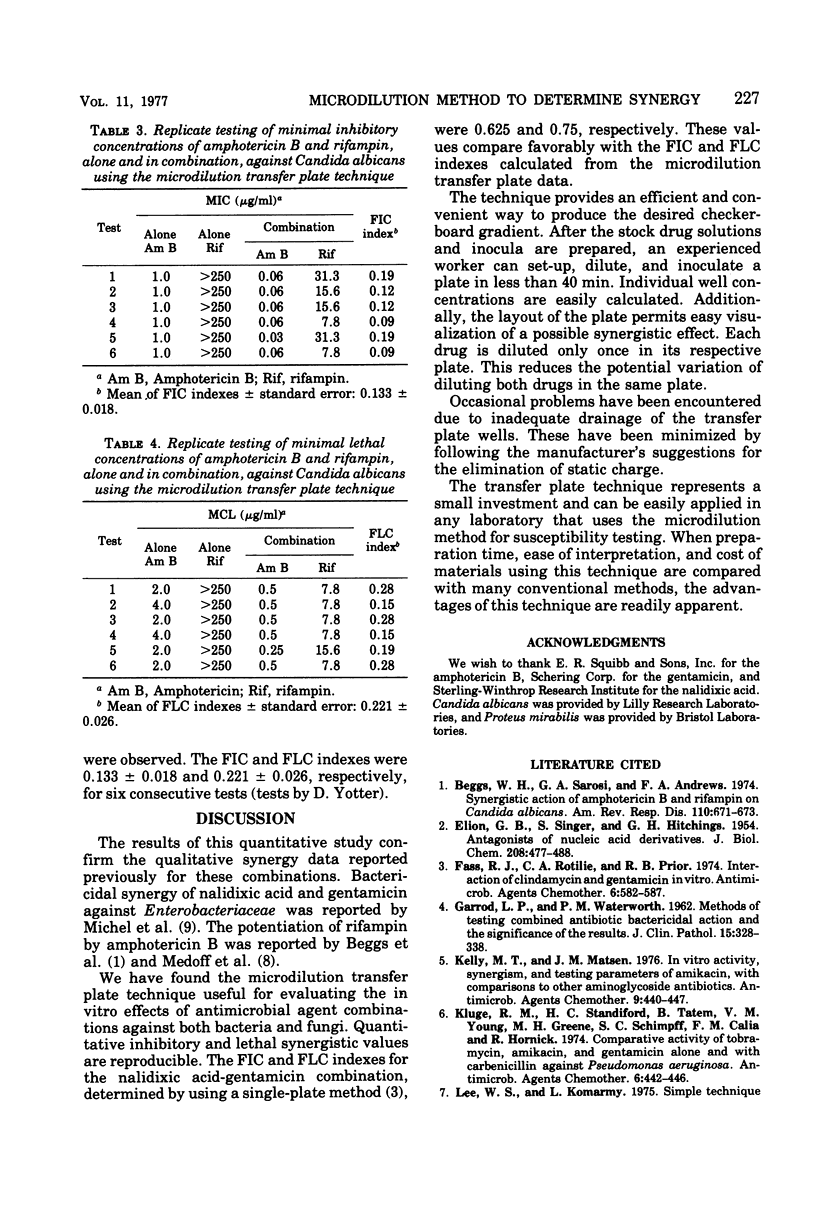
A microdilution transfer plate technique for determining in vitro synergy of antimicrobial agents is described. Combinations of gentamicin-nalidixic acid against Proteus mirabilis and rifampin-amphotericin B against Candida albicans are used as examples to demonstrate the technique. Results correlate with published data obtained by conventional methods. The technique is effective for evaluating the in vitro effects of antimicrobial agent combinations against both bacteria and fungi. The technique enables one to produce a checkerboard gradient in a fast, convenient, and reproducible way; results are easily visualized.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beggs W. H., Sarosi G. A., Andrews F. A. Synergistic action of amphotericin B and rifampin on Candida albicans. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Nov;110(5):671–673. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.5.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELION G. B., SINGER S., HITCHINGS G. H. Antagonists of nucleic acid derivatives. VIII. Synergism in combinations of biochemically related antimetabolites. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J., Rotilie C. A., Prior R. B. Interaction of clindamycin and gentamicin in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):582–587. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD L. P., WATERWORTH P. M. Methods of testing combined antibiotic bactericidal action and the significance of the results. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Jul;15:328–338. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.4.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., Matsen J. M. In vitro activity, synergism, and testing parameters of amikacin, with comparisons to other aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):440–447. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluge R. M., Standiford H. C., Tatem B., Young V. M., Greene W. H., Schimpff S. C., Calia F. M., Hornick R. B. Comparative activity of tobramycin, amikacin, and gentamicin alone and with carbenicillin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Oct;6(4):442–446. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.4.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S., Kwan C. N., Schlessinger D., Venkov P. Potentiation of rifampicin and 5-fluorocytosine as antifungal antibiotics by amphotericin B (yeast-membrane permeability-ribosomal RNA-eukaryotic cell-synergism). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):196–199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J., Luboshitzky R., Sacks T. Bactericidal effect of combinations of nalidixic acid and various antibiotics on Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):201–204. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Warren C. Activity of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim against Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):736–740. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J. E., Stewart P. R. Combined activity of sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, and polymyxin B against gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jul;6(1):84–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadomy S. In vitro studies with 5-fluorocytosine. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):871–877. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.871-877.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadomy S., Wagner G., Espinel-Ingroff E., Davis B. A. In vitro studies with combinations of 5-fluorocytosine and amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Aug;8(2):117–121. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Kleber I. In vitro additive effect of polymxin B and rifampin against Serratia marcesen. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jun;7(6):874–876. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.6.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinner S. H., Provonchee R. B., Elias K. S., Peter G. Effect of clindamycin on the in vitro activity of amikacin and gentamicin against gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):661–664. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


