Abstract
Colicins B-K260 and D-CA23 were purified by ammonium sulfate precipitation, gel filtration, and ion-exchange chromatography and were compared with respect to a number of physical and chemical properties. Both colicins were shown to be proteins and were found to have similar molecular weights, isoelectric points and amino acid compositions. The two colicins also have substantial antigenic similarities but are distinguished by the presence of non-cross-reacting antigens and by differences in stability and in sensitivity to heat and reducing conditions. In addition, strains of Escherichia coli K-12 producing colicins B-K260 and D-CA23 are not cross-immune. The similarities noted between the two colicins are compatible with their use of a common cell surface receptor while having different modes of action.
Full text
PDF


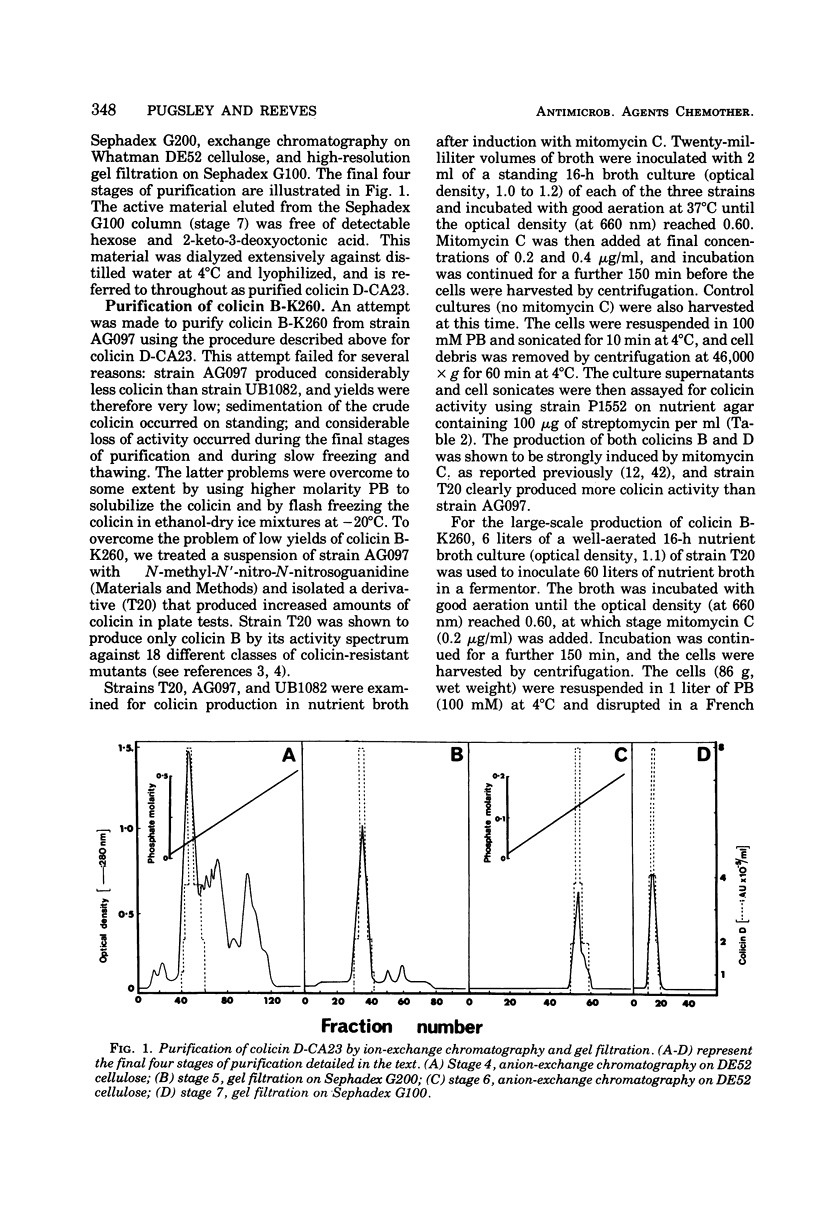
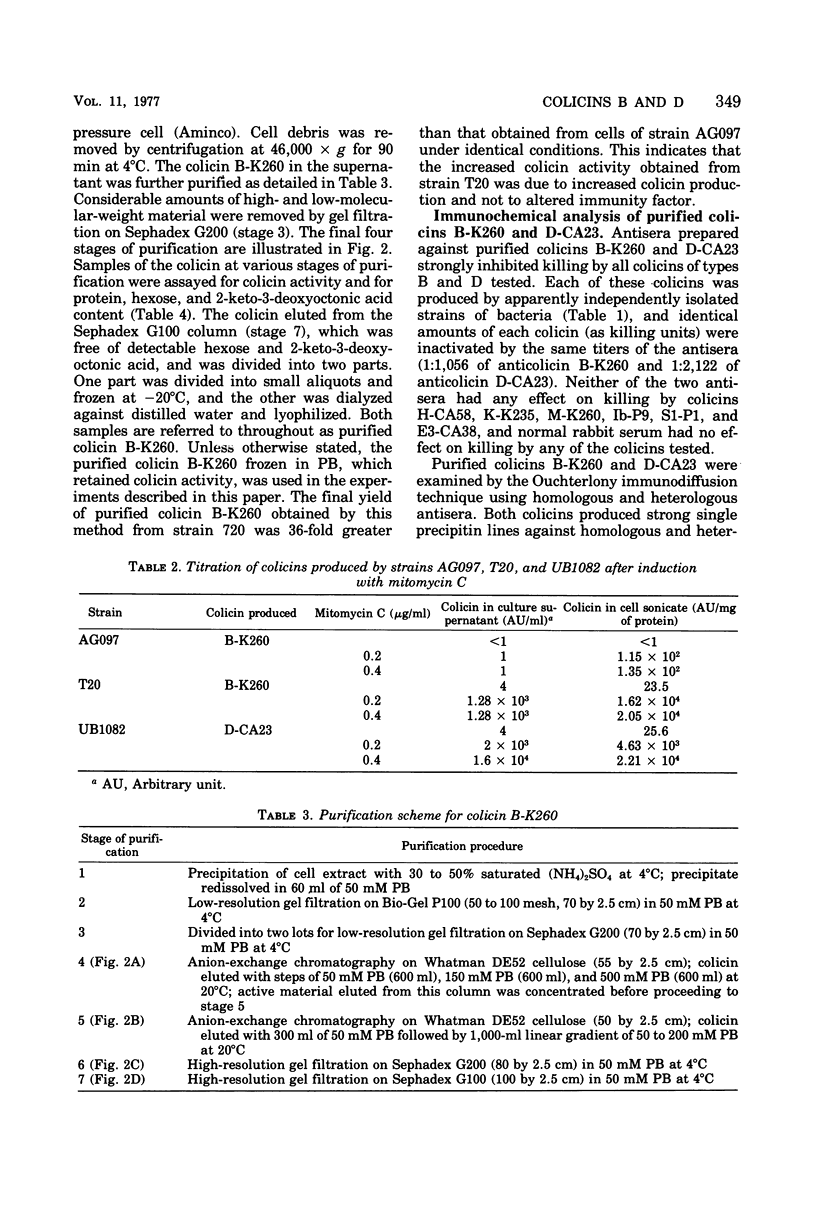








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boon T. Inactivation of ribosomes in vitro by colicin E 3 and its mechanism of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):549–552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Schaller K., Wabl M. R. Isolation, characterization, and action of colicin M. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 May;5(5):520–533. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.5.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. K., Reeves P. Genetics of resistance to colicins in Escherichia coli K-12: cross-resistance among colicins of group A. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):102–117. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.102-117.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. K., Reeves P. Genetics of resistance to colicins in Escherichia coli K-12: cross-resistance among colicins of group B. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):96–101. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.96-101.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Recherches sur la fréquence des souches transductrices des propriétés colicinogènes. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1956 Sep 26;150(5):1036–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Recherches sur les caractères et la distribution des souches productrices de diverses colicines dans les selles normales et pathologiques. Bull Acad R Med Belg. 1953 Feb;18(2):126–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredericq P., Smarda J. Complexité du facteur colicinogène B. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1970 Jun;118(6):767–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guterman S. K., Dann L. Excretion of enterochelin by exbA and exbB mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1225–1230. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1225-1230.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. G. Colicinogeny and related phenomena. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Dec;39(4):464–515. doi: 10.1128/br.39.4.464-515.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. G., Meynell G. G., Dowman J. E., Spratt B. G. Two major groups of colicin factors: their evolutionary significance. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Sep 12;125(3):217–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00270744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmann C., Clowes R. C. Mitomycin C and temperature induction of colicin B in the absence of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):633–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.633-635.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R., Helinski D. R. Purification and characterization of colicin E2 and colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5360–5368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inselburg J. Incompatibility exhibited by colicin plasmids E1, E2, and E3 in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):478–483. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.478-483.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levisohn R., Konisky J., Nomura M. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. IV. Immunity breakdown studied with colicins Ia and Ib. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):811–821. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.811-821.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor C. H., Schnaitman C. A., Normansell D. E. Purification and properties of nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5321–5327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr Acrylamide-gel electrophorograms by mechanical fractionation: radioactive adenovirus proteins. Science. 1966 Feb 25;151(3713):988–990. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3713.988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui E., Mizuno D. Stabilization of colicin E2 by bovine serum albumin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1136–1137. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1136-1137.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papavassiliou J. Sensitivity of Salmonella to colicines. Isr J Med Sci. 1965 Jul;1(4):627–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Reeves P. Characterization of group B colicin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12: colicin resistance and the role of enterochelin. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):218–228. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.218-228.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Reeves P. Increased production of the outer membrane receptors for colicins B, D and M by Escherichia coli under iron starvation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):846–853. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90669-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Reeves P. Iron uptake in colicin B-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1052–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1052-1062.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds B. L., Reeves P. R. Kinetics of adsorption of colicin CA42-E2 and reversal of its bactericidal activity. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):301–309. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.301-309.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringrose P. S. Effects of colicin E2 on DNA and the bacterial membrane in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 27;312(4):656–666. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabet S. F., Schnaitman C. A. Purification and properties of the colicin E3 receptor of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 10;248(5):1797–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smarda J., Adler J. A contribution to the problem of a commom receptor of the E-group colicins. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1971;37(4):507–518. doi: 10.1007/BF02218521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smarda J., Obdrzálek V. Colicine Q. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1966 Aug;200(4):493–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svendsen J., Axelsen N. H. A modified antigen--antibody crossed electrophoresis characterizing the specificity and titre of human precipiting against Candida albicans. J Immunol Methods. 1972 Jan;1(2):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(72)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmis K., Cabello F., Cohen S. N. Utilization of two distinct modes of replication by a hybrid plasmid constructed in vitro from separate replicons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4556–4560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmis K., Hedges A. J. The killing of sensitive cells by colicin D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):200–207. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90233-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmis K. Purification and characterization of colicin D. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):12–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.12-20.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARAVDEKAR V. S., SASLAW L. D. A sensitive colorimetric method for the estimation of 2-deoxy sugars with the use of the malonaldehyde-thiobarbituric acid reaction. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1945–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]