Abstract
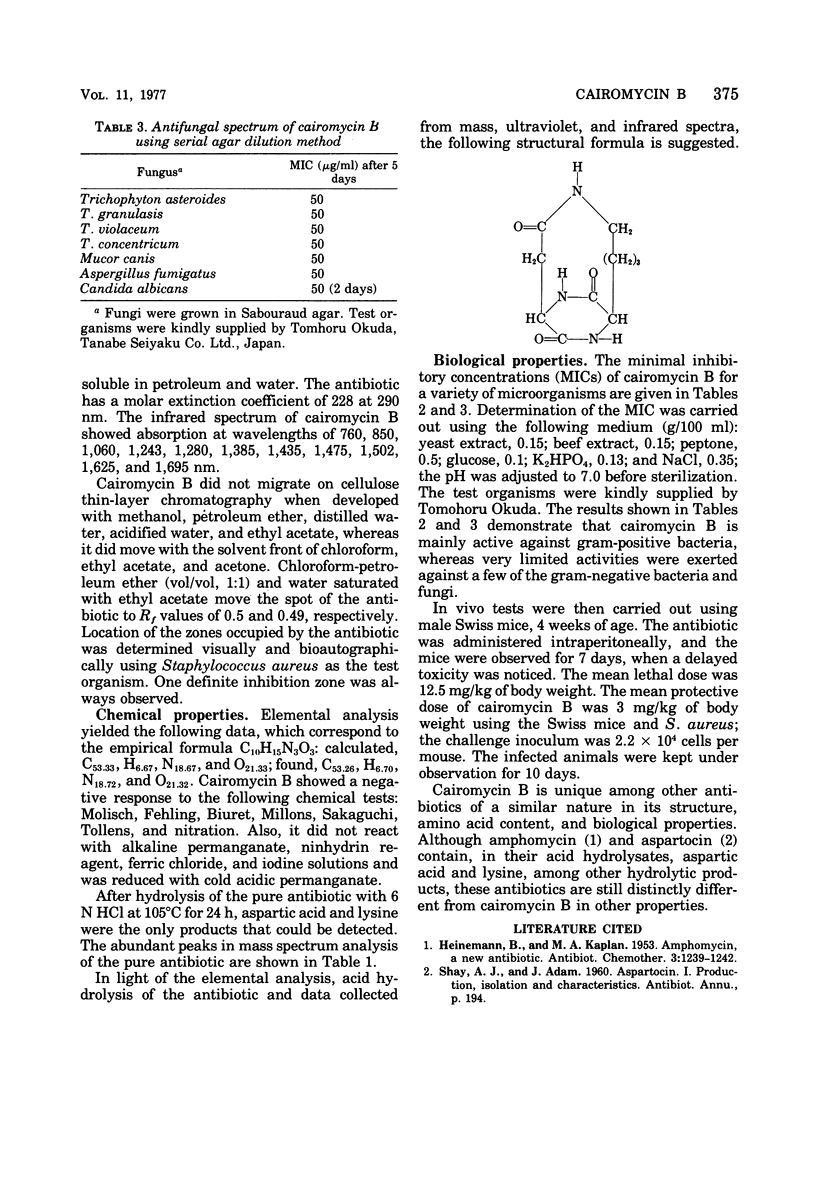
Cairomycin B is a new cyclic peptide antibiotic that was isolated from Streptomyces As-C-19 obtained from the soil of Cairo. The antibiotic had the following empirical formula: C10H15N3O3; on acid hydrolysis, it yielded aspartic acid and lysine. Spectral analysis and its chemical characteristics indicated that it was a cyclic peptide. The antibiotic melted at 120 to 121°C and was freely soluble in chloroform, ethyl acetate, and acetone, slightly soluble in alcohols, and rather insoluble in water and petroleum ether. Cairomycin B was mainly active against gram-positive bacteria, with high toxicity to experimental animals and weak serum-binding properties.
Full text
PDF