Abstract
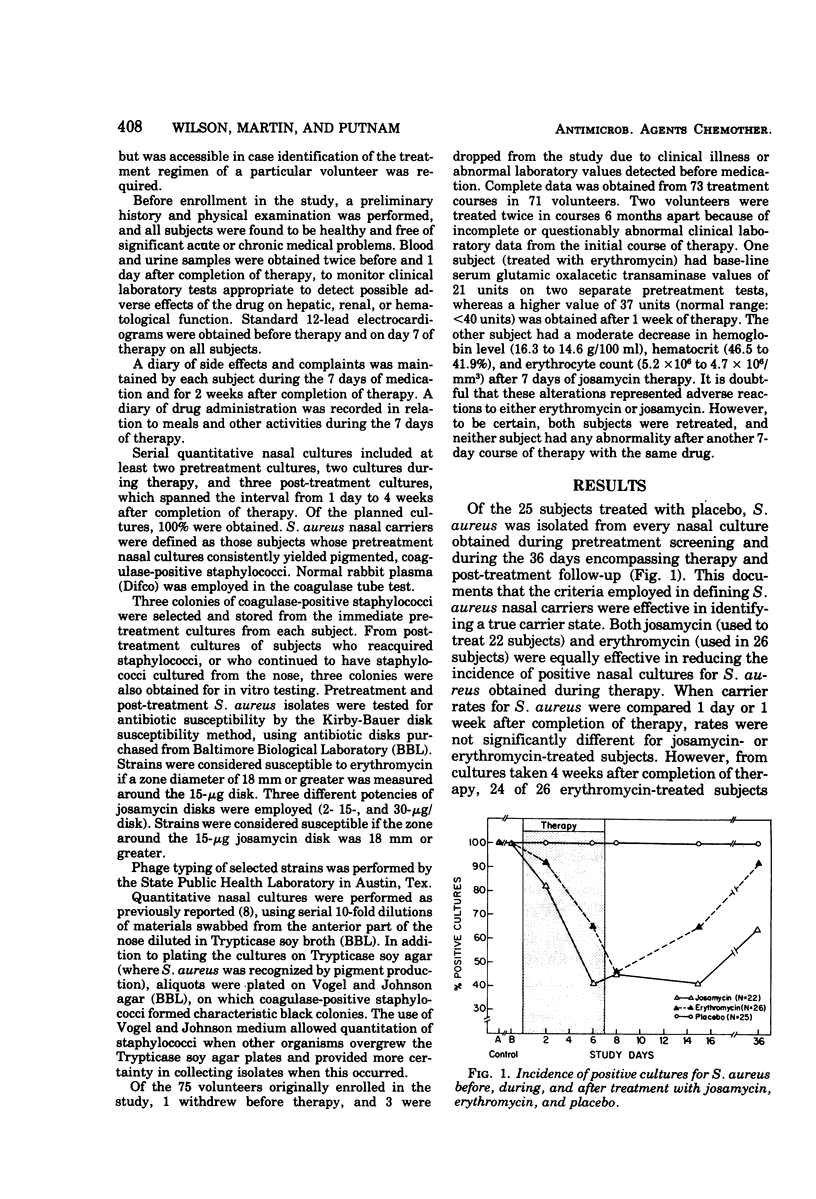
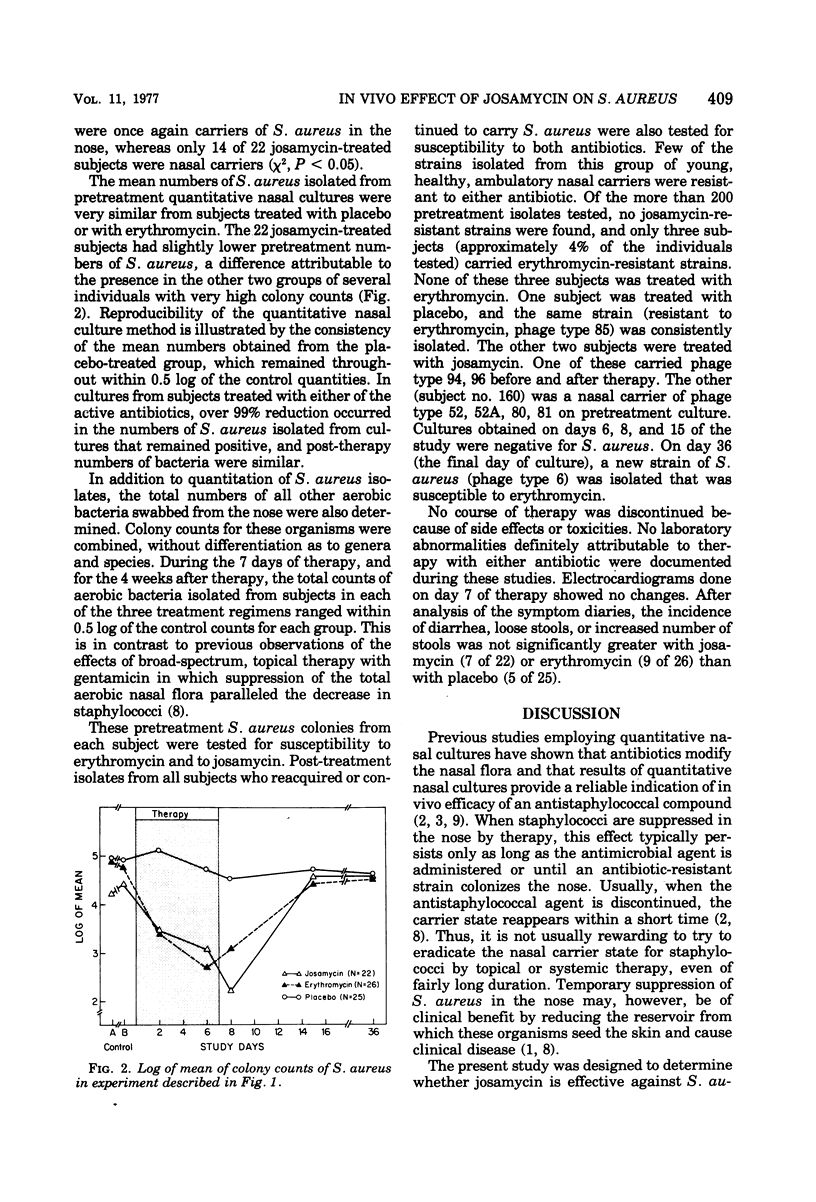
Healthy nasal carriers of Staphylococcus aureus were randomly assigned to one of three treatment regimens: josamycin (1.5 g/day), erythromycin stearate (1.0 g/day), or placebo, each administered orally for 7 days. Quantitative nasal cultures were obtained from each subject at intervals before, during, and after treatment. All 25 placebo-treated subjects had positive nasal cultures for S. aureus at all culture intervals. Both josamycin and erythromycin were equally effective in reducing the carrier rates and in decreasing the total numbers of S. aureus isolated from subjects with positive cultures during treatment. No increase in in vitro antibiotic resistance was detected in isolates obtained after therapy. Both antibiotics were well tolerated, and toxicity was not encountered with either drug.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EHRENKRANZ N. J. PERSON-TO-PERSON TRANSMISSION OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. QUANTITATIVE CHARACTERIZATION OF NASAL CARRIERS SPREADING INFECTION. N Engl J Med. 1964 Jul 30;271:225–230. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196407302710503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. R., White A. Quantitative nasal culture: a tool in antibiotic research. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Sep;22(3):397–400. doi: 10.1128/am.22.3.397-400.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausbaugh L. J., Dilworth J. A., Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Sande M. A. In vitro susceptibility studies with josamycin and erythromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):546–548. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE A., HEMMERLY T., MARTIN M. P., KNIGHT V. Studies on the origin of drug-resistant staphylococci in a mental hospital. Am J Med. 1959 Jul;27(1):26–39. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerman E. L., Williams T. W., Jr, Moreland N. In vitro activity of josamycin against aerobic gram-positive cocci and anaerobes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):988–993. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



