Abstract
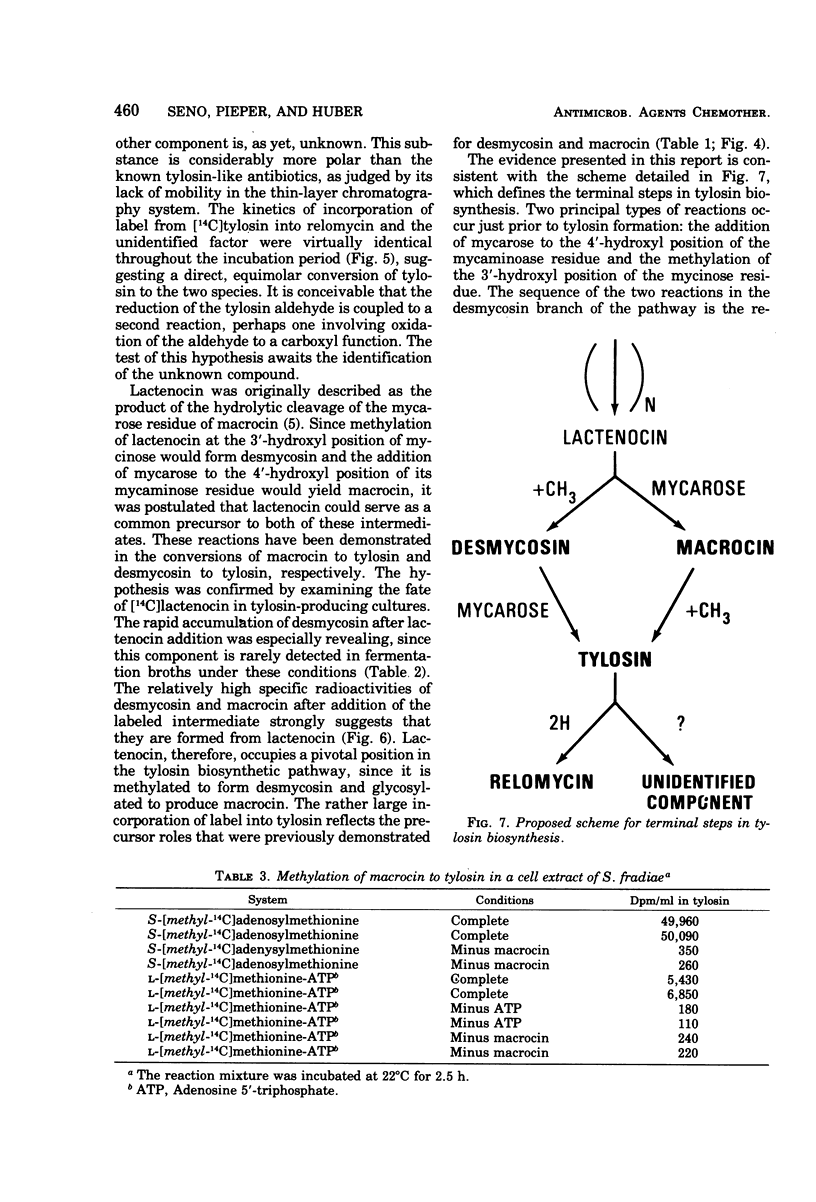
Tylosin, a macrolide antibiotic, was co-produced with four structurally similar antibiotics in fermentation cultures of Streptomyces fradiae. Macrocin, desmycosin, lactenocin, and relomycin were found to be components of a common pathway that functions in tylosin biosynthesis. Data obtained by the addition of the purified 14C-labeled antibiotics to cultures of S. fradiae revealed that macrocin and desmycosin were direct precursors of tylosin, whereas lactenocin was an immediate precursor of both macrocin and desmycosin. Incubation of these cultures with [14C]tylosin resulted in an equivalent distribution of radioactive label between relomycin and an unidentified component. The kinetics of incorporation of label into the two species were similar, suggesting that both were derived directly from tylosin. A system that supported that methylation of macrocin to tylosin by cell-free extracts of S. fradiae was developed. A proposed scheme defining the terminal stages of tylosin biosynthesis is presented.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CORCORAN J. W. Actinomycete antibiotics. II. Participation of the methionine methyl group in the biogenesis of L-cladinose, a branched chain monosaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jun;236:PC27–PC28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILL R. L., HANEY M. E., Jr, STAMPER M., WILEY P. F. Tylosin, a new antibiotic. II. Isolation, properties, and preparation of desmycosin, a microbiologically active degradation product. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1961 May;11:328–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILL R. L., STARK W. M. MACROCIN, A NEW ANTIBIOTIC, AND LACTENOCIN, AN ACTIVE DEGRADATION PRODUCT. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1964 Jul;17:133–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin R. B., Gorman M., Hamill R. L., Demarco P. V. The structure of tylosin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1970 Nov;(54):4737–4740. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(00)89382-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roudebush H. E. An automatic extraction procedure for the quantitative determination of the antibiotic tylosin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Nov 9;130(2):582–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb12601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



