Abstract
The effect of 3-methyleneoxindole (MO) on mengovirus and L-cell protein synthesis was investigated. MO was found to inhibit mengovirus multiplication and the incorporation of radioactive amino acids into both viral and cellular proteins. These results suggest that the antiviral effect of this compound is not specific but rather stems from its inhibition of the cellular translational machinery upon which mengovirus depends. We have also found that MO inhibits natural messenger ribonucleic acid (mengovirus and globin messenger ribonucleic acid) translation in cell-free extracts from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells but has no significant effect on polyuridylic acid translation. Additional data which suggest that MO inhibits protein synthesis at the level of initiation are shown.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abreu S. L., Lucas-Lenard J. Cellular protein synthesis shutoff by mengovirus: translation of nonviral and viral mRNA's in extracts from uninfected and infected Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):182–194. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.182-194.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu P. S., Tuli V. The Binding of Indole-3-acetic Acid and 3-Methyleneoxindole to Plant Macromolecules. Plant Physiol. 1972 Oct;50(4):507–509. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby D. S., Finnerty V., Lucas-Lenard J. Fate of mRNA of L-cells infected with mengovirus. J Virol. 1974 Apr;13(4):858–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.4.858-869.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggen K. L., Shatkin A. J. In vitro translation of cardiovirus ribonucleic acid by mammalian cell-free extracts. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):636–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.636-645.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKUYAMA T. T., MOYED H. S. INHIBITION OF CELL GROWTH BY PHOTOOXIDATION PRODUCTS OF INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2392–2397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINMAN R. L., BAUMAN C., LANG J. The conversion of indole-3-acetic acid to 3-methyleneoxindole in the presence of peroxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Jul 26;5:250–254. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebleu B., Marbaix G., Wérenne J., Burny A., Huez G. Effect of aurintricarboxylic acid and of NaF on the binding of globin messenger RNA to reticulocyte 40S ribosomal subunits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Aug 11;40(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90964-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M., Korner A. Mammalian cell-free protein synthesis directed by viral ribonucleic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):328–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
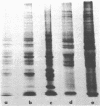
- Nakai K., Lucas-Lenard J. Processing of mengovirus precursor polypeptides in the presence of zinc ions and sulfhydryl compounds. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):918–925. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.918-925.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STILL C. C., FUKUYAMA T. T., MOYED H. S. INHIBITORY OXIDATION PRODUCTS OF INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID. MECHANISM OF ACTION AND ROUTE OF DETOXIFICATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2612–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. L., Grollman A. P., Huang M. T. Aurintricarboxylic acid: inhibitor of initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):97–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuli V. Mechanism of the antiviral action of 3-methyleneoxindole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 May;5(5):485–491. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.5.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuli V., Moyed H. S. Inhibitory oxidation products of indole-3-acetic Acid: 3-hydroxymethyloxindole and 3-methyleneoxindole as plant metabolites. Plant Physiol. 1967 Mar;42(3):425–430. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuli V., Moyed H. S., Stevenson D., Gordon I. Antiviral activity of 3-methyleneoxindole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 May;5(5):479–484. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.5.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelam J. M., Naora H. Interaction of informational macromolecules with ribosomes. VII. Restoration of RNA-binding ability of 40-S ribosome subunits and effect of aurintricarboxylic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 17;349(2):178–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]