Abstract
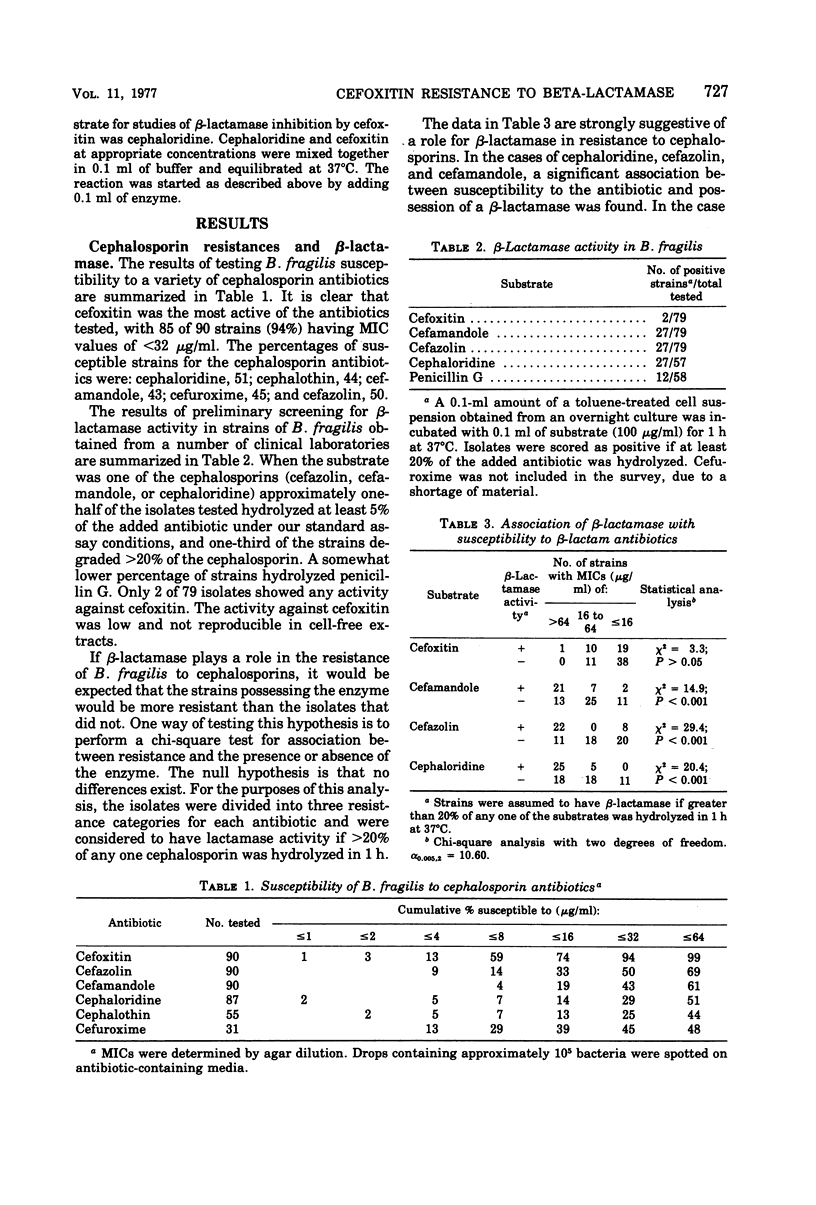
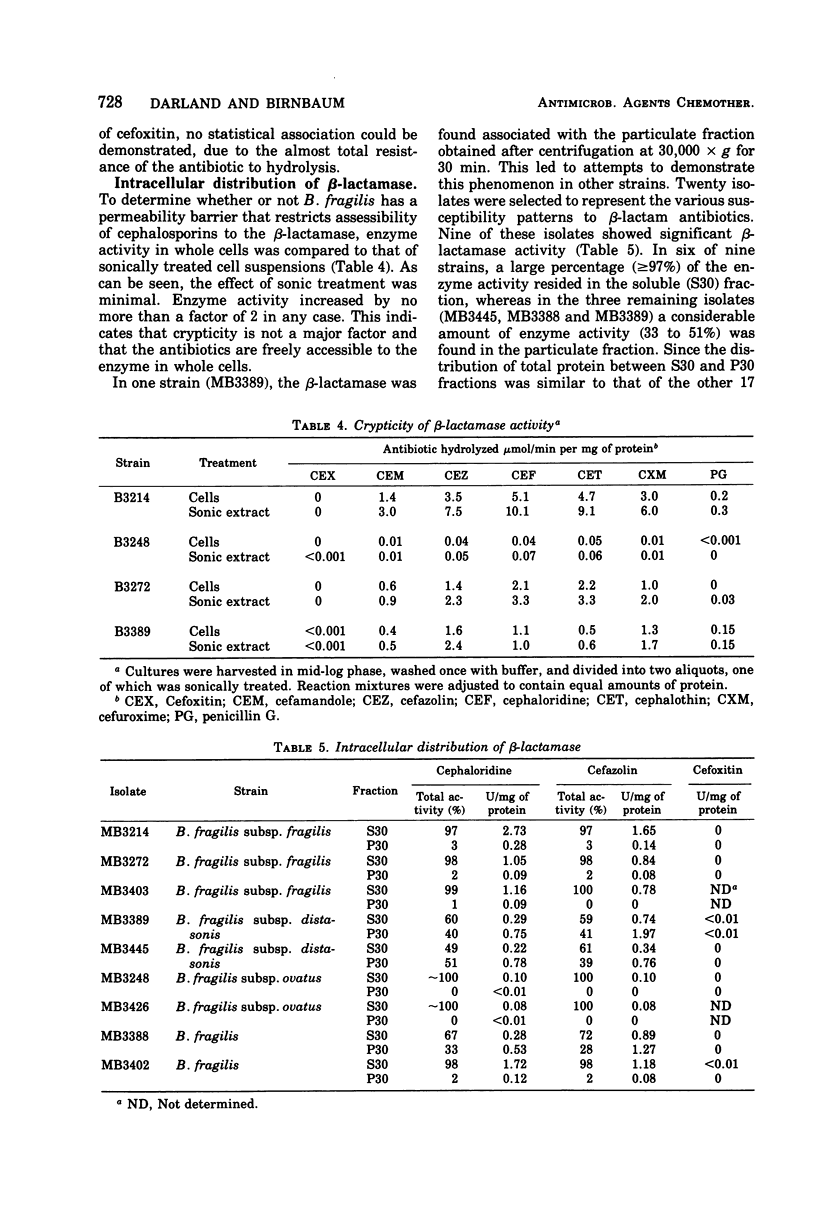
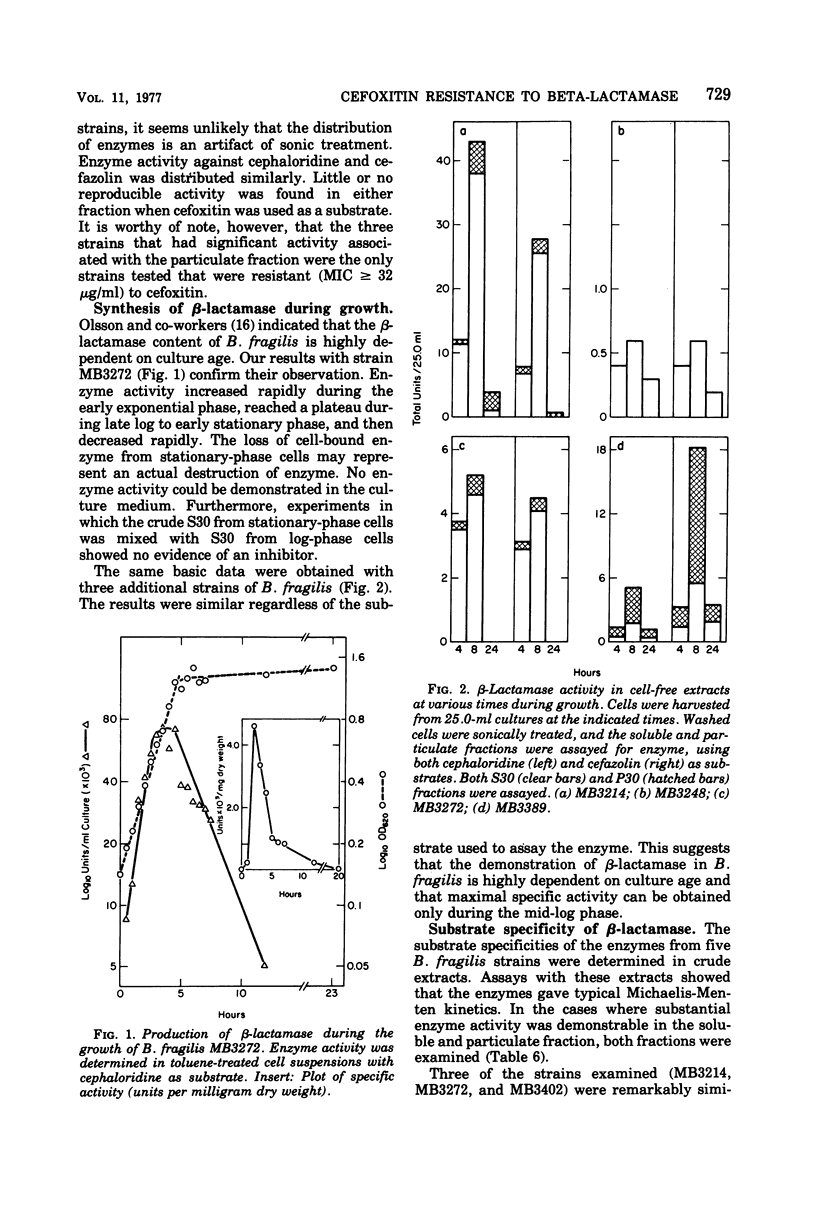
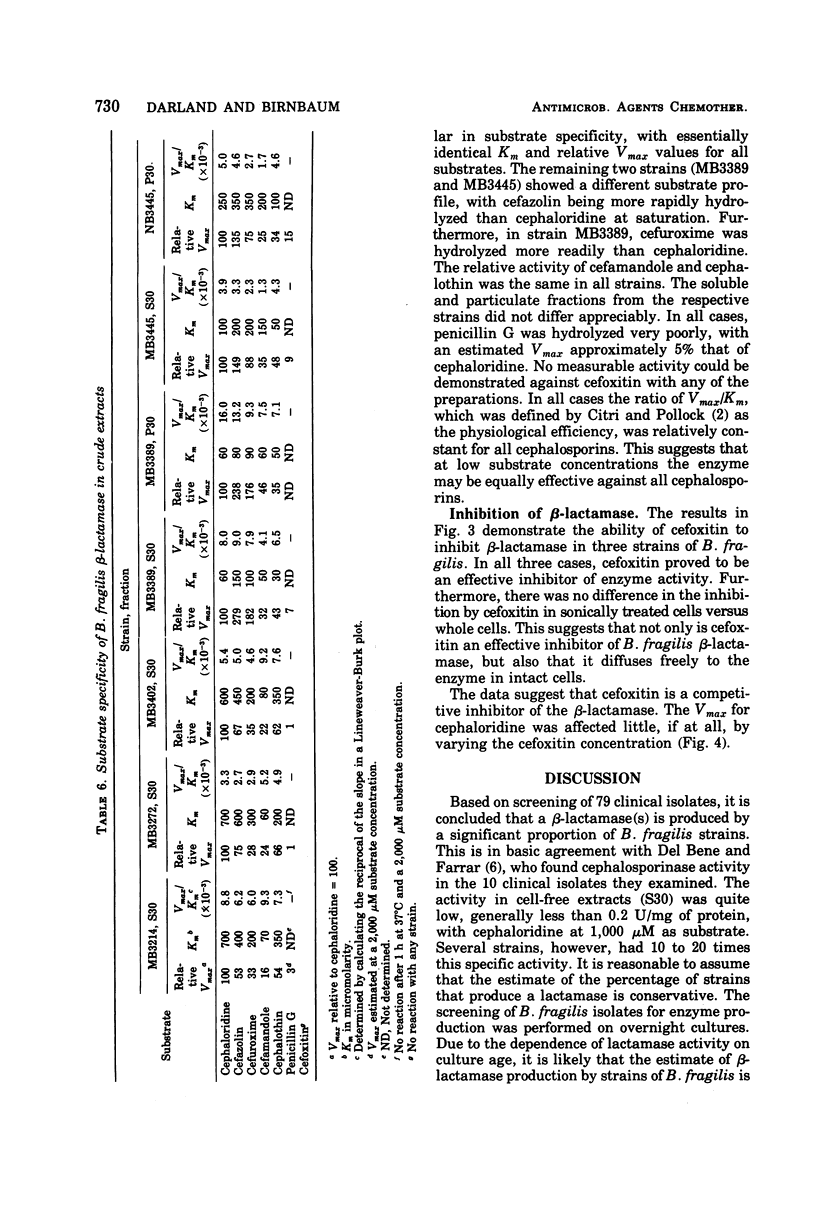
Toluene-treated cell suspensions of Bacteroides fragilis were used to screen clinical isolates for the production of β-lactamase. Approximately one-third of the isolates possessed considerable cephalosporinase activity. A significant correlation was found between β-lactamase production and resistance to cephalosporin antibiotics. Several isolates were resistant to cefuroxime and cefamandole and produced enzymes capable of hydrolyzing these antibiotics. However, none of the 79 strains tested could hydrolyze the cephamycin derivative, cefoxitin. A large percentage (>90%) of the strains were susceptible to cefoxitin. Therefore, resistance to lactamase hydrolysis is a major factor for the effectiveness of cefoxitin against B. fragilis. Detailed studies of four isolates suggest that two different enzymes may be produced. Both are cephalosporinases but differ with regard to cellular distribution and substrate specificity. Cefoxitin is not a substrate for either enzyme, but it is an excellent competitive inhibitor (Ki ≈ 0.1 μM).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. D., Sykes R. B. Characterisation of a -lactamase obtained from a strain of Bacteroides fragilis resistant to -lactam antibiotics. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):201–206. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri N., Pollock M. R. The biochemistry and function of beta-lactamase (penicillinase). Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1966;28:237–323. doi: 10.1002/9780470122730.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M., Elson S., Fullbrook P. D. Inhibition of the -lactamases of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella aerogenes by semi-synthetic penicillins. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):295–308. doi: 10.1042/bj1270295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Abraham E. P. Beta-lactamases from Yersinia enterocolitica. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):273–284. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daoust D. R., Onishi H. R., Wallick H., Hendlin D., Stapley E. O. Cephamycins, a new family of beta-lactam antibiotics: antibacterial activity and resistance to beta-lactamase degradation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):254–261. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Bene V. E., Farrar W. E., Jr Cephalosporinase activity in Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Mar;3(3):369–372. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.3.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldner M., Glass D. G., Fleming P. C. Characteristics of Aerobacter beta-lactamase. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Feb;14(2):139–145. doi: 10.1139/m68-023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kislak J. W. The susceptibility of Bacteroides fragilis to 24 antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):295–299. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., Gardner M., Washington J. A., 2nd In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria isolated from clinical specimens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Feb;1(2):148–158. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. Micro-iodometric assay for penicillinase. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:236–240. doi: 10.1042/bj0830236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Sykes R. B., Griffiths A., Thornton J. E. Cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic: activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):511–519. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C., Morris A. Inhibition of beta-lactamases by beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):442–448. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson B., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Formation of beta-lactamase in Bacteroides fragilis: cell-bound and extracellular activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):727–735. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. W., O'Callaghan C. H. Beta-lactamase assays. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:69–85. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Yaginuma S., Tai M., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Plasmid-mediated penicillin beta-lactamases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):55–60. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of Anaerobic bacteria to carbenicillin, cefoxitin, and related drugs. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):417–422. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Susceptibility of anaerobes to cefoxitin and other cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):128–132. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrich A. E., Del bene V. E. Beta-lactamase activity in anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):106–111. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma S., Terakado N., Mitsuhashi S. Biochemical properties of a penicillin beta-lactamase mediated by R factor from Bordetella bronchiseptica. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Sep;8(3):238–242. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.3.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemelman R., Olivari E. Carbenicillin as inhibitor of beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 26;235(56):121–122. doi: 10.1038/newbio235121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



