Abstract
When aerobically grown on complex media, Haemophilus influenzae b and unencapsulated variants, Rb strains, produced a bactericidal factor that was active against other Haemophilus species and certain genera of the Enterobacteriaceae. A total of 341 clinical isolates of Haemophilus were tested for susceptibility to the factor. Ninety-three percent of H. influenzae (nontypable), 75% of H. haemolyticus, 71% of H. parainfluenzae, and 22% of H. parahaemolyticus were susceptible. H. influenaze b strains were resistant producers of the bactericidal factor and H. influenzae f strains were susceptible nonproducers. Only one strain each of H. aegyptius and H. aphrophilus was isolated and each was susceptible and resistant, respectively. 143 clinical isolates of the Enterobacteriaceae were tested and of those 82% of Escherichia coli, 85% of Salmonella sp., and all Citrobacter sp., Shigella sp., and Yersinia sp. were sensitive to the bactericidal factor produced by H. influenzae b. Attempts to isolate the bactericidal activity from mechanically disrupted, solubilized, or osmotically shocked cells failed to release active bactericidal factor. However, we partially purified the bactericidal factor from the spent culture medium of aerobically grown H. influenzae b by a series of extractions. The ability to produce the bactericidal factor was transferable to nonproducer strains without also genetically transforming for type b encapsulation. The converse was also true in that type b capsules were produced by transformed H. influenzae Rd strains but no bactericidal factor was detected from these strains. Additionally, nitrosoguanidine-induced mutants of H. influenzae b lost the ability to produce bactericidal factor without loss of their type-specific capsule, demonstrating that production of the bactericidal factor was genetically separable from production of the type capsule of H. influenzae b.
Full text
PDF



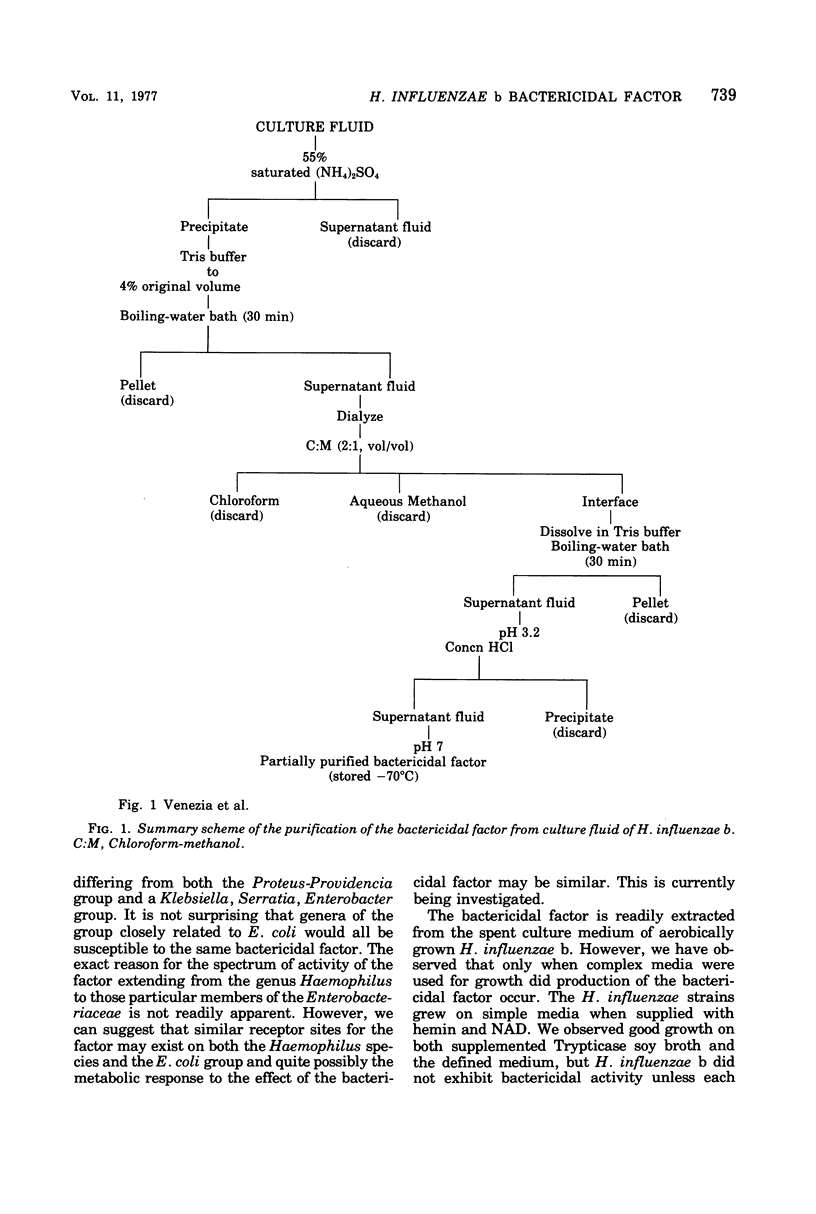
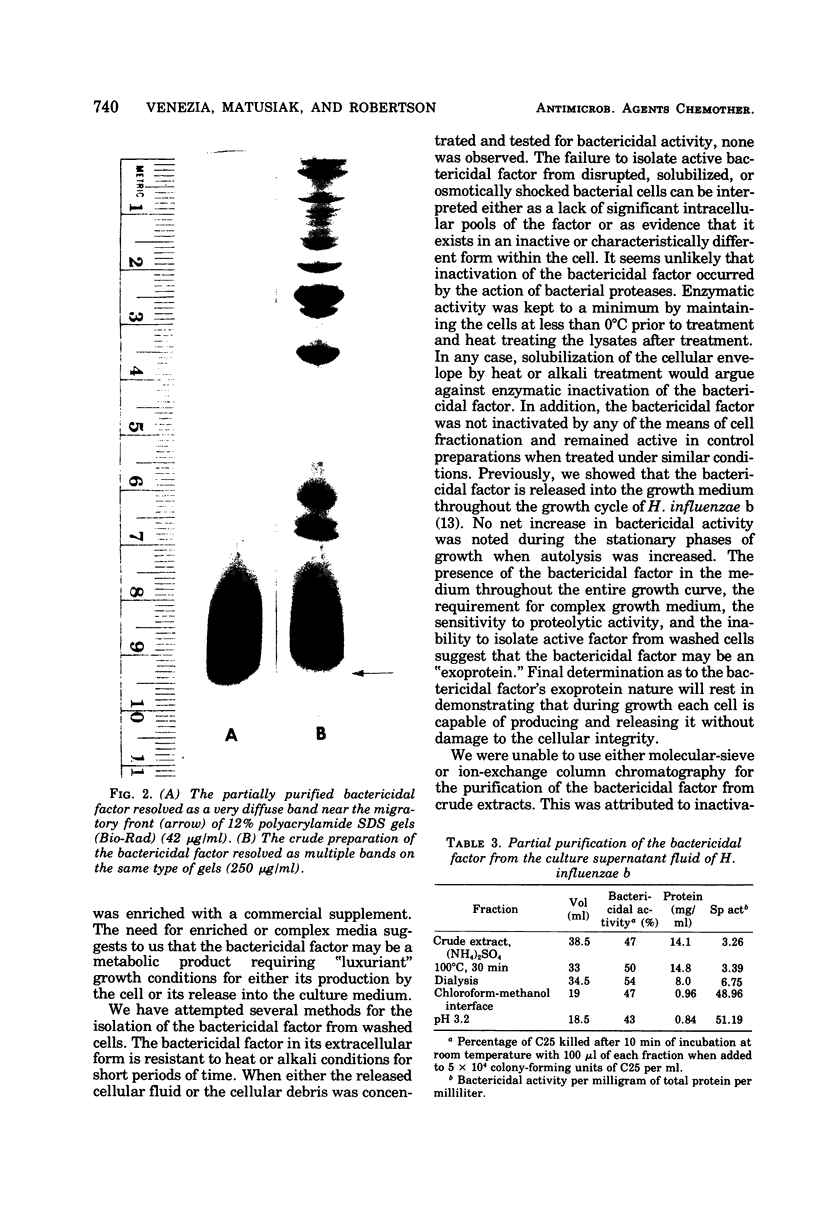


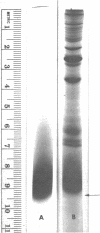
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNHART B. J., HERRIOTT R. M. PENETRATION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID INTO HEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 17;76:25–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODGAL S. H., HERRIOTT R. M. Studies on transformations of Hemophilus influenzae. I. Competence. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Jul;44:1201–1227. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.6.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalka J., Goodgal S. H. Genetic and physical map of the chromosome of Hemophilus influenzae. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 28;45(2):407–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. The gross conformation of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5161–5165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUNEVALL G. Studies on haemophilus influenzae; Haemophilus influenzae antigens studied by the gel precipitation method. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1953;32(1):193–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venezia R. A., Robertson R. G. Bactericidal substance produced by Haemophilus influenzae b. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Oct;21(10):1587–1594. doi: 10.1139/m75-232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E., Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Transformation and transfection in lysogenic strains of Bacillus subtilis: evidence for selective induction of prophage in competent cells. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):296–304. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.296-304.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]