Abstract
A Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain isolated at Besançon Hospital, France, proved to be highly resistant to carbenicillin and showed a high hydrolytic activity toward this antibiotic. We clearly demonstrated that two β-lactamases were synthetized: one of them, constitutive, has its enzymatic activity directed mainly toward penicillins, and carbenicillin appears to be its best substrate (higher Vmax); thus, this β-lactamase is a “carbenicillinase” that differs from the well-known “TEM-like” enzymes. The isoelectric point of this carbenicillinase is 5.30 ± 0.03. The other one is an inducible cephalosporinase, very similar to the cephalosporinases usually found in these organisms. Its isoelectric point is 8.66 ± 0.04. These two enzymes have been separated by affinity chromatography and isoelectric focusing. The kinetic constants were measured by computerized microacidimetry.
Full text
PDF
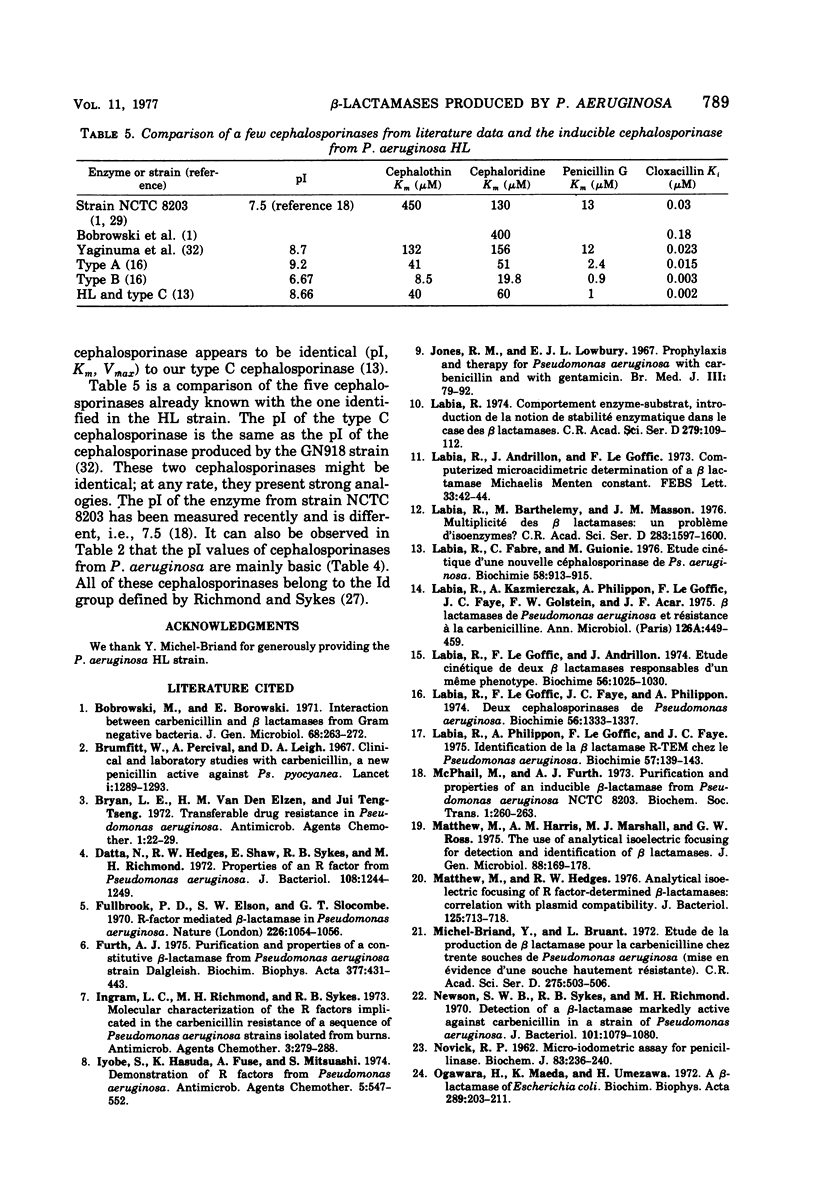

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bobrowski M., Borowski E. Interaction between carbenicillin and beta-lactamases from Gram-negative bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Nov;68(3):263–272. doi: 10.1099/00221287-68-3-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumfitt W., Percival A., Leigh D. A. Clinical and laboratory studies with carbenicillin. A new penicillin active against Pseudomonas pyocyanea. Lancet. 1967 Jun 17;1(7503):1289–1293. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91590-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van Den Elzen H. M., Tseng J. T. Transferable drug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jan;1(1):22–29. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W., Shaw E. J., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Properties of an R factor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1244–1249. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1244-1249.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullbrook P. D., Elson S. W., Slocombe B. R-factor mediated beta-lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nature. 1970 Jun 13;226(5250):1054–1056. doi: 10.1038/2261054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth A. J. Purification and properties of a constitutive beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain Dalgleish. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 19;377(2):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. C., Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. Molecular characterization of the R factors implicated in the carbenicillin resistance of a sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from burns. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):279–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyobe S., Hasuda K., Fuse A., Mitsuhashi S. Demonstration of R factors from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jun;5(6):547–552. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.6.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J., Lowbury E. J. Prophylaxis and therapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection with carbenicillin and with gentamicin. Br Med J. 1967 Jul 8;3(5557):79–82. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5557.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Andrillon J., Le Goffic F. Computerized microacidimetric determination of beta lactamase Michaelis-Menten constants. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jun 15;33(1):42–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Barthélémy M., Masson J. M. Multiplicité des beta lactamases: un probléme d'isoenzymes. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1976 Nov 29;283(14):1597–1600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R. Comportement enzyme-substrat. Introduction de la notion de stabilité enzymatique dans le cas des beta lactamases. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1974 Jul 1;279(1):109–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Fabre C., Guionie M. Etude cinétique d'une nouvelle céphalosporinase de Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochimie. 1976;58(8):913–915. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(76)80279-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Kazmierczak A., Philippon A., Le Goffic F., Faye J. C., Goldstein F. W., Acar J. F. beta-Lactamases de Pseudomonas aeruginosa et résistance a la carbénicilline. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1975 May-Jun;126A(4):449–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Le Goffic F., Andrillon J. Etude cinétique de deux beta lactamases responsables d'un møeme phénotype. Biochimie. 1974;56(8):1025–1030. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(74)80092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Le Goffic F., Faye J. C., Philippon A. Deux céphalosporinases de Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochimie. 1974;56(10):1333–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Philippon A., Le Goffic F., Faye J. C. Identification de la beta lactamase R-TEM chez Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochimie. 1975;57(2):139–143. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M., Hedges R. W. Analytical isoelectric focusing of R factor-determined beta-lactamases: correlation with plasmid compatibility. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):713–718. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.713-718.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel-Briand Y., Bruand L. Etude de la production de -lactamase pour la Carbénicilline, chez trente souches de Pseudomonas aeruginosa (mise en évidence d'une souche hautement résistante. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1972 Jul 17;275(3):503–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. Micro-iodometric assay for penicillinase. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:236–240. doi: 10.1042/bj0830236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsom S. W., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Detection of a beta-lactamase markedly active against carbenicillin in a strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):1079–1080. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.1079-1080.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawara H., Maeda K., Umezawa H. A -lactamase of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 10;289(1):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRET C. J. Iodometric assay of penicillinase. Nature. 1954 Nov 27;174(4439):1012–1013. doi: 10.1038/1741012a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitton J. S. -lactamases à dépendance plasmidique chez les entérobactériacées. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1973;39(1):3–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Finland M. Resistance of penicillins and cephalosporins to beta-lactamases from Gram-negative bacilli: some correlations with antibacterial activity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Sep 27;145(2):237–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb50222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Jago M., Abraham E. P. Cephalosporinase and penicillinase activities of a beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas pyocyanea. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):739–752. doi: 10.1042/bj0960739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Yaginuma S., Tai M., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Plasmid-mediated penicillin beta-lactamases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):55–60. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Intergeneric transfer of a beta-lactamase gene between Ps. aeruginosa and E. coli. Nature. 1970 Jun 6;226(5249):952–954. doi: 10.1038/226952a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma S., Sawai T., Ono H., Yamagishi S., Mitsuhashi S. Biochemical properties of a cephalosporin beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Microbiol. 1973 Mar;17(2):141–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1973.tb00718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi S., O'Hara K., Sawai T., Mitsuhashi S. The purification and properties of penicillin beta-lactamases mediated by transmissible R factors in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1969 Jul;66(1):11–20. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]