Abstract
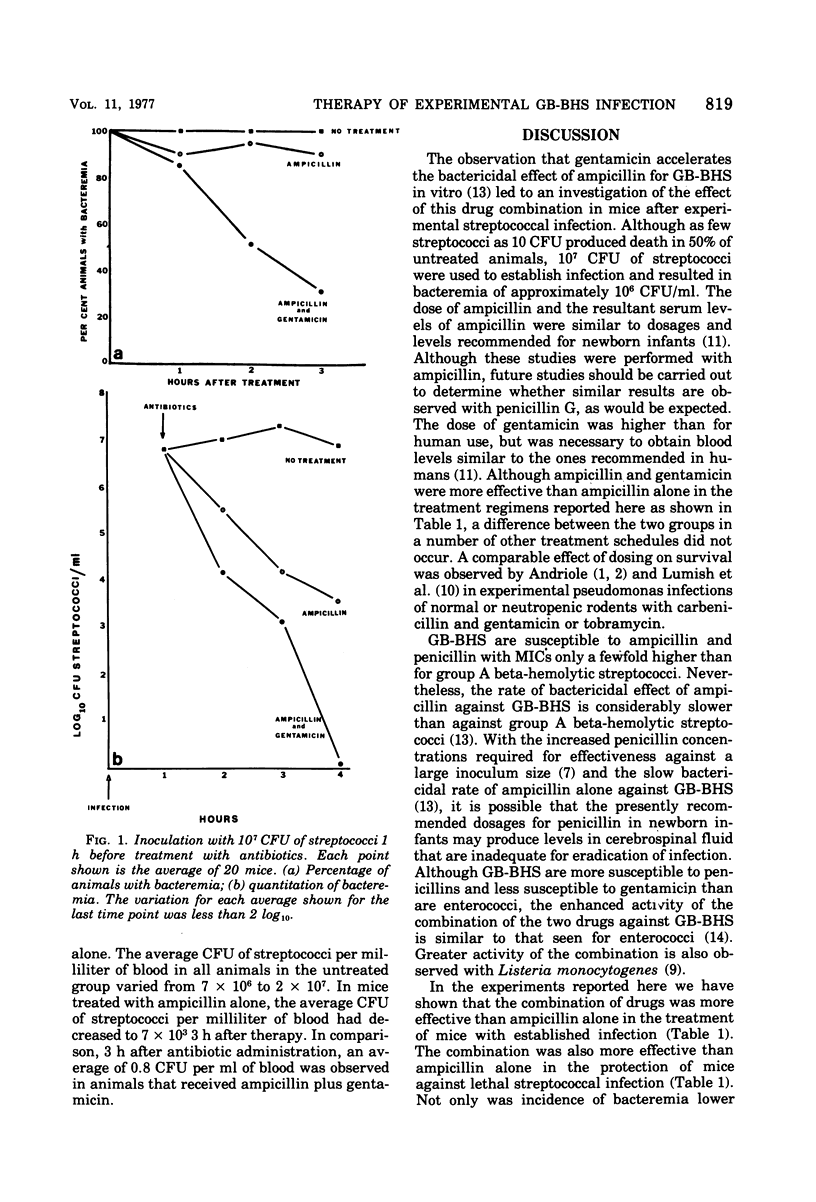
Group B beta-hemolytic streptococci (GB-BHS) frequently cause severe infection in newborns. Previous in vitro studies showed accelerated killing of GB-BHS by ampicillin plus gentamicin as compared with ampicillin alone. To extend the in vitro observations, mice were infected experimentally with GB-BHS and treated with gentamicin plus ampicillin or ampicillin alone. Untreated mice died within 10 to 48 h. Compared with treatment with ampicillin alone, ampicillin-and-gentamicin therapy resulted in improved survival when the antibiotics were given in established infection or as a single dose at the time of infection. Ampicillin and gentamicin accelerated the clearing of bacteremia as compared with treatment with ampicillin alone. In view of these findings, the therapy of GB-BHS infection in newborns and other patients should be reconsidered in that a combination of ampicillin or penicillin G plus gentamicin might be superior to the use of ampicillin or penicillin G alone.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andriole V. T. Antibiotic synergy in experimental infection with Pseudomonas. II. The effect of carbenicillin, cephalothin, or cephanone combined with tobramycin or gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):124–133. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Barrett F. F., Gordon R. C., Yow M. D. Suppurative meningitis due to streptococci of Lancefield group B: a study of 33 infants. J Pediatr. 1973 Apr;82(4):724–729. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80606-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Barrett F. F. Transmission of group B streptococci among parturient women and their neonates. J Pediatr. 1973 Dec;83(6):919–925. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80524-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergqvist G., Hurvell B., Malmborg A. S., Rylander M., Tunell R. Neonatal infections caused by group B streptococci. Scand J Infect Dis. 1971;3(2):157–162. doi: 10.3109/inf.1971.3.issue-2.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EICKHOFF T. C., KLEIN J. O., DALY A. K., INGALL D., FINLAND M. NEONATAL SEPSIS AND OTHER INFECTIONS DUE TO GROUP B BETA-HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI. N Engl J Med. 1964 Dec 10;271:1221–1228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196412102712401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman W. E. Concentrations of bacteria in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with bacterial meningitis. J Pediatr. 1976 Apr;88(4 Pt 1):549–552. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giamarellou H., Zimelis V. M., Matulionis D. O., Jackson G. G. Assay of aminoglycoside antibiotics in clinical specimens. J Infect Dis. 1975 Oct;132(4):399–406. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.4.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. C., Barrett F. F., Clark D. J. Influence of several antibiotics, singly and in combination, on the growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Pediatr. 1972 Apr;80(4):667–670. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumish R. M., Norden C. W. Therapy of neutropenic rats infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1976 May;133(5):538–547. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.5.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Feldman W. E. Editorial: Neonatal group B streptococcal infection. J Pediatr. 1976 Aug;89(2):203–204. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Eichenwald H. F. Antimicrobiol therapy: therapeutic recommendations and a review of newer drugs. Part I. Therapy of infectious conditions. J Pediatr. 1974 Sep;85(3):297–312. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf V., Deveikis A., Riff L., Serota A. Antibiotic-killing kinetics of group B streptococci. J Pediatr. 1976 Aug;89(2):194–198. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80446-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C. Penicillin combined with gentamicin or streptomycin: synergism against enterococci. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):581–586. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


