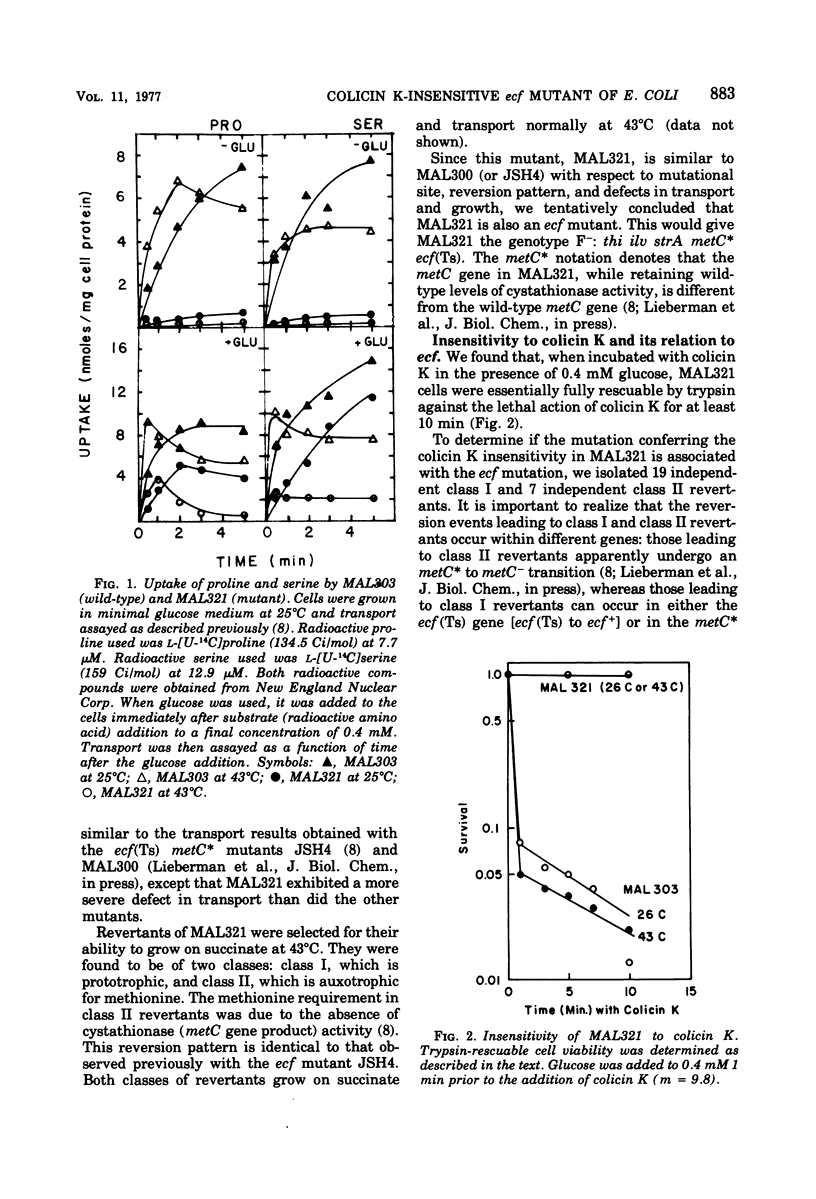
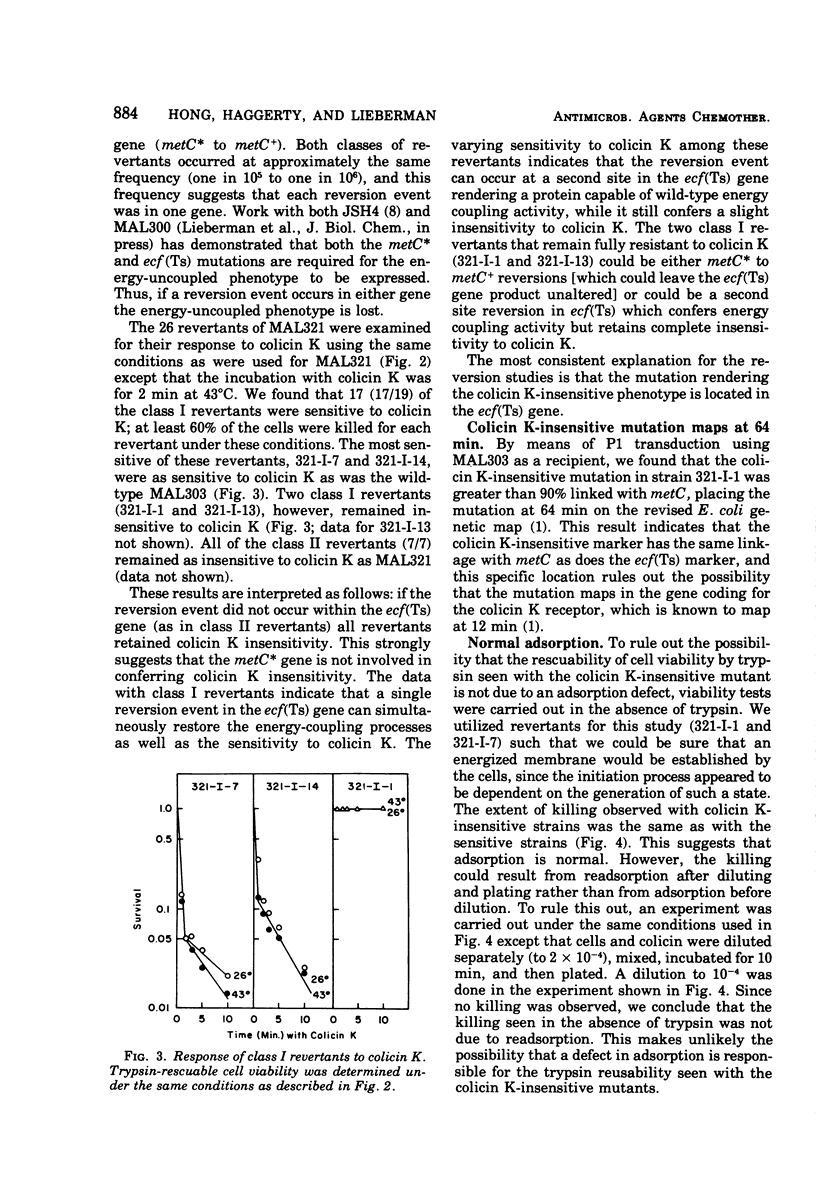
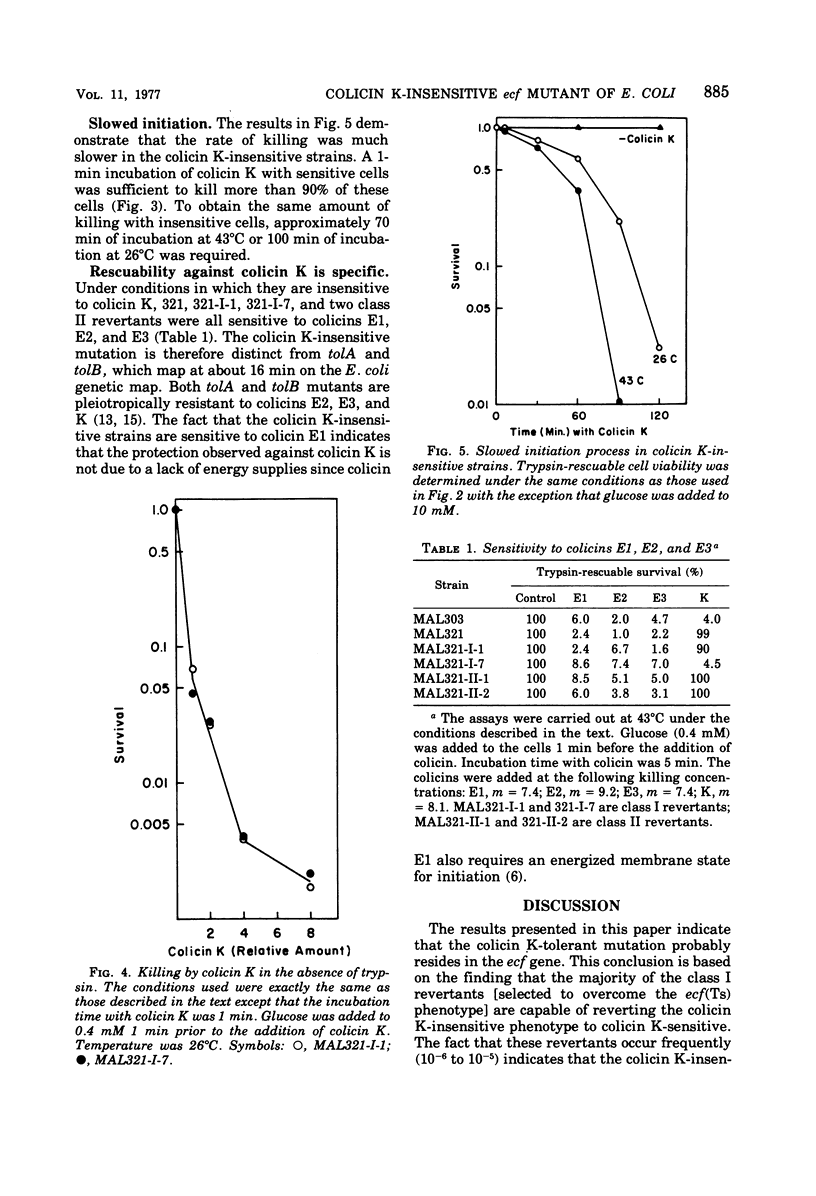
Abstract
We isolated a colicin K-insensitive energy uncoupled mutant of Escherichia coli. This mutant was presumed to be an ecf mutant as evidenced by its similarity to a known ecf mutant (M. A. Lieberman and J.-S. Hong, 1974) with respect to the mutational site, reversion pattern, and defects in transport and growth. The mutation conferring the colicin K-insensitivity resided in the ecf gene as the majority of the secondary mutations overcoming the ecf phenotype reverted the colicin K-insensitive phenotype to colicin K-sensitive. The insensitivity of the mutant to colicin K was not due to either a defect in adsorption or to a lack of the energized membrane state. The defect was most probably due to the inability of colicin K molecules to interact with their target. Our previous studies concerning the role of the ecf gene product in energy coupling to active transport and oxidative phosphorylation support the contention that the ECF protein is itself the direct target of colicin K.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B., Taylor A. L. Recalibrated linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):116–167. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.116-167.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on cellular metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):64–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.64-77.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on transport systems. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.57-63.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., SIMINOVITCH L., WOLLMAN E. Sur la biosynthèse d'une colicine et sur son mode d'action. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1952 Sep;83(3):295–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Jetten M. E. Energy requirement for the initiation of colicin action in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 14;387(1):12–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunugita K., Matsuhashi M. Purification and properties of colicin K. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):1017–1019. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.1017-1019.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. A., Hong J. S. A mutant of Escherichia coli defective in the coupling of metabolic energy to active transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4395–4399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. A., Hong J. S. Changes in active transport, intracellular adenosine 5'-triphosphate levels, macromolecular syntheses, and glycolysis in an energy-uncoupled mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1024–1031. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1024-1031.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. A., Hong J. S. Energization of osmotic shock-sensitive transport systems in Escherichia coli requires more than ATP. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jan;172(1):312–315. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusk J. E., Nelson D. L. Effects of colicins E1 and K on permeability to magnesium and cobaltous ions. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):148–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.148-160.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel de Zwaig R., Luria S. E. Genetics and physiology of colicin-tolerant mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1112–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1112-1123.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Witten C. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. 3. Colicin-tolerant mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1093–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1093-1111.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate C. A. Mutant of Escherichia coli defective in response to colicin K and in active transport. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):467–474. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.467-474.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate C. A., Suit J. L., Jetten A. M., Luria S. E. Effects of colicin K on a mutant of Escherichia coli deficient in Ca 2+, Mg 2+-activated adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6138–6143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. A., Helinski D. R. Purification and characterization of colicin E1. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6318–6327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendt L. Mechanism of colicin action: early events. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1236–1241. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1236-1241.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



